Friendshoring reduces supply chain risks by relocating production to politically stable, allied countries, fostering reliable trade partnerships and economic security. Nearshoring focuses on moving manufacturing closer to home markets to cut transportation costs and improve lead times, benefiting regions like North America and Latin America. Explore the strategic advantages and economic impacts of friendshoring and nearshoring to understand their roles in reshaping global trade.
Why it is important
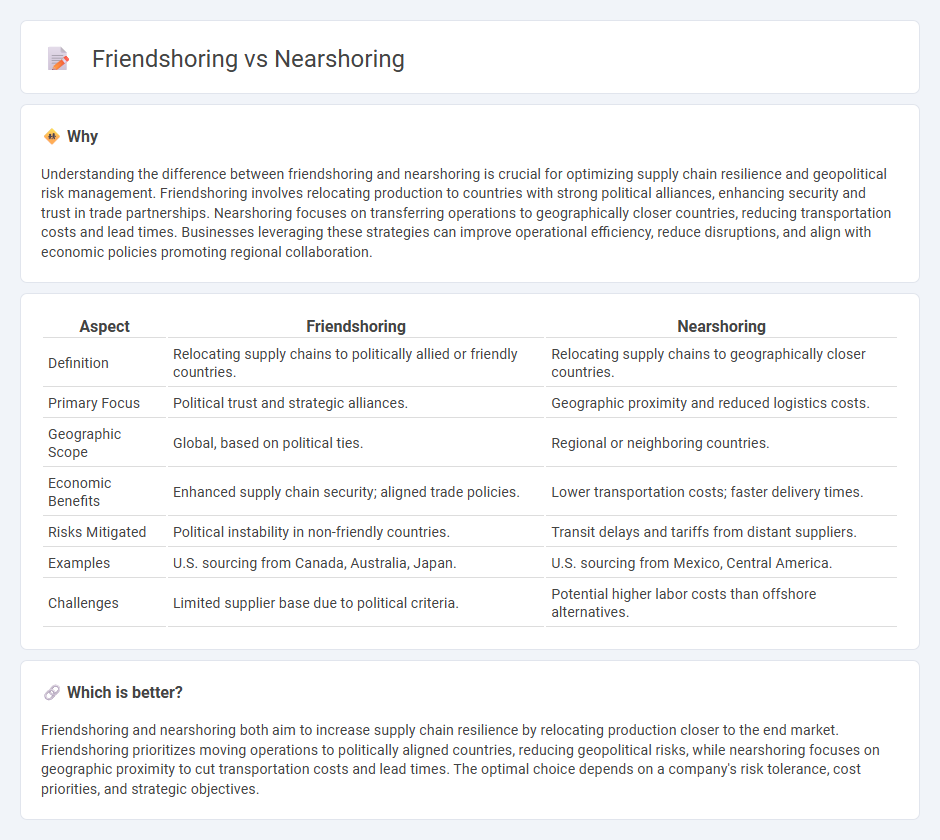
Understanding the difference between friendshoring and nearshoring is crucial for optimizing supply chain resilience and geopolitical risk management. Friendshoring involves relocating production to countries with strong political alliances, enhancing security and trust in trade partnerships. Nearshoring focuses on transferring operations to geographically closer countries, reducing transportation costs and lead times. Businesses leveraging these strategies can improve operational efficiency, reduce disruptions, and align with economic policies promoting regional collaboration.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Friendshoring | Nearshoring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Relocating supply chains to politically allied or friendly countries. | Relocating supply chains to geographically closer countries. |
| Primary Focus | Political trust and strategic alliances. | Geographic proximity and reduced logistics costs. |
| Geographic Scope | Global, based on political ties. | Regional or neighboring countries. |
| Economic Benefits | Enhanced supply chain security; aligned trade policies. | Lower transportation costs; faster delivery times. |
| Risks Mitigated | Political instability in non-friendly countries. | Transit delays and tariffs from distant suppliers. |
| Examples | U.S. sourcing from Canada, Australia, Japan. | U.S. sourcing from Mexico, Central America. |
| Challenges | Limited supplier base due to political criteria. | Potential higher labor costs than offshore alternatives. |
Which is better?
Friendshoring and nearshoring both aim to increase supply chain resilience by relocating production closer to the end market. Friendshoring prioritizes moving operations to politically aligned countries, reducing geopolitical risks, while nearshoring focuses on geographic proximity to cut transportation costs and lead times. The optimal choice depends on a company's risk tolerance, cost priorities, and strategic objectives.
Connection
Friendshoring and nearshoring both aim to enhance supply chain resilience by relocating production closer to home or to politically aligned countries, minimizing risks associated with global disruptions. Friendshoring prioritizes shifting manufacturing to friend or allied countries to secure economic and strategic interests, while nearshoring focuses on moving operations to geographically proximate markets to reduce transportation costs and lead times. Together, these strategies support economic stability by strengthening regional supply networks and improving cross-border trade efficiencies.
Key Terms
Supply Chain Diversification
Nearshoring involves relocating supply chain operations closer to the company's home country to reduce transportation costs and improve lead times, primarily benefiting North American and European manufacturers. Friendshoring emphasizes establishing supply chain partnerships with politically stable, allied countries to mitigate geopolitical risks and ensure continuity in sectors like electronics and automotive. Explore the strategic advantages of nearshoring and friendshoring to enhance supply chain diversification and resilience.
Geopolitical Risk
Nearshoring involves relocating supply chains closer to home countries, reducing exposure to geopolitical risks such as trade wars and regional conflicts. Friendshoring prioritizes partnerships with politically aligned or allied nations to enhance supply chain security amid global instability. Explore how both strategies mitigate geopolitical risk and impact global trade resilience.
Production Relocation
Production relocation strategies such as nearshoring and friendshoring aim to optimize supply chain resilience and reduce operational risks by moving manufacturing closer to end markets or trusted allies. Nearshoring typically involves relocating production to neighboring countries with lower labor costs and reduced logistical complexities, while friendshoring emphasizes partnerships with politically aligned and economically stable nations to ensure supply chain security. Explore the key differences and benefits of nearshoring versus friendshoring for informed production relocation decisions.
Source and External Links
Nearshoring - Nearshoring is the practice of outsourcing business processes to companies in nearby countries, often sharing borders.
Nearshoring in Mexico - This strategy can provide economic benefits to countries like Mexico by relocating production closer to consumers.
What is Nearshoring? - Nearshoring combines the benefits of onshore and offshore outsourcing, offering cost savings, cultural alignment, and geographical proximity.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com