Rentvesting enables individuals to rent in preferred locations while investing in affordable properties elsewhere, maximizing financial growth and housing flexibility. Co-owning involves shared property ownership, reducing entry costs and spreading financial responsibilities among multiple parties. Discover which strategy aligns best with your financial goals and lifestyle preferences.
Why it is important
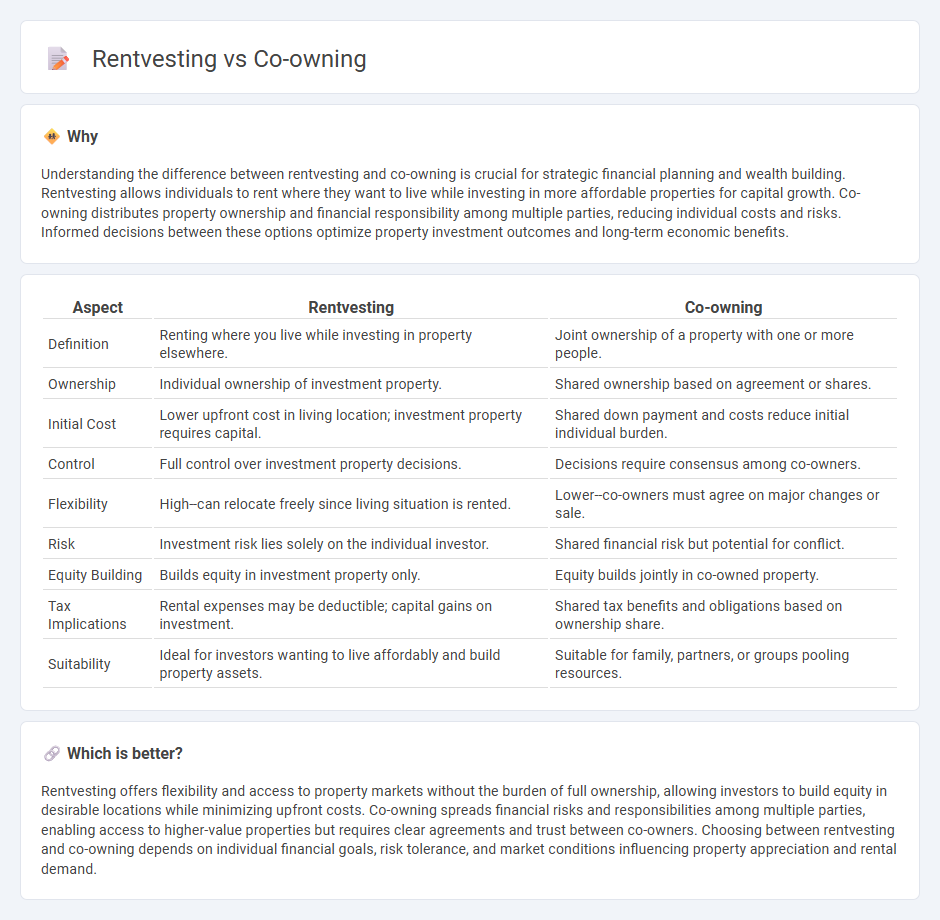
Understanding the difference between rentvesting and co-owning is crucial for strategic financial planning and wealth building. Rentvesting allows individuals to rent where they want to live while investing in more affordable properties for capital growth. Co-owning distributes property ownership and financial responsibility among multiple parties, reducing individual costs and risks. Informed decisions between these options optimize property investment outcomes and long-term economic benefits.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Rentvesting | Co-owning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Renting where you live while investing in property elsewhere. | Joint ownership of a property with one or more people. |
| Ownership | Individual ownership of investment property. | Shared ownership based on agreement or shares. |
| Initial Cost | Lower upfront cost in living location; investment property requires capital. | Shared down payment and costs reduce initial individual burden. |
| Control | Full control over investment property decisions. | Decisions require consensus among co-owners. |
| Flexibility | High--can relocate freely since living situation is rented. | Lower--co-owners must agree on major changes or sale. |
| Risk | Investment risk lies solely on the individual investor. | Shared financial risk but potential for conflict. |
| Equity Building | Builds equity in investment property only. | Equity builds jointly in co-owned property. |
| Tax Implications | Rental expenses may be deductible; capital gains on investment. | Shared tax benefits and obligations based on ownership share. |
| Suitability | Ideal for investors wanting to live affordably and build property assets. | Suitable for family, partners, or groups pooling resources. |
Which is better?
Rentvesting offers flexibility and access to property markets without the burden of full ownership, allowing investors to build equity in desirable locations while minimizing upfront costs. Co-owning spreads financial risks and responsibilities among multiple parties, enabling access to higher-value properties but requires clear agreements and trust between co-owners. Choosing between rentvesting and co-owning depends on individual financial goals, risk tolerance, and market conditions influencing property appreciation and rental demand.
Connection
Rentvesting and co-owning are connected through their shared approach to property investment that maximizes affordability and ownership opportunities. Rentvesting allows individuals to rent where they want to live while investing in property elsewhere, often through co-owning arrangements to share costs and risks. This combination enables broader market access and diversified real estate portfolios, enhancing financial flexibility and wealth accumulation.
Key Terms
Equity
Co-owning a property builds equity directly by increasing ownership stake over time through mortgage payments and property appreciation. Rentvesting allows individuals to live in a preferred location while investing in property elsewhere to accumulate equity in more affordable markets. Explore more insights on how each strategy impacts your long-term financial growth and equity building.
Cash Flow
Co-owning property allows shared mortgage payments and expenses, potentially improving cash flow by splitting financial responsibilities among owners. Rentvesting, where individuals rent where they live and invest in property elsewhere, can generate positive cash flow by owning rental properties in lower-cost markets with higher rental yields. Explore the financial impacts of both strategies to optimize your real estate investment cash flow.
Asset Appreciation
Co-owning property allows investors to directly benefit from asset appreciation through shared ownership, potentially leading to significant equity growth over time. Rentvesting, on the other hand, enables individuals to live in affordable rental housing while investing in properties in high-growth areas, thus leveraging market appreciation without the need to reside in the asset. Explore detailed strategies to maximize asset appreciation through both co-owning and rentvesting models.
Source and External Links
How Does a Co-Ownership Mortgage Work? - Guidance Residential - Co-ownership allows two or more parties to jointly own and finance a property, with ownership structures like joint tenancy ensuring equal rights and shared responsibilities among all parties.
Explore the rise of non-romantic home co-buying ... - JW Surety Bonds - Co-owning a home with friends or family is increasingly popular, offering benefits such as cost-sharing, access to better properties, and investment opportunities, with nearly 15% of Americans having already co-purchased a home outside of romantic partnerships.
CoBuy: Plan, Co-buy & Co-own Your Home with Co-ownerOS(tm) - Platforms like CoBuy provide digital tools to manage all aspects of co-ownership--from planning contributions and expenses to drafting flexible co-ownership agreements and securely organizing documents throughout the property's lifecycle.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com