De-dollarization involves reducing reliance on the US dollar in international trade and reserves, aiming to enhance national monetary sovereignty by allowing countries greater control over their own currency policies. This shift can mitigate exposure to dollar fluctuations and external economic pressures while promoting diversified economic stability. Discover how de-dollarization strategies impact global financial systems and national economic independence.
Why it is important
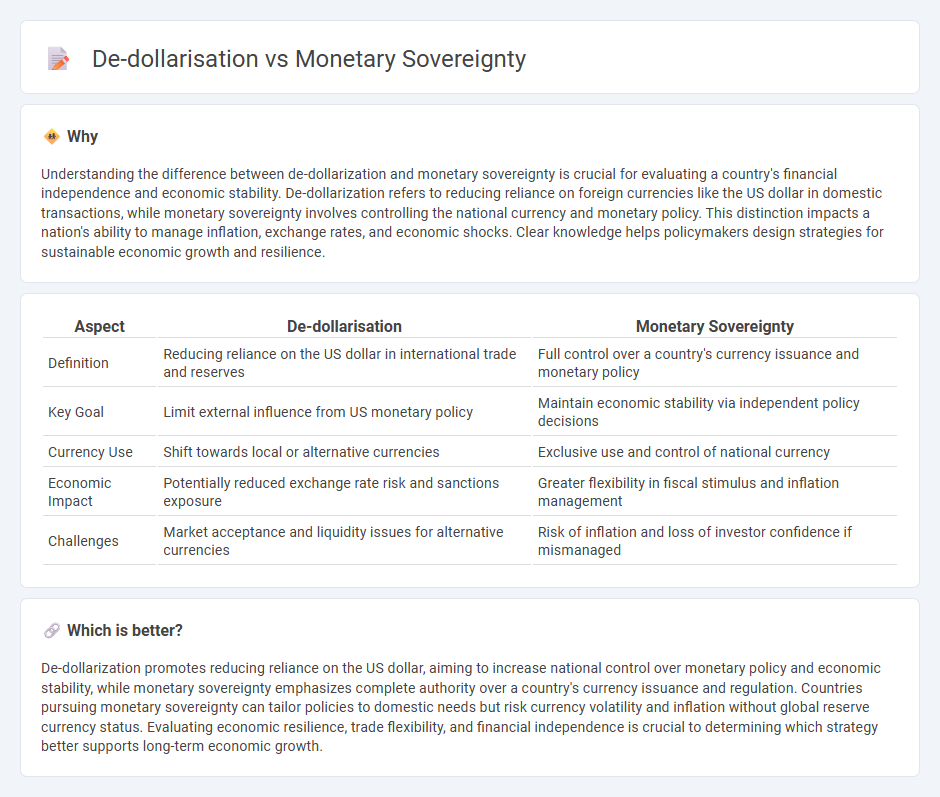
Understanding the difference between de-dollarization and monetary sovereignty is crucial for evaluating a country's financial independence and economic stability. De-dollarization refers to reducing reliance on foreign currencies like the US dollar in domestic transactions, while monetary sovereignty involves controlling the national currency and monetary policy. This distinction impacts a nation's ability to manage inflation, exchange rates, and economic shocks. Clear knowledge helps policymakers design strategies for sustainable economic growth and resilience.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | De-dollarisation | Monetary Sovereignty |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reducing reliance on the US dollar in international trade and reserves | Full control over a country's currency issuance and monetary policy |
| Key Goal | Limit external influence from US monetary policy | Maintain economic stability via independent policy decisions |
| Currency Use | Shift towards local or alternative currencies | Exclusive use and control of national currency |
| Economic Impact | Potentially reduced exchange rate risk and sanctions exposure | Greater flexibility in fiscal stimulus and inflation management |
| Challenges | Market acceptance and liquidity issues for alternative currencies | Risk of inflation and loss of investor confidence if mismanaged |
Which is better?
De-dollarization promotes reducing reliance on the US dollar, aiming to increase national control over monetary policy and economic stability, while monetary sovereignty emphasizes complete authority over a country's currency issuance and regulation. Countries pursuing monetary sovereignty can tailor policies to domestic needs but risk currency volatility and inflation without global reserve currency status. Evaluating economic resilience, trade flexibility, and financial independence is crucial to determining which strategy better supports long-term economic growth.
Connection
De-dollarisation strengthens monetary sovereignty by reducing dependence on the US dollar, allowing countries to regain control over their monetary policies and stabilize their economies. This process involves increasing the use of local currencies in international trade, foreign reserves, and debt settlements, enhancing financial independence. By minimizing external currency risks, nations can better manage inflation, exchange rates, and economic growth aligned with domestic priorities.
Key Terms
Currency Issuance
Monetary sovereignty enables a nation to issue its own currency and control its monetary policy without external constraints, preserving economic independence and policy flexibility. De-dollarisation involves reducing reliance on the U.S. dollar in international trade and finance, which can enhance a country's monetary sovereignty by promoting the use of local currency in cross-border transactions. Explore the complexities of currency issuance and its impact on financial autonomy to understand these dynamics better.
Exchange Rate Regime
Monetary sovereignty allows countries to control their own currency and exchange rate regimes, enabling tailored policy responses to economic fluctuations. In contrast, de-dollarization seeks to reduce reliance on the US dollar in international trade and reserves, compelling nations to recalibrate their exchange rate mechanisms and stabilize local currencies independently. Explore deeper insights into how exchange rate regimes impact monetary sovereignty and de-dollarization efforts globally.
Reserve Currency
Monetary sovereignty is the ability of a nation to control its own currency and monetary policy without external constraints, while de-dollarization involves reducing reliance on the U.S. dollar as the global reserve currency to mitigate exposure to U.S. economic policies. The dominance of the U.S. dollar as the world's primary reserve currency grants the United States significant economic influence, prompting many countries to explore alternatives like the euro, yuan, or emerging digital currencies. Discover how shifts in reserve currency dynamics impact global economic stability and national monetary sovereignty.
Source and External Links
Monetary Sovereignty - Wikipedia - Monetary sovereignty refers to a state's exclusive legal control over its currency and monetary policy, including the authority to designate legal tender and manage its issuance and retirement.
From Territorial to Monetary Sovereignty - This article discusses the shift from territorial to monetary sovereignty in the context of rising credit-based financial systems, highlighting how states can surrender their monetary sovereignty through various means.
How to Rethink Monetary Sovereignty - This article proposes reevaluating monetary sovereignty in the context of financial globalization by focusing on what states can practically achieve within global constraints.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com