Greenhushing involves companies deliberately underreporting their environmental efforts to avoid scrutiny or high expectations, while greenwashing refers to misleading claims that exaggerate sustainability practices. Both tactics impact market trust and consumer behavior, affecting the overall effectiveness of corporate environmental responsibility initiatives. Explore how these practices influence the global economy and investor decisions in the sustainability sector.
Why it is important
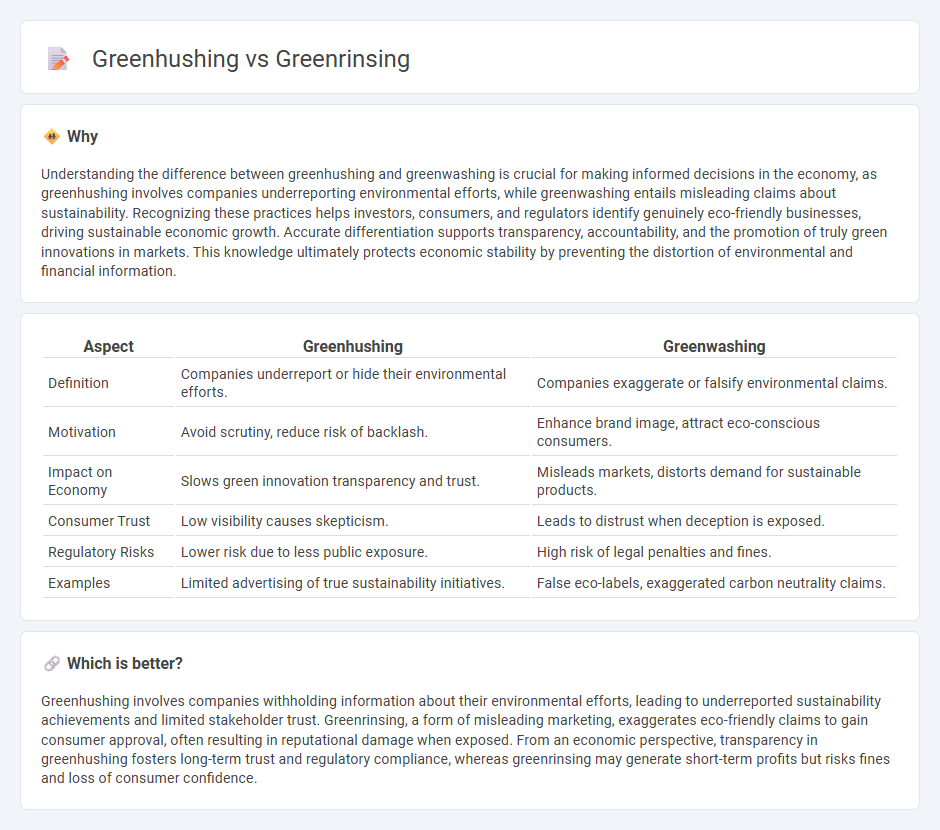
Understanding the difference between greenhushing and greenwashing is crucial for making informed decisions in the economy, as greenhushing involves companies underreporting environmental efforts, while greenwashing entails misleading claims about sustainability. Recognizing these practices helps investors, consumers, and regulators identify genuinely eco-friendly businesses, driving sustainable economic growth. Accurate differentiation supports transparency, accountability, and the promotion of truly green innovations in markets. This knowledge ultimately protects economic stability by preventing the distortion of environmental and financial information.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Greenhushing | Greenwashing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Companies underreport or hide their environmental efforts. | Companies exaggerate or falsify environmental claims. |
| Motivation | Avoid scrutiny, reduce risk of backlash. | Enhance brand image, attract eco-conscious consumers. |
| Impact on Economy | Slows green innovation transparency and trust. | Misleads markets, distorts demand for sustainable products. |
| Consumer Trust | Low visibility causes skepticism. | Leads to distrust when deception is exposed. |
| Regulatory Risks | Lower risk due to less public exposure. | High risk of legal penalties and fines. |
| Examples | Limited advertising of true sustainability initiatives. | False eco-labels, exaggerated carbon neutrality claims. |
Which is better?
Greenhushing involves companies withholding information about their environmental efforts, leading to underreported sustainability achievements and limited stakeholder trust. Greenrinsing, a form of misleading marketing, exaggerates eco-friendly claims to gain consumer approval, often resulting in reputational damage when exposed. From an economic perspective, transparency in greenhushing fosters long-term trust and regulatory compliance, whereas greenrinsing may generate short-term profits but risks fines and loss of consumer confidence.
Connection
Greenhushing and greenwashing both undermine corporate transparency and environmental accountability, hindering genuine sustainability efforts. Greenhushing involves companies underreporting or concealing their environmental initiatives to avoid scrutiny, while greenwashing entails exaggerating or falsely promoting eco-friendly practices to mislead stakeholders. These tactics distort market signals, impede investor decision-making, and slow progress toward a sustainable economy.
Key Terms
Sustainability Reporting
Greenwashing involves companies exaggerating or falsifying their sustainability efforts in reporting to appear more environmentally responsible. In contrast, greenhushing refers to organizations deliberately underreporting or withholding information on sustainability initiatives to avoid scrutiny or criticism. Explore the distinctions and implications of these practices in sustainability reporting for deeper insights.
Corporate Transparency
Greenrinsing involves companies exaggerating their environmental efforts to appear more sustainable, while greenhushing refers to the deliberate underreporting of such initiatives to avoid scrutiny or criticism. Both practices undermine corporate transparency by obscuring the true impact of sustainability measures and hindering stakeholder trust. Discover more about how transparent corporate communication can drive authentic environmental responsibility.
Regulatory Compliance
Greenwashing involves misleading claims about environmental practices to appear eco-friendly, often breaching advertising regulations and consumer protection laws. Greenhushing, the deliberate silence on genuine sustainable efforts, complicates regulatory compliance by withholding transparency required under ESG reporting standards. Explore more to understand how businesses navigate these challenges in environmental communication and compliance frameworks.
Source and External Links
6 Types of Greenwashing: Companies Mislead on Sustainability - This webpage discusses greenrinsing as a practice where companies change their Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) targets to evade accountability.
Greenwashing, Greenhushing, Greenrinsing - Do You Understand the Difference? - This blog explains greenrinsing as changing sustainability targets to appear more favorable to stakeholders, sometimes driven by less worthy motives.
Greenwashing: A Guide To Spotting All Kinds of Greenwashing - This guide describes greenrinsing as a tactic where companies modify their ESG targets right before achieving them to avoid scrutiny.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com