A polycrisis involves multiple, interconnected economic disruptions affecting global markets, supply chains, and financial stability simultaneously, leading to complex challenges for policymakers. In contrast, a balance of payments crisis specifically refers to a country struggling to finance its international transactions, often resulting in currency devaluation and capital flight. Explore the nuances and implications of these economic phenomena to better understand global financial vulnerabilities.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between polycrisis and balance of payments crisis is crucial for effective economic policy-making and crisis management. Polycrisis involves simultaneous, interconnected crises affecting multiple sectors or countries, while a balance of payments crisis specifically refers to a country's inability to pay for essential imports or service its international debt. Recognizing this distinction helps allocate resources efficiently and tailor appropriate interventions to stabilize the economy. Accurate diagnosis supports targeted strategies that minimize economic disruptions and promote sustainable growth.
Comparison Table
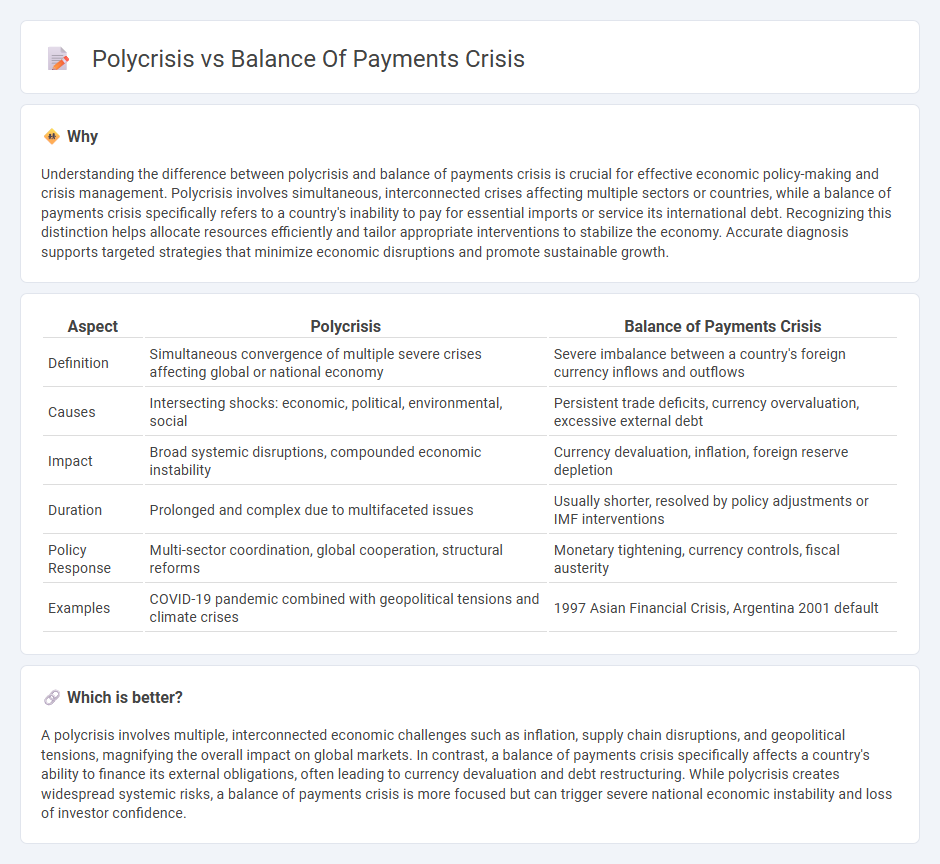
| Aspect | Polycrisis | Balance of Payments Crisis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Simultaneous convergence of multiple severe crises affecting global or national economy | Severe imbalance between a country's foreign currency inflows and outflows |
| Causes | Intersecting shocks: economic, political, environmental, social | Persistent trade deficits, currency overvaluation, excessive external debt |
| Impact | Broad systemic disruptions, compounded economic instability | Currency devaluation, inflation, foreign reserve depletion |
| Duration | Prolonged and complex due to multifaceted issues | Usually shorter, resolved by policy adjustments or IMF interventions |
| Policy Response | Multi-sector coordination, global cooperation, structural reforms | Monetary tightening, currency controls, fiscal austerity |
| Examples | COVID-19 pandemic combined with geopolitical tensions and climate crises | 1997 Asian Financial Crisis, Argentina 2001 default |
Which is better?
A polycrisis involves multiple, interconnected economic challenges such as inflation, supply chain disruptions, and geopolitical tensions, magnifying the overall impact on global markets. In contrast, a balance of payments crisis specifically affects a country's ability to finance its external obligations, often leading to currency devaluation and debt restructuring. While polycrisis creates widespread systemic risks, a balance of payments crisis is more focused but can trigger severe national economic instability and loss of investor confidence.
Connection
Polycrisis, characterized by simultaneous economic, social, and political challenges, can exacerbate a balance of payments crisis by intensifying external vulnerabilities and disrupting trade flows. A balance of payments crisis occurs when a country cannot finance its international obligations, often triggered by capital flight, currency depreciation, or declining foreign reserves due to compounded shocks in a polycrisis. The interplay between these crises undermines economic stability, leading to inflation, reduced investor confidence, and increased debt burdens.
Key Terms
**Balance of Payments Crisis:**
A balance of payments crisis occurs when a country cannot meet its international financial obligations due to a severe deficit in its current or capital accounts, often resulting in currency devaluation and foreign exchange reserves depletion. Key examples include the 1997 Asian financial crisis and Argentina's 2001 economic collapse, highlighting vulnerabilities in external debt and monetary policy mismanagement. Explore how balance of payments crises impact global economic stability and the mechanisms countries use to recover.
Current Account Deficit
A balance of payments crisis typically arises when a country faces a severe Current Account Deficit, reflecting an unsustainable gap between imports and exports that depletes foreign reserves rapidly. In contrast, a polycrisis involves multiple, interconnected crises such as economic, environmental, and geopolitical shocks, where the Current Account Deficit may be a contributing factor but is intertwined with broader systemic risks. Explore how the Current Account Deficit plays distinct roles in these complex scenarios to better understand economic vulnerabilities.
Foreign Exchange Reserves
A balance of payments crisis occurs when a country depletes its foreign exchange reserves due to excessive external debt or trade deficits, forcing abrupt currency devaluation and economic instability. In contrast, a polycrisis involves multiple interconnected crises, including geopolitical tensions, climate change, and financial shocks, which collectively exacerbate the strain on foreign exchange reserves and hamper effective economic response. Explore deeper insights into how foreign exchange reserves play a critical role in managing these complex economic challenges.
Source and External Links
Balance of payments - Wikipedia - A balance of payments (BoP) crisis occurs when a country can no longer pay for essential imports or service its external debt, often leading to a rapid currency devaluation and economic instability as foreign reserves are depleted.
Sudden stops: A primer on balance-of-payments crises | CEPR - A BoP crisis happens when a sudden stop or reversal of capital flows forces a country to abruptly adjust its external accounts, typically causing recession, high unemployment, and government spending cuts as financing for current account deficits dries up.
Bolivia's Balance of Payments Crisis Brings Back Bad Memories - Bolivia's current BoP crisis, driven by declining gas exports and shrinking foreign reserves, has resulted in dollar scarcity, import difficulties, and the emergence of unofficial currency markets as the government struggles to maintain economic stability.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com