Onshoring involves relocating business processes and manufacturing back to the company's home country to reduce supply chain risks and enhance quality control, while homeshoring focuses on outsourcing tasks to remote workers within the same country, leveraging local talent for cost efficiency and flexibility. Both strategies aim to mitigate challenges related to offshoring, such as extended delivery times and cultural barriers. Explore deeper insights on how onshoring and homeshoring are reshaping modern economic practices.
Why it is important
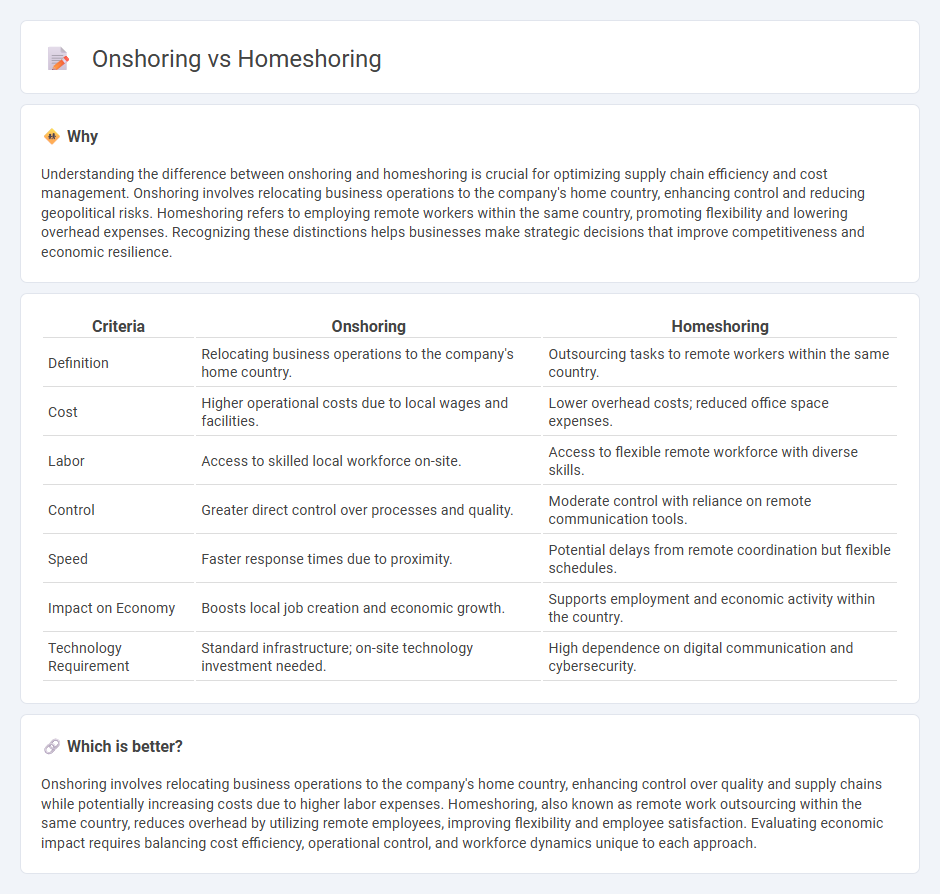
Understanding the difference between onshoring and homeshoring is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and cost management. Onshoring involves relocating business operations to the company's home country, enhancing control and reducing geopolitical risks. Homeshoring refers to employing remote workers within the same country, promoting flexibility and lowering overhead expenses. Recognizing these distinctions helps businesses make strategic decisions that improve competitiveness and economic resilience.
Comparison Table
| Criteria | Onshoring | Homeshoring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Relocating business operations to the company's home country. | Outsourcing tasks to remote workers within the same country. |
| Cost | Higher operational costs due to local wages and facilities. | Lower overhead costs; reduced office space expenses. |
| Labor | Access to skilled local workforce on-site. | Access to flexible remote workforce with diverse skills. |
| Control | Greater direct control over processes and quality. | Moderate control with reliance on remote communication tools. |
| Speed | Faster response times due to proximity. | Potential delays from remote coordination but flexible schedules. |
| Impact on Economy | Boosts local job creation and economic growth. | Supports employment and economic activity within the country. |
| Technology Requirement | Standard infrastructure; on-site technology investment needed. | High dependence on digital communication and cybersecurity. |
Which is better?
Onshoring involves relocating business operations to the company's home country, enhancing control over quality and supply chains while potentially increasing costs due to higher labor expenses. Homeshoring, also known as remote work outsourcing within the same country, reduces overhead by utilizing remote employees, improving flexibility and employee satisfaction. Evaluating economic impact requires balancing cost efficiency, operational control, and workforce dynamics unique to each approach.
Connection
Onshoring and homeshoring both aim to bring business operations closer to a company's home country to reduce costs and improve control over production. Onshoring involves relocating manufacturing or services back to the domestic market, while homeshoring specifically refers to outsourcing jobs to remote workers within the same country. These strategies enhance economic growth by creating local jobs and minimizing reliance on international supply chains.
Key Terms
Labor Costs
Labor costs in homeshoring are significantly lower due to reduced overhead expenses and flexible work arrangements, compared to onshoring, where wages align with local market rates and include additional operational expenses. Onshoring offers advantages in quality control and proximity, but the higher labor costs can impact overall budget efficiency. Explore the detailed breakdown of labor cost implications between homeshoring and onshoring to make informed outsourcing decisions.
Supply Chain
Homeshoring involves relocating supply chain operations to domestic remote employees, enhancing flexibility and reducing overhead compared to traditional onshoring, which centralizes production within local facilities to ensure tighter quality control and faster response times. Supply chains leveraging homeshoring benefit from distributed workforces and cost savings, while onshoring prioritizes proximity to raw materials and markets for improved logistics and inventory management. Discover in-depth analysis on optimizing your supply chain strategy through homeshoring and onshoring approaches.
Domestic Production
Homeshoring involves outsourcing business processes to remote workers within the same country, leveraging local talent while reducing operational costs and maintaining domestic production standards. Onshoring refers to relocating business operations back to the company's home country, focusing on enhancing quality control, compliance with local regulations, and boosting the national economy. Explore the advantages and strategic benefits of homeshoring and onshoring in optimizing domestic production.
Source and External Links
Homeshoring and telecommuting: what are the differences? - Homeshoring is a form of work outsourcing where freelancers provide services to companies from their own homes under service contracts, differentiating it from traditional employee telecommuting.
Home Is Where Your Work Is: The Rising Trends of Homeshoring - Homeshoring refers to companies shifting their workforce to remote work, eliminating the need for physical offices and enabling staff to work from home with digital tools and communication platforms.
HOMESHORING definition in American English - Homeshoring is the practice of paying employees to work from home rather than in an office, also known as homesourcing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com