Reshoring involves bringing manufacturing and services back to the company's home country, enhancing control over production and reducing dependency on foreign suppliers. Nearshoring relocates operations to nearby countries with lower labor costs and shorter supply chains, improving efficiency and responsiveness to market demands. Explore detailed insights on reshoring and nearshoring strategies to understand their impact on global economic competitiveness.
Why it is important
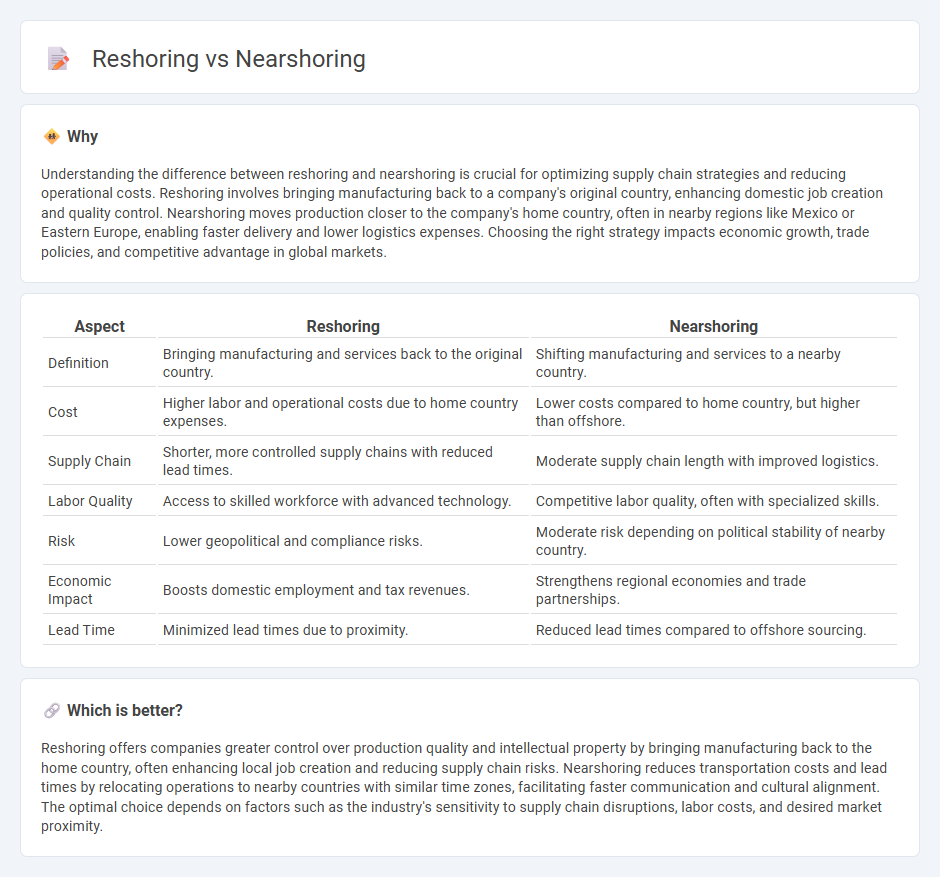
Understanding the difference between reshoring and nearshoring is crucial for optimizing supply chain strategies and reducing operational costs. Reshoring involves bringing manufacturing back to a company's original country, enhancing domestic job creation and quality control. Nearshoring moves production closer to the company's home country, often in nearby regions like Mexico or Eastern Europe, enabling faster delivery and lower logistics expenses. Choosing the right strategy impacts economic growth, trade policies, and competitive advantage in global markets.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Reshoring | Nearshoring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Bringing manufacturing and services back to the original country. | Shifting manufacturing and services to a nearby country. |
| Cost | Higher labor and operational costs due to home country expenses. | Lower costs compared to home country, but higher than offshore. |
| Supply Chain | Shorter, more controlled supply chains with reduced lead times. | Moderate supply chain length with improved logistics. |
| Labor Quality | Access to skilled workforce with advanced technology. | Competitive labor quality, often with specialized skills. |
| Risk | Lower geopolitical and compliance risks. | Moderate risk depending on political stability of nearby country. |
| Economic Impact | Boosts domestic employment and tax revenues. | Strengthens regional economies and trade partnerships. |
| Lead Time | Minimized lead times due to proximity. | Reduced lead times compared to offshore sourcing. |
Which is better?
Reshoring offers companies greater control over production quality and intellectual property by bringing manufacturing back to the home country, often enhancing local job creation and reducing supply chain risks. Nearshoring reduces transportation costs and lead times by relocating operations to nearby countries with similar time zones, facilitating faster communication and cultural alignment. The optimal choice depends on factors such as the industry's sensitivity to supply chain disruptions, labor costs, and desired market proximity.
Connection
Reshoring and nearshoring both focus on relocating production closer to a company's home country to reduce supply chain risks and lower transportation costs. Reshoring involves bringing manufacturing back to the domestic market, while nearshoring shifts operations to neighboring or nearby countries with favorable trade agreements. Both strategies aim to enhance economic resilience, improve lead times, and boost local employment.
Key Terms
Supply Chain Optimization
Nearshoring reduces supply chain complexity by relocating manufacturing closer to end markets, thereby minimizing transit times and lowering logistics costs. Reshoring emphasizes bringing production back domestically to enhance control, improve quality, and reduce risks associated with global disruptions. Explore deeper insights into how nearshoring and reshoring strategies can drive supply chain optimization and competitive advantage.
Labor Costs
Labor costs significantly influence decisions between nearshoring and reshoring, with nearshoring often providing access to lower-wage markets closer to home, such as Mexico or Eastern Europe, reducing transportation and operational expenses. Reshoring brings manufacturing back to the domestic market, usually resulting in higher labor costs but benefiting from improved quality control and faster response times. Explore the impact of labor cost dynamics on supply chain strategies to make informed nearshoring or reshoring choices.
Geopolitical Risk
Nearshoring involves relocating business processes closer to the company's home country, often within neighboring regions, to mitigate geopolitical risks such as trade restrictions, tariffs, and political instability. Reshoring refers to bringing manufacturing and services back to the company's original country to gain greater control over supply chains and reduce exposure to global disruptions and shifting international policies. Explore the strategic advantages of nearshoring versus reshoring to navigate geopolitical risks effectively.
Source and External Links
Nearshoring - Wikipedia - Nearshoring is the outsourcing of business processes, often IT, to companies in a nearby country, usually sharing a border, offering proximity advantages.
Nearshoring in Mexico | Deloitte Insights - Nearshoring moves production closer to the final consumer to reduce costs and supply chain risks, with Mexico benefiting from tariffs, trade agreements, and global disruptions as incentives.
What is Nearshoring? Definition and Benefits - TTEC - Nearshoring combines cultural, logistical, and cost advantages by outsourcing to neighboring countries with similar time zones and languages, offering savings and operational ease.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com