Gigification transforms traditional jobs into flexible, short-term tasks performed by independent contractors through digital platforms, driving the modern economy's shift toward decentralized labor markets. Crowdsourcing harnesses collective intelligence by outsourcing tasks to a large, undefined group of people online, enabling businesses to access diverse skills and ideas efficiently. Discover how gigification and crowdsourcing are reshaping economic models and workforce dynamics today.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between gigification and crowdsourcing is crucial for optimizing workforce management and economic strategies in the digital economy. Gigification refers to the shift towards short-term, flexible jobs often facilitated by digital platforms, while crowdsourcing involves obtaining services, ideas, or content by soliciting contributions from a large group of people. Businesses leverage gigification to manage labor costs and enhance flexibility, whereas crowdsourcing drives innovation and problem-solving through collective intelligence. Clear differentiation allows policymakers and companies to design tailored regulations and operational models that maximize economic growth and worker protections.
Comparison Table
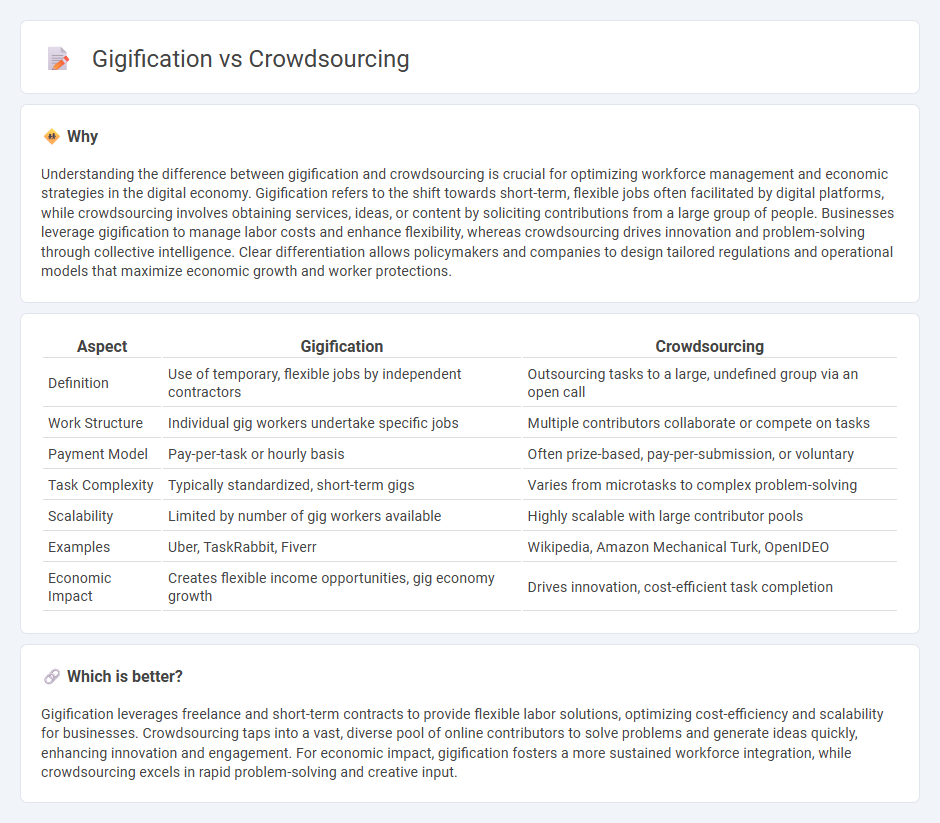
| Aspect | Gigification | Crowdsourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Use of temporary, flexible jobs by independent contractors | Outsourcing tasks to a large, undefined group via an open call |
| Work Structure | Individual gig workers undertake specific jobs | Multiple contributors collaborate or compete on tasks |
| Payment Model | Pay-per-task or hourly basis | Often prize-based, pay-per-submission, or voluntary |
| Task Complexity | Typically standardized, short-term gigs | Varies from microtasks to complex problem-solving |
| Scalability | Limited by number of gig workers available | Highly scalable with large contributor pools |
| Examples | Uber, TaskRabbit, Fiverr | Wikipedia, Amazon Mechanical Turk, OpenIDEO |
| Economic Impact | Creates flexible income opportunities, gig economy growth | Drives innovation, cost-efficient task completion |
Which is better?
Gigification leverages freelance and short-term contracts to provide flexible labor solutions, optimizing cost-efficiency and scalability for businesses. Crowdsourcing taps into a vast, diverse pool of online contributors to solve problems and generate ideas quickly, enhancing innovation and engagement. For economic impact, gigification fosters a more sustained workforce integration, while crowdsourcing excels in rapid problem-solving and creative input.
Connection
Gigification transforms traditional employment by enabling individuals to perform short-term, flexible tasks through digital platforms, while crowdsourcing leverages a large, distributed workforce to complete specific projects or problems. Both models rely heavily on digital connectivity and cloud-based platforms to match demand with a global supply of freelance labor. This interconnectedness reduces operational costs for businesses, increases access to diverse skill sets, and reshapes the labor market by promoting decentralized, task-oriented economic activity.
Key Terms
Labor Market
Crowdsourcing leverages a large, undefined pool of online workers for specific tasks, enhancing flexibility and reducing labor costs in the gig economy. Gigification transforms traditional employment by breaking jobs into short-term, task-oriented gigs, impacting job security and worker benefits in the evolving labor market. Explore the distinct effects of crowdsourcing and gigification on workforce dynamics and job quality.
Incentive Structures
Crowdsourcing leverages a diverse, large-scale workforce incentivized primarily through micro-tasks with financial rewards or intrinsic motivation, while gigification emphasizes flexible, on-demand labor driven by dynamic pricing and reputation-based incentives. Incentive structures in crowdsourcing often include badges, points, and community recognition, fostering sustained engagement, whereas gigification relies on immediate payments and ratings to ensure quality and timely completion. Explore the nuances of these incentive mechanisms to better understand workforce management strategies.
Task Distribution
Task distribution in crowdsourcing leverages a diverse online workforce to complete microtasks efficiently, often emphasizing scalability and speed through open participation. Gigification, however, structures task allocation within a more controlled network of skilled freelancers or gig workers, prioritizing quality and specialized expertise for complex assignments. Explore the nuances between crowdsourcing and gigification to optimize your project's task management strategy.
Source and External Links
What is Crowdsourcing? Definition - Examples - Applications - Crowdsourcing is a process where businesses outsource tasks or ideas to a large community ("the crowd") instead of individual providers, leveraging the intelligence of many people, either paid or unpaid, as exemplified by Wikipedia and historical projects like the Oxford English Dictionary.
What is crowdsourcing? | Definition from TechTarget - Crowdsourcing is obtaining knowledge, goods, or services from a broad group of people, facilitated by the internet or social media, offering benefits like access to diverse expertise quickly and cheaply but also presenting challenges in managing quality and evaluating contributions.
Crowdsourcing - Wikipedia - Crowdsourcing involves many dispersed participants contributing ideas, tasks, or funds via digital platforms, allowing organizations to reduce costs, increase speed and diversity, and use methods such as contests or micro-tasks to harness collective intelligence for various purposes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com