De-dollarization refers to reducing reliance on the US dollar for international trade and reserves, while yuanization describes the increasing use of the Chinese yuan in global financial transactions and reserves. Countries pursue these strategies to diversify currency risk and enhance monetary sovereignty amid shifting geopolitical dynamics. Explore the implications of de-dollarization and yuanization on the global economy to understand emerging financial trends.
Why it is important
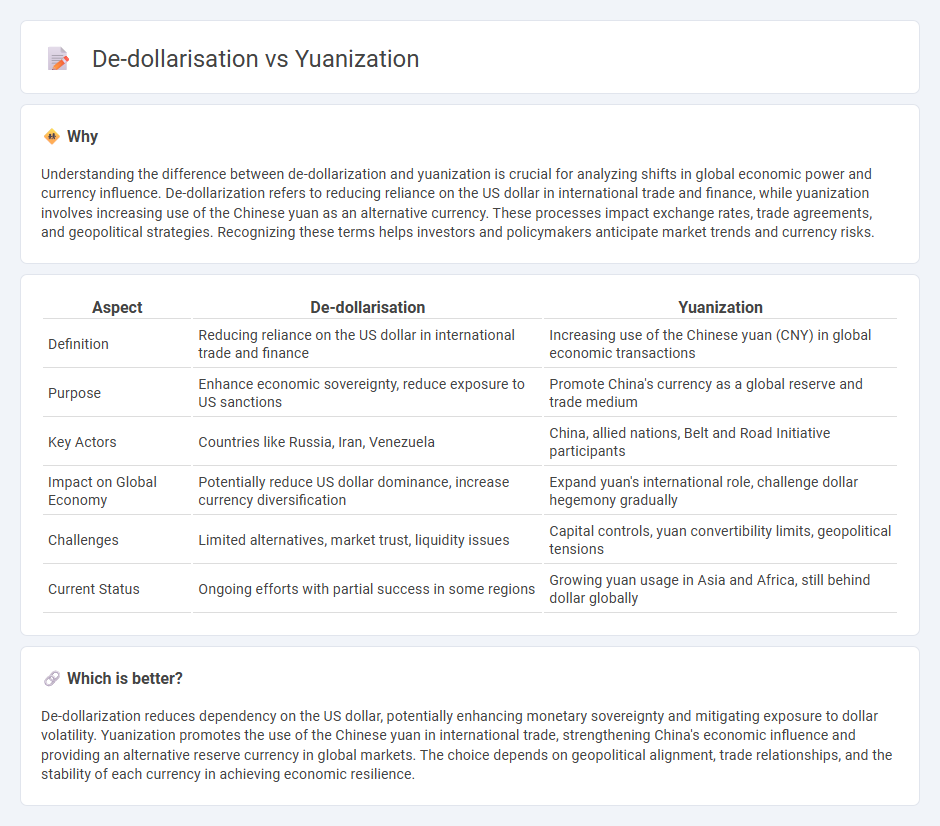
Understanding the difference between de-dollarization and yuanization is crucial for analyzing shifts in global economic power and currency influence. De-dollarization refers to reducing reliance on the US dollar in international trade and finance, while yuanization involves increasing use of the Chinese yuan as an alternative currency. These processes impact exchange rates, trade agreements, and geopolitical strategies. Recognizing these terms helps investors and policymakers anticipate market trends and currency risks.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | De-dollarisation | Yuanization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reducing reliance on the US dollar in international trade and finance | Increasing use of the Chinese yuan (CNY) in global economic transactions |
| Purpose | Enhance economic sovereignty, reduce exposure to US sanctions | Promote China's currency as a global reserve and trade medium |
| Key Actors | Countries like Russia, Iran, Venezuela | China, allied nations, Belt and Road Initiative participants |
| Impact on Global Economy | Potentially reduce US dollar dominance, increase currency diversification | Expand yuan's international role, challenge dollar hegemony gradually |
| Challenges | Limited alternatives, market trust, liquidity issues | Capital controls, yuan convertibility limits, geopolitical tensions |
| Current Status | Ongoing efforts with partial success in some regions | Growing yuan usage in Asia and Africa, still behind dollar globally |
Which is better?
De-dollarization reduces dependency on the US dollar, potentially enhancing monetary sovereignty and mitigating exposure to dollar volatility. Yuanization promotes the use of the Chinese yuan in international trade, strengthening China's economic influence and providing an alternative reserve currency in global markets. The choice depends on geopolitical alignment, trade relationships, and the stability of each currency in achieving economic resilience.
Connection
De-dollarisation involves reducing reliance on the US dollar in international trade and finance, while yuanization refers to the increasing use of the Chinese yuan as an alternative currency. Both processes are linked by efforts of countries and institutions to diversify foreign exchange reserves and enhance economic sovereignty amid shifting geopolitical dynamics. Rising bilateral trade agreements and cross-border investments denominated in yuan accelerate the transition away from dollar dependency.
Key Terms
Currency Substitution
Currency substitution involves the replacement of the US dollar by the Chinese yuan in international trade and finance, reflecting yuanization trends driven by China's expanding economic influence and financial market reforms. De-dollarization represents broader efforts by countries to reduce reliance on the US dollar due to geopolitical risks, economic sanctions, and the pursuit of monetary sovereignty. Explore the dynamics and implications of these currency shifts to understand future global financial strategies.
Exchange Rate Regimes
Yuanization refers to the increasing use of the Chinese yuan (RMB) in international trade and finance, challenging the dominance of the US dollar. De-dollarisation involves reducing reliance on the US dollar in global transactions, often through alternative exchange rate regimes that promote currency diversification. Explore how these shifts influence global exchange rate policies and economic sovereignty.
Reserve Currency
Yuanization refers to the increasing use of the Chinese yuan in international trade and finance, while de-dollarization involves reducing reliance on the US dollar as the global reserve currency. The yuan's growing role is driven by China's expanding economic influence and strategic efforts to promote the renminbi in global markets, whereas de-dollarization reflects geopolitical shifts and diversification among central banks. Explore the dynamics shaping the future of reserve currencies and their impact on global finance.
Source and External Links
Dedollarization: How the West boosts China's yuan - Yuanization refers to the increasing use of China's yuan (renminbi) in international trade and finance, notably boosted by Western sanctions on Russia, which led to a surge in bilateral transactions using the yuan instead of the US dollar.
What Are the Limits to Russia's "Yuanization"? - Yuanization describes Russia's shift towards using the Chinese yuan for foreign trade and financial transactions, which has become significant due to sanctions and alternative payment systems replacing SWIFT between China and Russia.
The Fed - Internationalization of the Chinese renminbi - Yuanization also refers to the broader internationalization of the Chinese renminbi, the official currency of China, which while growing, still accounts for a small fraction of global currency use compared to the US dollar.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com