Micro-mobility options such as e-scooters and bike-sharing services offer cost-effective, environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional car rentals, reducing urban congestion and carbon emissions. Car rental remains essential for long-distance travel or when carrying multiple passengers, but micro-mobility gains traction in densely populated cities where short trips dominate. Explore how these evolving transportation models reshape urban economies and consumer choices.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between micro-mobility and car rental is crucial for optimizing urban transportation costs and reducing environmental impact. Micro-mobility options like e-scooters and bike-sharing offer affordable, flexible, and eco-friendly short-distance travel, decreasing traffic congestion and carbon emissions. Car rentals provide longer-range, high-capacity transportation suitable for trips requiring more space or distance, impacting fleet management and infrastructure demand differently. Differentiating these transportation modes aids policymakers in designing sustainable economic strategies and allocating resources efficiently.
Comparison Table
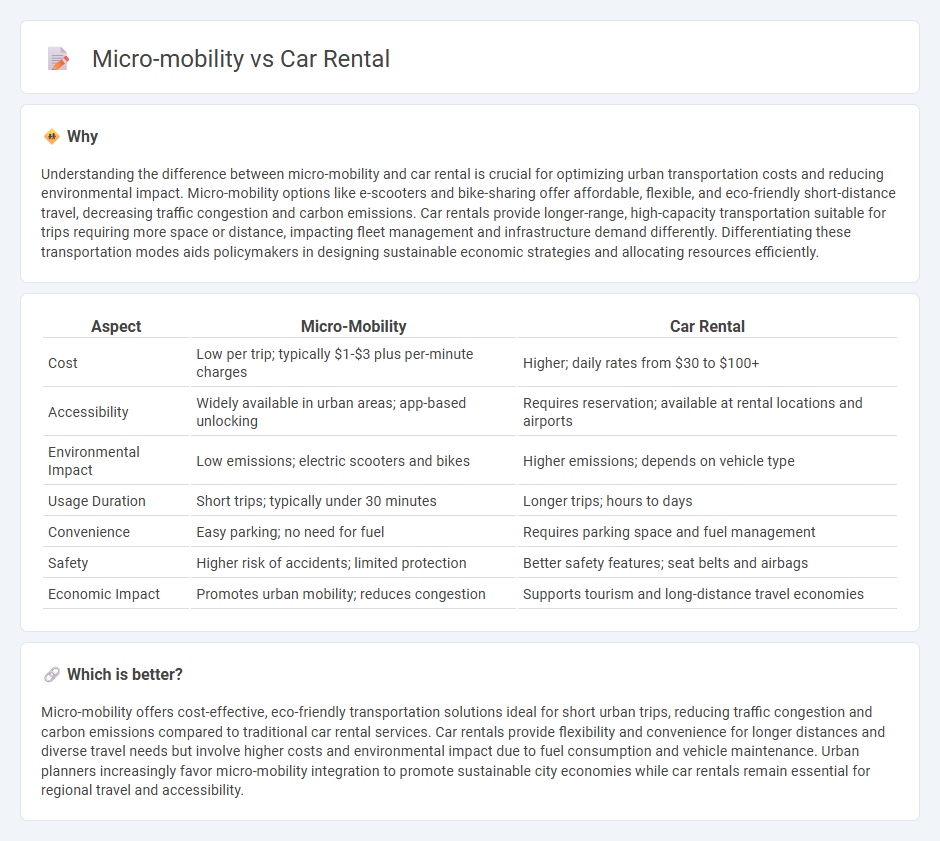
| Aspect | Micro-Mobility | Car Rental |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Low per trip; typically $1-$3 plus per-minute charges | Higher; daily rates from $30 to $100+ |
| Accessibility | Widely available in urban areas; app-based unlocking | Requires reservation; available at rental locations and airports |
| Environmental Impact | Low emissions; electric scooters and bikes | Higher emissions; depends on vehicle type |
| Usage Duration | Short trips; typically under 30 minutes | Longer trips; hours to days |
| Convenience | Easy parking; no need for fuel | Requires parking space and fuel management |
| Safety | Higher risk of accidents; limited protection | Better safety features; seat belts and airbags |
| Economic Impact | Promotes urban mobility; reduces congestion | Supports tourism and long-distance travel economies |
Which is better?
Micro-mobility offers cost-effective, eco-friendly transportation solutions ideal for short urban trips, reducing traffic congestion and carbon emissions compared to traditional car rental services. Car rentals provide flexibility and convenience for longer distances and diverse travel needs but involve higher costs and environmental impact due to fuel consumption and vehicle maintenance. Urban planners increasingly favor micro-mobility integration to promote sustainable city economies while car rentals remain essential for regional travel and accessibility.
Connection
Micro-mobility and car rental services complement urban transportation by offering flexible, eco-friendly alternatives that reduce reliance on private car ownership. Integration of micro-mobility options like e-scooters and bike-sharing with car rental platforms enhances first- and last-mile connectivity, optimizing overall travel efficiency. This synergy supports sustainable economic growth by lowering transportation costs, decreasing traffic congestion, and promoting green mobility solutions.
Key Terms
Asset Utilization
Car rental services achieve higher asset utilization by maximizing vehicle deployment across multiple customers daily, reducing idle time and increasing revenue per asset. Micro-mobility solutions, such as e-scooters and bikes, further optimize asset utilization through continuous usage cycles and rapid turnover in high-density urban areas. Explore the benefits and challenges of asset utilization in car rental versus micro-mobility to understand which model suits urban transportation needs best.
Revenue Model
Car rental revenue models primarily rely on hourly, daily, or weekly rental fees combined with insurance and mileage charges, generating predictable income streams from extended use. Micro-mobility services, such as e-scooters and bikes, focus on pay-per-minute or pay-per-ride fees, leveraging high turnover and urban accessibility to maximize usage frequency and customer reach. Explore detailed insights into how these distinct revenue strategies impact market scalability and profitability.
Cost Structure
Car rental services typically involve fixed costs such as vehicle maintenance, insurance, and depreciation alongside variable expenses like fuel and mileage fees, resulting in higher average expenditure per trip. Micro-mobility options, such as e-scooters and bike-sharing, generally offer lower cost structures with minimal maintenance and no fuel costs, promoting affordability for short-distance travel. Explore further to understand how these distinct cost models impact your transportation budget and choices.
Source and External Links
Uber Rent - Allows users to book a variety of rental cars in Woodstock, GA, with options for delivery or pick-up at a chosen location.
Enterprise Rent-A-Car - Offers car rentals in Woodstock with requirements that include a valid driver's license and a major credit or debit card.
KAYAK - Compares car rental prices in Woodstock from various agencies, helping users find the best deals.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com