Gigification transforms the economy by enabling flexible, on-demand labor through digital platforms, increasing workforce participation and entrepreneurial opportunities. Automation drives efficiency by replacing repetitive tasks with advanced technologies like AI and robotics, reshaping industries and reducing operational costs. Explore how gigification and automation intersect to shape the future of work and economic growth.
Why it is important
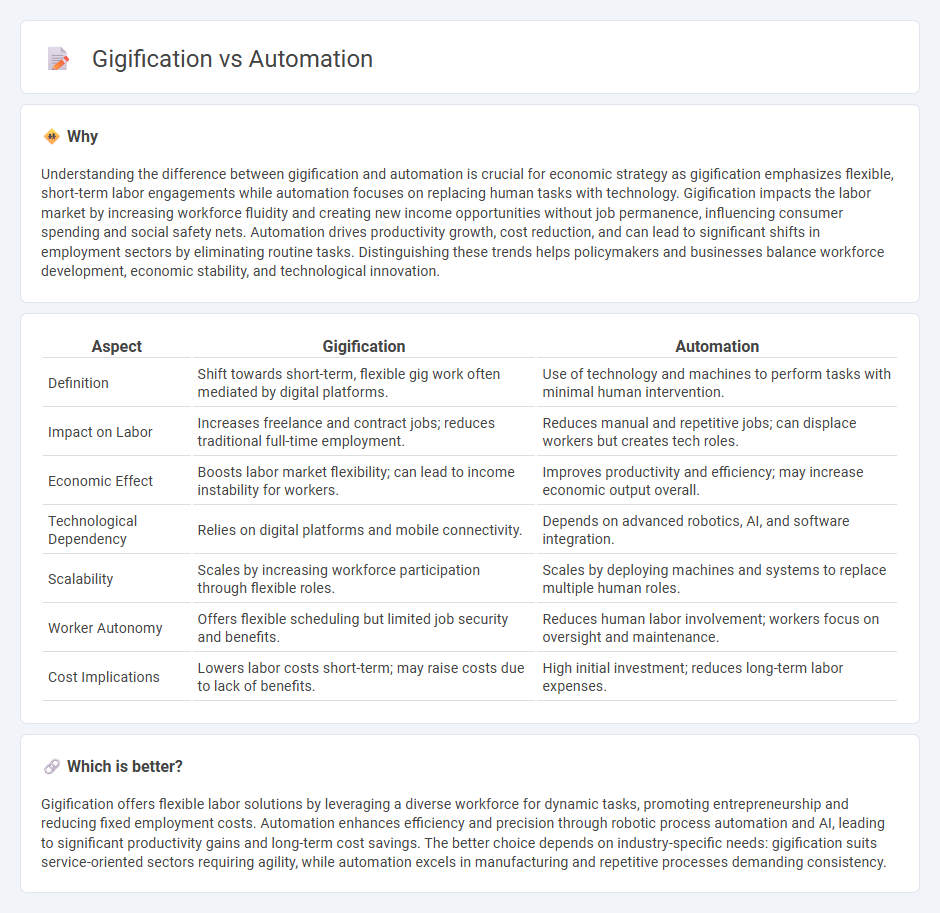
Understanding the difference between gigification and automation is crucial for economic strategy as gigification emphasizes flexible, short-term labor engagements while automation focuses on replacing human tasks with technology. Gigification impacts the labor market by increasing workforce fluidity and creating new income opportunities without job permanence, influencing consumer spending and social safety nets. Automation drives productivity growth, cost reduction, and can lead to significant shifts in employment sectors by eliminating routine tasks. Distinguishing these trends helps policymakers and businesses balance workforce development, economic stability, and technological innovation.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Gigification | Automation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shift towards short-term, flexible gig work often mediated by digital platforms. | Use of technology and machines to perform tasks with minimal human intervention. |
| Impact on Labor | Increases freelance and contract jobs; reduces traditional full-time employment. | Reduces manual and repetitive jobs; can displace workers but creates tech roles. |
| Economic Effect | Boosts labor market flexibility; can lead to income instability for workers. | Improves productivity and efficiency; may increase economic output overall. |
| Technological Dependency | Relies on digital platforms and mobile connectivity. | Depends on advanced robotics, AI, and software integration. |
| Scalability | Scales by increasing workforce participation through flexible roles. | Scales by deploying machines and systems to replace multiple human roles. |
| Worker Autonomy | Offers flexible scheduling but limited job security and benefits. | Reduces human labor involvement; workers focus on oversight and maintenance. |
| Cost Implications | Lowers labor costs short-term; may raise costs due to lack of benefits. | High initial investment; reduces long-term labor expenses. |
Which is better?
Gigification offers flexible labor solutions by leveraging a diverse workforce for dynamic tasks, promoting entrepreneurship and reducing fixed employment costs. Automation enhances efficiency and precision through robotic process automation and AI, leading to significant productivity gains and long-term cost savings. The better choice depends on industry-specific needs: gigification suits service-oriented sectors requiring agility, while automation excels in manufacturing and repetitive processes demanding consistency.
Connection
Gigification and automation intersect by transforming labor markets through technology-driven work models and machine-driven processes. Automation reduces reliance on traditional employment by enabling gig platforms to efficiently connect freelance workers with demand, optimizing task allocation. This synergy accelerates economic shifts toward flexible, scalable labor, impacting productivity and job structures worldwide.
Key Terms
Labor Market
Automation is rapidly transforming the labor market by replacing repetitive tasks with advanced technologies such as AI and robotics, leading to significant shifts in job availability and skill requirements across industries. Gigification, characterized by the rise of freelance, short-term, and platform-based work, is reshaping employment structures by prioritizing flexibility and independent contracting over traditional full-time roles. Explore the evolving dynamics between automation and gigification to better understand their impact on future workforce trends and economic policies.
Flexibility
Automation enhances operational efficiency by reducing manual tasks, whereas gigification prioritizes workforce flexibility through short-term, project-based roles. Flexibility in gigification allows businesses to quickly adapt to market changes and scale labor according to demand without long-term commitments. Explore how balancing automation and gig work can optimize flexibility in modern business models.
Job Security
Automation drastically reduces job security by replacing repetitive and manual roles with AI and robotics, threatening millions of workers in manufacturing, retail, and customer service sectors. Gigification, characterized by short-term contracts and freelance work, offers flexibility but often lacks benefits and stable income, creating uncertainty for gig economy participants such as drivers and delivery couriers. Explore the deeper impacts of automation and gigification on career stability and labor market dynamics.
Source and External Links
Automation - Wikipedia - Automation is a broad technology field that reduces human intervention in processes by using predetermined criteria and control systems, ranging from simple household devices to complex industrial systems like factories and aircraft; it involves various mechanical and electronic methods to improve efficiency and precision.
What Is Automation? - IBM - Automation refers to using technology, robotics, or software to perform tasks with minimal human involvement, enhancing productivity, reducing costs, and enabling businesses to streamline routine workflows across industries such as finance, healthcare, and manufacturing.
Understanding automation - Red Hat - Automation is the use of technology to perform repetitive tasks with less human help, widely applied in manufacturing, IT, cloud management, business process automation, and robotic process automation, often combining AI and machine learning to improve adaptability and efficiency.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com