Price gouging involves sellers increasing prices exorbitantly during emergencies, exploiting urgent demand and limited supply. Market manipulation entails deliberate actions like spreading false information or creating artificial scarcity to distort market prices for unfair profit. Explore more to understand the economic impacts and legal implications of these practices.
Why it is important
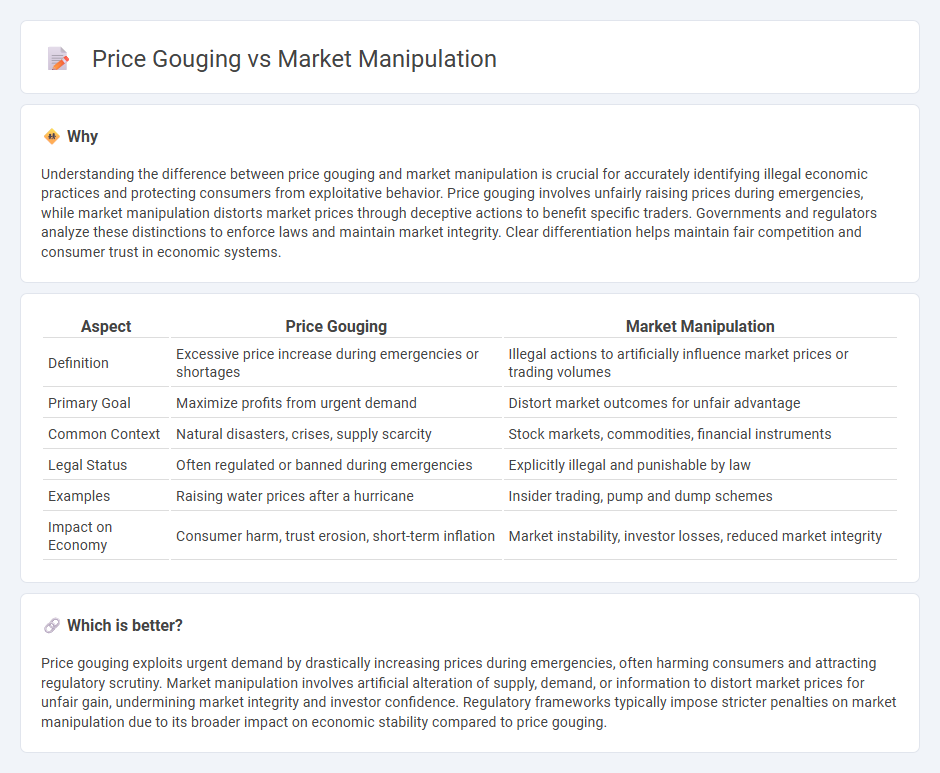
Understanding the difference between price gouging and market manipulation is crucial for accurately identifying illegal economic practices and protecting consumers from exploitative behavior. Price gouging involves unfairly raising prices during emergencies, while market manipulation distorts market prices through deceptive actions to benefit specific traders. Governments and regulators analyze these distinctions to enforce laws and maintain market integrity. Clear differentiation helps maintain fair competition and consumer trust in economic systems.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Price Gouging | Market Manipulation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Excessive price increase during emergencies or shortages | Illegal actions to artificially influence market prices or trading volumes |
| Primary Goal | Maximize profits from urgent demand | Distort market outcomes for unfair advantage |
| Common Context | Natural disasters, crises, supply scarcity | Stock markets, commodities, financial instruments |
| Legal Status | Often regulated or banned during emergencies | Explicitly illegal and punishable by law |
| Examples | Raising water prices after a hurricane | Insider trading, pump and dump schemes |
| Impact on Economy | Consumer harm, trust erosion, short-term inflation | Market instability, investor losses, reduced market integrity |
Which is better?
Price gouging exploits urgent demand by drastically increasing prices during emergencies, often harming consumers and attracting regulatory scrutiny. Market manipulation involves artificial alteration of supply, demand, or information to distort market prices for unfair gain, undermining market integrity and investor confidence. Regulatory frameworks typically impose stricter penalties on market manipulation due to its broader impact on economic stability compared to price gouging.
Connection
Price gouging and market manipulation are connected through their impact on market efficiency and consumer trust, where price gouging involves artificially inflating prices during high demand or emergencies, while market manipulation distorts fair trading practices to create deceptive price movements. Both practices disrupt the natural supply-demand equilibrium, leading to inflated prices and reduced market transparency. Regulatory bodies actively monitor and enforce laws to prevent these unethical behaviors that harm economic stability and consumer welfare.
Key Terms
Artificial pricing
Artificial pricing involves deliberately distorting market prices through tactics like spoofing or wash trading, which falls under market manipulation and undermines fair trading. Price gouging refers to unjustifiably raising prices during emergencies, exploiting consumer vulnerability rather than manipulating market mechanisms. Explore the detailed distinctions and legal ramifications of artificial pricing in market manipulation for deeper insights.
Supply and demand
Market manipulation involves artificially influencing supply or demand to distort prices for profit, often through tactics like stock hoarding or spreading false information. Price gouging occurs when sellers exploit scarcity or high demand by significantly increasing prices beyond fair market value, particularly during emergencies. Explore further to understand their distinct impacts on market dynamics and consumer protection.
Consumer exploitation
Market manipulation involves deceptive practices to artificially influence asset prices, often misleading consumers and causing unfair market conditions. Price gouging exploits consumers by drastically increasing prices during emergencies or shortages, taking advantage of urgent demand and limited supply. Explore how regulatory frameworks protect consumers from these exploitative behaviors.
Source and External Links
Market Manipulation | EBSCO Research Starters - Market manipulation is the intentional interference with financial markets through deceptive practices like spreading false information or artificially inflating stock prices to benefit manipulators financially, often illegal and policed by regulators such as the SEC.
Market Manipulation - Overview, How It Works, and ... - Market manipulation involves artificially inflating or deflating security prices for personal gain and can be difficult to detect, with smaller companies' stocks being more vulnerable due to lower regulatory scrutiny.
Market Manipulation - Market manipulation occurs when someone artificially affects the supply or demand for a security, using tactics like false information or rigging trades to influence prices significantly, with microcap stocks especially susceptible.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com