De-dollarization involves reducing reliance on the US dollar in global trade and finance, aiming to enhance national economic sovereignty and decrease vulnerability to dollar fluctuations. Petrodollar recycling refers to oil-exporting countries reinvesting their dollar earnings into Western financial markets, thereby sustaining demand for the dollar. Explore the dynamics between these shifts and their implications for global economic stability.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between de-dollarisation, which involves reducing reliance on the US dollar in global trade, and petrodollar recycling, where oil-exporting countries reinvest US dollar revenues into global financial markets, is crucial for analyzing shifts in international economic power. De-dollarisation impacts currency stability and global reserve dynamics, whereas petrodollar recycling influences capital flows and liquidity in dollar-denominated assets. Recognizing these concepts helps investors and policymakers anticipate changes in exchange rates, trade policies, and global financial stability. This knowledge is essential for navigating the evolving landscape of global finance and economic diplomacy.
Comparison Table
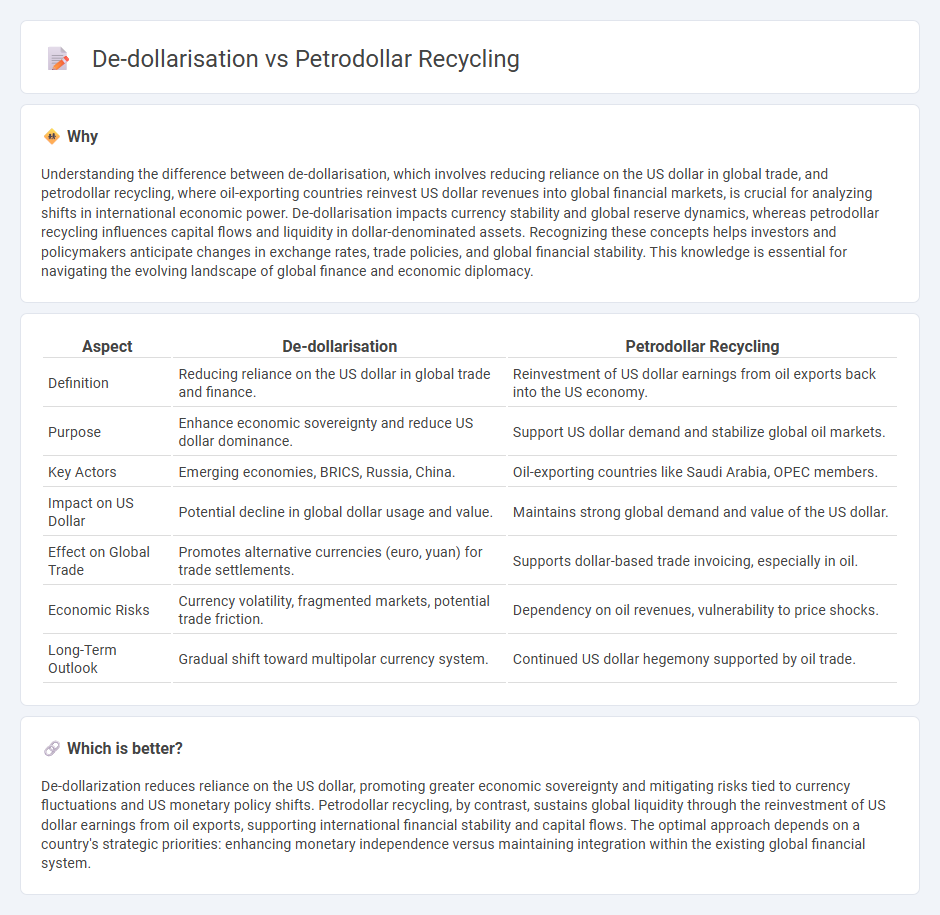
| Aspect | De-dollarisation | Petrodollar Recycling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reducing reliance on the US dollar in global trade and finance. | Reinvestment of US dollar earnings from oil exports back into the US economy. |
| Purpose | Enhance economic sovereignty and reduce US dollar dominance. | Support US dollar demand and stabilize global oil markets. |
| Key Actors | Emerging economies, BRICS, Russia, China. | Oil-exporting countries like Saudi Arabia, OPEC members. |
| Impact on US Dollar | Potential decline in global dollar usage and value. | Maintains strong global demand and value of the US dollar. |
| Effect on Global Trade | Promotes alternative currencies (euro, yuan) for trade settlements. | Supports dollar-based trade invoicing, especially in oil. |
| Economic Risks | Currency volatility, fragmented markets, potential trade friction. | Dependency on oil revenues, vulnerability to price shocks. |
| Long-Term Outlook | Gradual shift toward multipolar currency system. | Continued US dollar hegemony supported by oil trade. |
Which is better?
