Greedflation occurs when companies increase prices beyond justified cost rises, driven by profit motives rather than supply constraints, intensifying inflation independently of wages. The wage-price spiral describes a feedback loop where rising wages lead to higher production costs and, consequently, increased prices, prompting workers to demand further wage hikes. Explore the intricate dynamics between greedflation and the wage-price spiral to understand their impact on overall economic inflation.
Why it is important
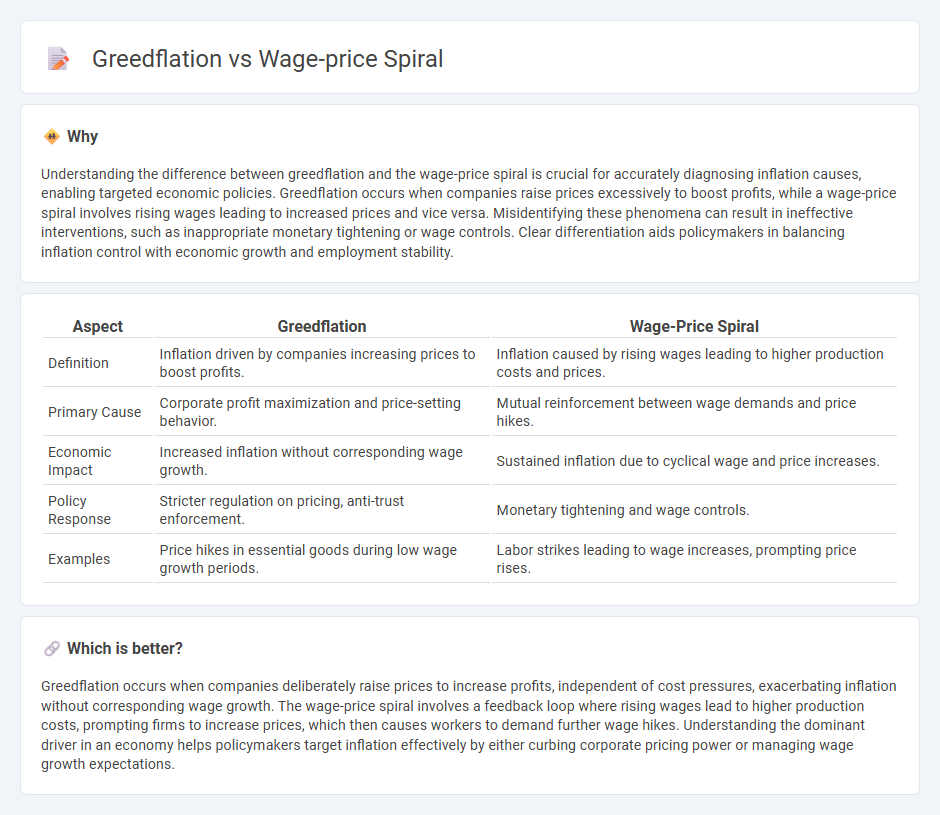
Understanding the difference between greedflation and the wage-price spiral is crucial for accurately diagnosing inflation causes, enabling targeted economic policies. Greedflation occurs when companies raise prices excessively to boost profits, while a wage-price spiral involves rising wages leading to increased prices and vice versa. Misidentifying these phenomena can result in ineffective interventions, such as inappropriate monetary tightening or wage controls. Clear differentiation aids policymakers in balancing inflation control with economic growth and employment stability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Greedflation | Wage-Price Spiral |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inflation driven by companies increasing prices to boost profits. | Inflation caused by rising wages leading to higher production costs and prices. |
| Primary Cause | Corporate profit maximization and price-setting behavior. | Mutual reinforcement between wage demands and price hikes. |
| Economic Impact | Increased inflation without corresponding wage growth. | Sustained inflation due to cyclical wage and price increases. |
| Policy Response | Stricter regulation on pricing, anti-trust enforcement. | Monetary tightening and wage controls. |
| Examples | Price hikes in essential goods during low wage growth periods. | Labor strikes leading to wage increases, prompting price rises. |
Which is better?
Greedflation occurs when companies deliberately raise prices to increase profits, independent of cost pressures, exacerbating inflation without corresponding wage growth. The wage-price spiral involves a feedback loop where rising wages lead to higher production costs, prompting firms to increase prices, which then causes workers to demand further wage hikes. Understanding the dominant driver in an economy helps policymakers target inflation effectively by either curbing corporate pricing power or managing wage growth expectations.
Connection
Greedflation and the wage-price spiral are interconnected phenomena impacting inflation dynamics. Greedflation occurs when companies increase prices beyond cost pressures to boost profits, intensifying inflationary expectations. These higher prices prompt workers to demand increased wages, fueling the wage-price spiral as rising labor costs lead to further price hikes, perpetuating inflation.
Key Terms
Inflation
The wage-price spiral occurs when rising wages increase production costs, leading to higher prices and further wage demands, perpetuating inflationary pressure. Greedflation refers to price increases driven primarily by corporate profit-seeking behavior rather than fundamental cost changes. Explore how these inflation dynamics shape economic policy and consumer impact.
Cost-push
The wage-price spiral describes a cycle where rising wages lead to higher production costs, prompting businesses to increase prices, which then fuels further wage demands. Greedflation, in contrast, involves companies exploiting cost-push conditions by raising prices beyond necessary levels to increase profit margins. Discover how these dynamics differ and impact inflation trends by exploring detailed economic analyses.
Profit margins
The wage-price spiral occurs when rising wages increase production costs, prompting businesses to raise prices, which then leads workers to demand higher wages, perpetuating inflation. Greedflation, on the other hand, centers on companies expanding profit margins by increasing prices beyond cost pressures, driven by market power and reduced competition. Explore the dynamics of profit margins to understand the distinct impacts of wage-price spirals and greedflation on inflation.
Source and External Links
Wage-price spiral - Economics Help - The wage-price spiral describes a self-reinforcing cycle where rising wages increase production costs and push prices up, leading workers to demand even higher wages to keep up with inflation, perpetuating further inflation.
Wage-price spiral - Wikipedia - In macroeconomics, a wage-price spiral is a feedback loop in which wage increases cause price increases, which in turn lead to further wage demands, driving ongoing inflation.
How worried should we be about wage-price spirals? | Brookings - Economists debate the risk of wage-price spirals, where rising wages and prices push each other ever higher, but recent research suggests that wages can sometimes outpace inflation without causing uncontrollable inflation, depending on economic context.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com