Onshoring involves relocating business operations closer to a company's primary market to enhance control, reduce shipping costs, and improve supply chain reliability. Multisourcing diversifies suppliers across multiple regions, mitigating risks related to geopolitical tensions and local disruptions. Explore the strategic advantages and economic implications of onshoring versus multisourcing to optimize your business model.
Why it is important
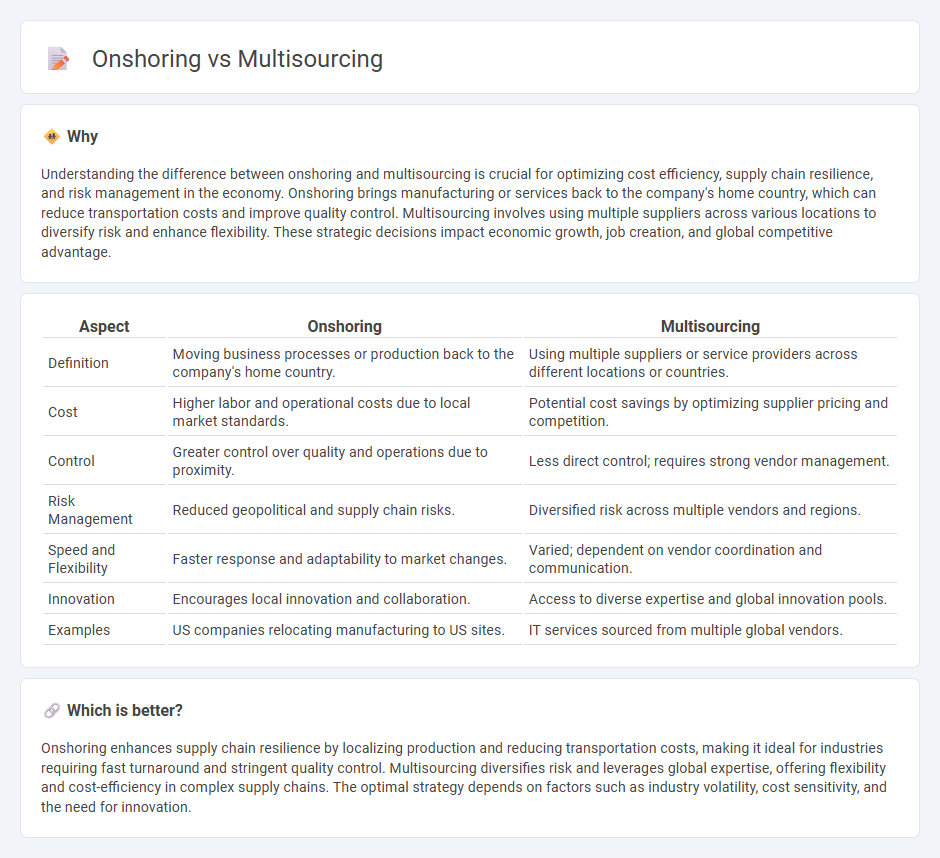
Understanding the difference between onshoring and multisourcing is crucial for optimizing cost efficiency, supply chain resilience, and risk management in the economy. Onshoring brings manufacturing or services back to the company's home country, which can reduce transportation costs and improve quality control. Multisourcing involves using multiple suppliers across various locations to diversify risk and enhance flexibility. These strategic decisions impact economic growth, job creation, and global competitive advantage.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Onshoring | Multisourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Moving business processes or production back to the company's home country. | Using multiple suppliers or service providers across different locations or countries. |
| Cost | Higher labor and operational costs due to local market standards. | Potential cost savings by optimizing supplier pricing and competition. |
| Control | Greater control over quality and operations due to proximity. | Less direct control; requires strong vendor management. |
| Risk Management | Reduced geopolitical and supply chain risks. | Diversified risk across multiple vendors and regions. |
| Speed and Flexibility | Faster response and adaptability to market changes. | Varied; dependent on vendor coordination and communication. |
| Innovation | Encourages local innovation and collaboration. | Access to diverse expertise and global innovation pools. |
| Examples | US companies relocating manufacturing to US sites. | IT services sourced from multiple global vendors. |
Which is better?
Onshoring enhances supply chain resilience by localizing production and reducing transportation costs, making it ideal for industries requiring fast turnaround and stringent quality control. Multisourcing diversifies risk and leverages global expertise, offering flexibility and cost-efficiency in complex supply chains. The optimal strategy depends on factors such as industry volatility, cost sensitivity, and the need for innovation.
Connection
Onshoring reduces dependency on distant suppliers by relocating production closer to the home market, enhancing supply chain resilience. Multisourcing complements this strategy by diversifying suppliers across multiple geographic regions, mitigating risks associated with single-source reliance. Together, onshoring and multisourcing optimize operational flexibility and stabilize economic outputs in volatile markets.
Key Terms
Supplier Diversification
Multisourcing enhances supplier diversification by engaging multiple vendors across different locations, reducing dependency on a single source and mitigating risks related to geopolitical instability or supply chain disruptions. Onshoring centralizes suppliers within the home country, which can simplify logistics but may limit diversification opportunities and increase vulnerability to local challenges. Explore how strategic supplier diversification through multisourcing compares with the benefits of onshoring for your business resilience and flexibility.
Cost Structure
Multisourcing spreads IT and business services across multiple vendors, optimizing cost structure through competitive pricing and risk diversification, while onshoring centralizes operations domestically, often incurring higher labor expenses but benefiting from reduced communication gaps and quicker response times. Cost structure in multisourcing includes variable expenses linked to vendor performance and contract management, whereas onshoring demands fixed costs related to local salaries and infrastructure investments. Explore the detailed cost implications between multisourcing and onshoring to make informed strategic decisions.
Geographic Location
Multisourcing leverages multiple geographic locations, often combining onshore, nearshore, and offshore providers to optimize cost, talent access, and risk diversification. Onshoring confines operations within the company's home country, emphasizing proximity, cultural alignment, and regulatory compliance. Explore the geographic advantages of each strategy to determine the best fit for your business needs.
Source and External Links
What is multisourcing? | Outsource Accelerator - Multisourcing is the practice of outsourcing to multiple service providers to meet rising business demands, which improves operational efficiency and reduces vendor risk by distributing tasks among different suppliers.
Multisourcing - Wikipedia - Multisourcing involves working with multiple competing suppliers and can be managed under Prime Contractor or Client models, providing buyers with supply assurance beyond sole-sourcing.
Multiple Sourcing -- Explained + 3 Examples - Procurement Tactics - Multiple sourcing allows companies to reduce reliance on a single supplier, improve supply flexibility, and avoid bottlenecks by spreading demand across different vendors.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com