Gigification transforms the economy by promoting flexible, on-demand work through digital platforms, contrasting sharply with the stability and benefits of formal employment. This shift impacts income consistency, labor rights, and social security coverage for millions of workers worldwide. Discover how the rise of gigification reshapes modern labor markets and what it means for the future of work.
Why it is important
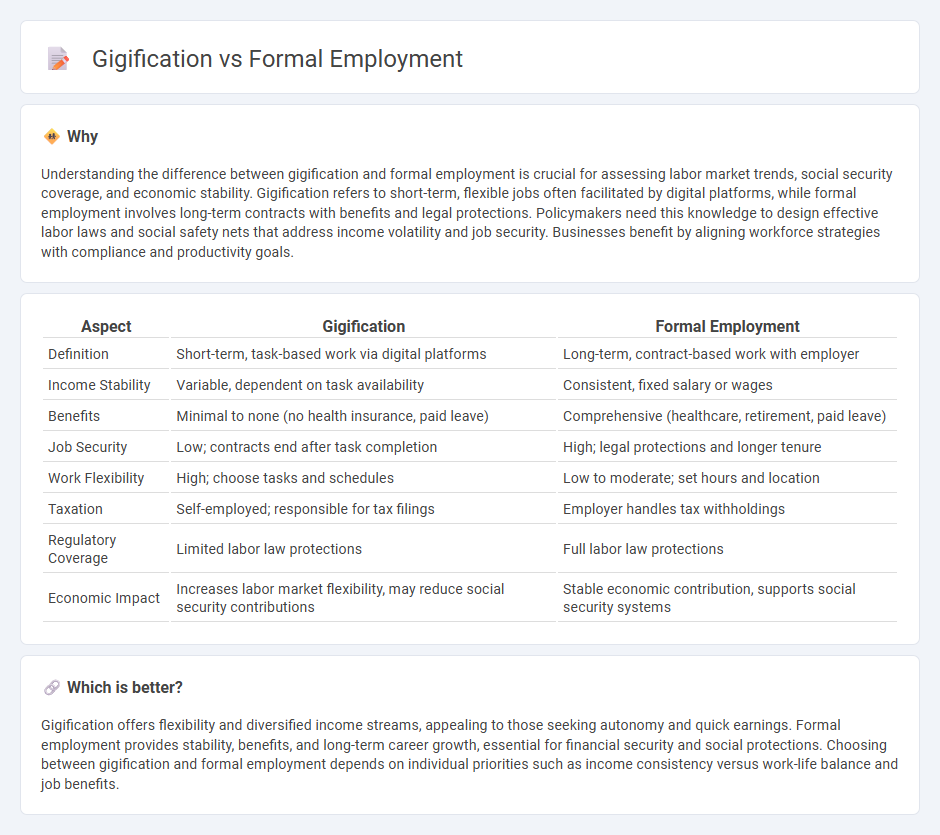
Understanding the difference between gigification and formal employment is crucial for assessing labor market trends, social security coverage, and economic stability. Gigification refers to short-term, flexible jobs often facilitated by digital platforms, while formal employment involves long-term contracts with benefits and legal protections. Policymakers need this knowledge to design effective labor laws and social safety nets that address income volatility and job security. Businesses benefit by aligning workforce strategies with compliance and productivity goals.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Gigification | Formal Employment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Short-term, task-based work via digital platforms | Long-term, contract-based work with employer |
| Income Stability | Variable, dependent on task availability | Consistent, fixed salary or wages |
| Benefits | Minimal to none (no health insurance, paid leave) | Comprehensive (healthcare, retirement, paid leave) |
| Job Security | Low; contracts end after task completion | High; legal protections and longer tenure |
| Work Flexibility | High; choose tasks and schedules | Low to moderate; set hours and location |
| Taxation | Self-employed; responsible for tax filings | Employer handles tax withholdings |
| Regulatory Coverage | Limited labor law protections | Full labor law protections |
| Economic Impact | Increases labor market flexibility, may reduce social security contributions | Stable economic contribution, supports social security systems |
Which is better?
Gigification offers flexibility and diversified income streams, appealing to those seeking autonomy and quick earnings. Formal employment provides stability, benefits, and long-term career growth, essential for financial security and social protections. Choosing between gigification and formal employment depends on individual priorities such as income consistency versus work-life balance and job benefits.
Connection
Gigification reshapes labor markets by increasing freelance and short-term contract roles, impacting the stability and benefits traditionally associated with formal employment. Formal employment structures adapt by incorporating flexible work practices and digital platforms to remain competitive and meet evolving workforce expectations. This synergy influences economic productivity, labor rights, and social protection systems globally.
Key Terms
Job Security
Formal employment offers structured job security through contracts, benefits, and labor protections, ensuring stable income and legal rights for workers. Gigification, characterized by flexible, short-term tasks, often lacks these protections, exposing workers to income volatility and limited social safety nets. Explore comprehensive insights on how these employment models impact job security in today's evolving labor market.
Flexibility
Formal employment offers structured work hours and job security but often limits flexibility in scheduling and task variety. Gigification provides highly flexible work arrangements, enabling individuals to choose when, where, and how much they work, appealing to those seeking autonomy and diverse income streams. Discover how shifting labor trends impact workforce dynamics and personal work-life balance.
Benefits
Formal employment offers structured benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, paid leave, and job security, providing financial stability and predictable income. Gigification, characterized by freelance and contract work, often lacks these traditional benefits but offers flexibility, autonomy, and diverse income streams. Explore how evolving work models impact employee benefits and compensation strategies.
Source and External Links
formal employment Definition - Formal employment is any employment defined under a 'contract of service' in legal terms, typically excluding self-employment, and includes jobs in government, public, or private institutions with formal agreements and protections.
Informal vs. Formal Workplaces: What's the Difference? - A formal workplace involves a formal working agreement such as a contract, regular working hours, a consistent place of work, and usually a salary, contrasted with informal workplaces which lack formal agreements and often have irregular conditions.
Informality and formality - two ends of the employment continuum - Formal employment typically provides higher wages, legal protections, and benefits compared to informal employment, but formality and informality exist on a continuum where not all formal jobs offer full benefits.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com