De-dollarization reduces reliance on the US dollar, promoting greater economic sovereignty and mitigating risks tied to currency fluctuations and US monetary policy shifts. Petrodollar recycling, by contrast, sustains global liquidity through the reinvestment of US dollar earnings from oil exports, supporting international financial stability and capital flows. The optimal approach depends on a country's strategic priorities: enhancing monetary independence versus maintaining integration within the existing global financial system.
Connection
De-dollarisation reduces global reliance on the US dollar in trade and finance, directly impacting the petrodollar recycling system where oil-exporting countries reinvest dollar earnings into US assets. As nations diversify reserves away from the dollar, the flow of petrodollars into US Treasury securities and dollar-denominated investments diminishes, altering global capital movements. This interconnected shift reshapes international economic dynamics by challenging the dollar's dominance and affecting liquidity in dollar-based markets.
Key Terms
Balance of Payments
Petrodollar recycling refers to the process where oil-exporting countries invest their US dollar earnings back into the US economy through Treasury securities, affecting the balance of payments by sustaining the US current account deficit and capital account surplus. De-dollarization involves reducing reliance on the US dollar in international trade and finance, leading to shifts in reserve currencies and potential impacts on global liquidity and balance of payments patterns for involved countries. Explore the evolving dynamics between petrodollar flows and the shift to de-dollarization in global economic relations.
Foreign Exchange Reserves
Petrodollar recycling involves the reinvestment of oil-exporting countries' dollar earnings into global financial markets, bolstering the U.S. dollar's dominance in foreign exchange reserves. In contrast, de-dollarisation reflects a strategic move by nations to reduce reliance on the U.S. dollar by diversifying their foreign exchange reserves into currencies like the euro, yuan, or gold. Explore deeper insights into how these dynamics shape global currency strategies and forex reserve management.
Currency Swap Agreements
Petrodollar recycling involves using revenues from oil sales in U.S. dollars to finance global trade and investment, maintaining the dollar's dominance through mechanisms like currency swap agreements that facilitate liquidity and reduce exchange rate risks between nations. De-dollarization refers to efforts by countries to reduce reliance on the U.S. dollar by promoting alternative currencies, often employing bilateral or multilateral currency swap agreements to bypass dollar transactions and strengthen financial sovereignty. Explore how evolving currency swap agreements shape the balance between petrodollar recycling and de-dollarization strategies in the global economy.
Source and External Links
What Is the Petrodollar? Benefits and Drawbacks | Tony Robbins - Petrodollar recycling is the process where oil-producing countries reinvest surplus U.S. dollars earned from oil exports back into their economies, other countries, or the U.S. economy through assets and securities, helping maintain low interest rates and reduce currency risks.
Petrodollar recycling - Wikipedia - Petrodollar recycling describes the international spending or investment of the revenues petroleum-exporting countries earn from oil exports, often exceeding what they can invest domestically and creating large-scale financial flows between oil producers and consumers.
Petrodollar Recycling And Global Imbalances | IMF - Petrodollar recycling refers to the reflow of oil-exporting countries' revenues into global markets through consumption or investment abroad, which influences global trade balances and investment patterns.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com