A soft landing in the economy occurs when growth slows gradually, allowing inflation and unemployment to stabilize without triggering a recession. In contrast, a hard landing involves a sharp economic downturn characterized by significant job losses and declining consumer spending. Explore the key indicators and strategies behind these differing economic outcomes to understand their impact.
Why it is important
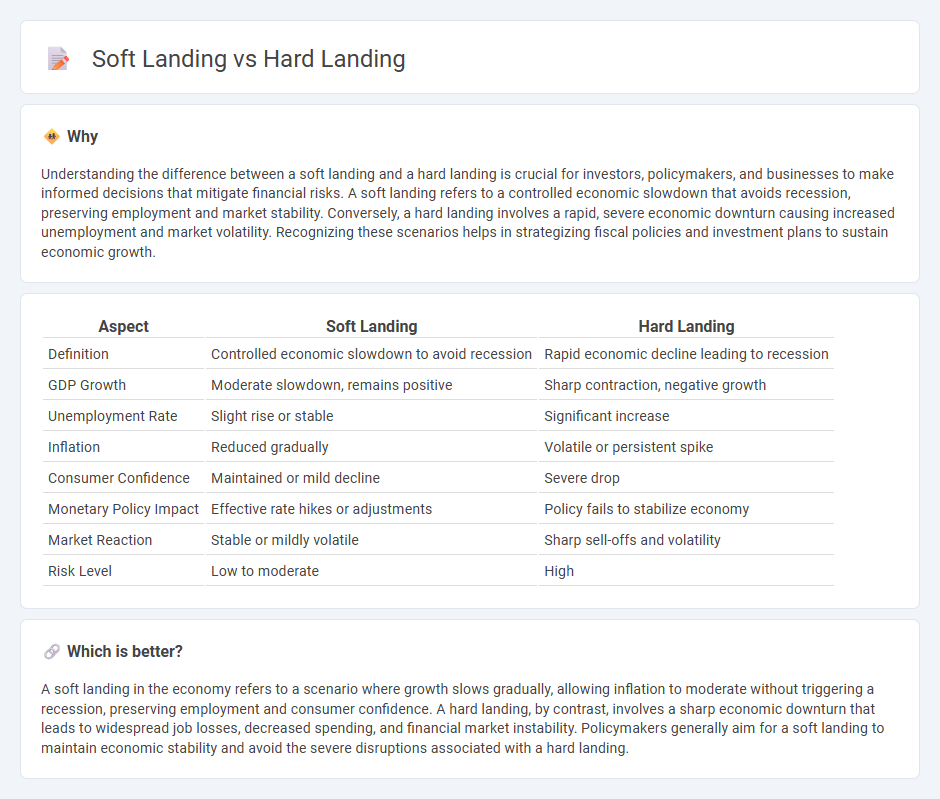
Understanding the difference between a soft landing and a hard landing is crucial for investors, policymakers, and businesses to make informed decisions that mitigate financial risks. A soft landing refers to a controlled economic slowdown that avoids recession, preserving employment and market stability. Conversely, a hard landing involves a rapid, severe economic downturn causing increased unemployment and market volatility. Recognizing these scenarios helps in strategizing fiscal policies and investment plans to sustain economic growth.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Soft Landing | Hard Landing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Controlled economic slowdown to avoid recession | Rapid economic decline leading to recession |
| GDP Growth | Moderate slowdown, remains positive | Sharp contraction, negative growth |
| Unemployment Rate | Slight rise or stable | Significant increase |
| Inflation | Reduced gradually | Volatile or persistent spike |
| Consumer Confidence | Maintained or mild decline | Severe drop |
| Monetary Policy Impact | Effective rate hikes or adjustments | Policy fails to stabilize economy |
| Market Reaction | Stable or mildly volatile | Sharp sell-offs and volatility |
| Risk Level | Low to moderate | High |
Which is better?
A soft landing in the economy refers to a scenario where growth slows gradually, allowing inflation to moderate without triggering a recession, preserving employment and consumer confidence. A hard landing, by contrast, involves a sharp economic downturn that leads to widespread job losses, decreased spending, and financial market instability. Policymakers generally aim for a soft landing to maintain economic stability and avoid the severe disruptions associated with a hard landing.
Connection
A soft landing in the economy occurs when growth slows gradually, avoiding a recession, while a hard landing involves a rapid economic decline leading to a recession or financial crisis. Central banks influence these outcomes through monetary policy adjustments, such as interest rate changes, to control inflation without stalling growth. The balance achieved between managing inflation and sustaining demand determines whether the economy experiences a soft landing or slips into a hard landing scenario.
Key Terms
Monetary Policy
Hard landing in monetary policy refers to aggressive interest rate hikes to curb inflation, often resulting in slowed economic growth and increased unemployment. Soft landing aims for gradual rate adjustments that moderate inflation while sustaining steady economic expansion and labor market stability. Explore detailed analysis to understand how central banks balance these outcomes amid shifting economic conditions.
Recession
A hard landing occurs when an economy rapidly slows down, leading to a sharp rise in unemployment and a significant contraction in GDP, often triggering a recession. In contrast, a soft landing refers to a gradual slowdown that avoids deep economic downturns, maintaining moderate growth and stable employment levels. Learn more about the economic indicators that distinguish hard landings from soft landings and their impact on recession risks.
Inflation
A hard landing in the economy occurs when aggressive monetary tightening leads to a sharp decline in inflation but triggers a significant slowdown in growth and rising unemployment. In contrast, a soft landing carefully moderates inflation to target levels without causing a recession, maintaining steady employment and consumer confidence. Explore the nuances of inflation control strategies and their impacts on economic stability to understand these economic outcomes better.
Source and External Links
Hard landing - Wikipedia - A hard landing occurs when an aircraft or spacecraft hits the ground with greater vertical speed and force than in a normal landing, often requiring inspection for potential damage before further flight.
Hard landing (economics) - Wikipedia - In economics, a hard landing describes an economy rapidly shifting from growth to slow-growth or recession, typically as a result of government policies aimed at controlling inflation.
TOP 10 HARDEST LANDINGS At Madeira Airport - YouTube - This video compilation showcases extreme aircraft landings at Madeira Airport, including instances where planes grounded due to excessive impact forces that triggered mandatory maintenance checks.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com