Doom spending occurs when consumers increase expenditure driven by fear of future shortages or inflation, boosting short-term economic activity but risking long-term instability. Doom saving, on the other hand, involves heightened saving rates due to economic uncertainty, reducing demand and slowing growth. Explore how these contrasting behaviors impact market trends and fiscal policies.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between doom spending and doom saving is crucial for making informed financial decisions during economic downturns. Doom spending involves excessive, impulsive purchases driven by fear, which can lead to debt accumulation and financial instability. Doom saving refers to compulsive savings out of anxiety, potentially restricting spending and slowing economic recovery. Recognizing these behaviors helps individuals and policymakers balance consumption and saving to support economic stability and growth.
Comparison Table
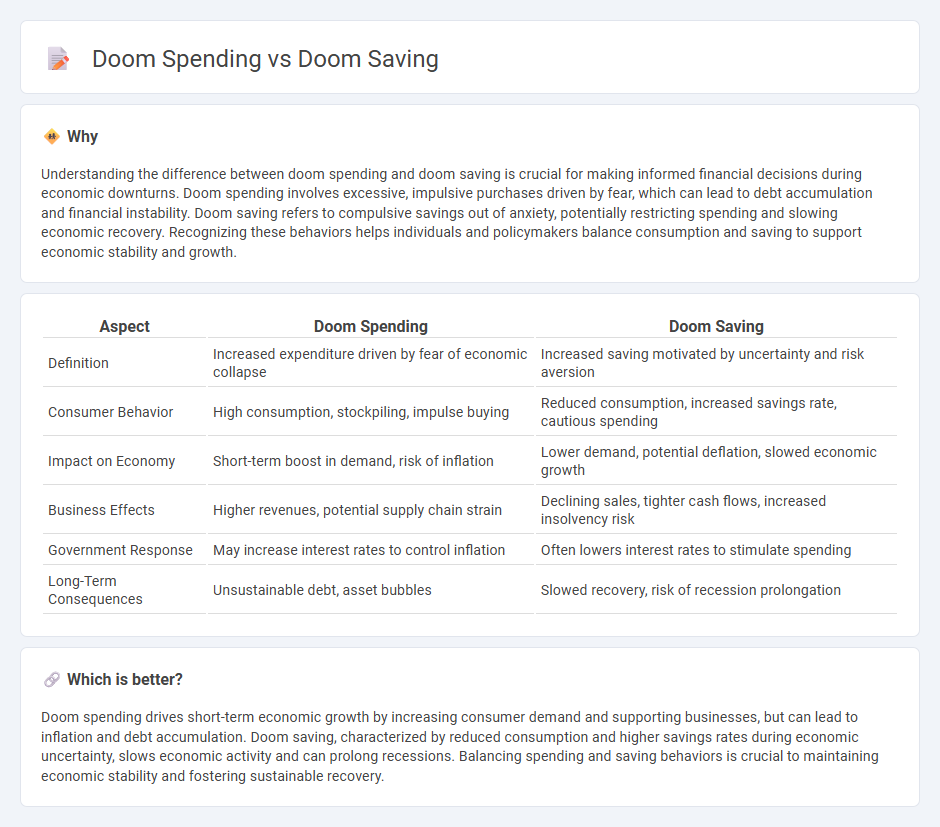
| Aspect | Doom Spending | Doom Saving |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Increased expenditure driven by fear of economic collapse | Increased saving motivated by uncertainty and risk aversion |
| Consumer Behavior | High consumption, stockpiling, impulse buying | Reduced consumption, increased savings rate, cautious spending |
| Impact on Economy | Short-term boost in demand, risk of inflation | Lower demand, potential deflation, slowed economic growth |
| Business Effects | Higher revenues, potential supply chain strain | Declining sales, tighter cash flows, increased insolvency risk |
| Government Response | May increase interest rates to control inflation | Often lowers interest rates to stimulate spending |
| Long-Term Consequences | Unsustainable debt, asset bubbles | Slowed recovery, risk of recession prolongation |
Which is better?
Doom spending drives short-term economic growth by increasing consumer demand and supporting businesses, but can lead to inflation and debt accumulation. Doom saving, characterized by reduced consumption and higher savings rates during economic uncertainty, slows economic activity and can prolong recessions. Balancing spending and saving behaviors is crucial to maintaining economic stability and fostering sustainable recovery.
Connection
Doom spending and doom saving are psychological responses to economic uncertainty that impact consumer behavior and market stability. Doom spending occurs when individuals increase consumption to gain immediate gratification amidst fear, while doom saving involves hoarding resources for future security, reducing overall demand. Both behaviors exacerbate economic volatility by creating unpredictable fluctuations in spending and saving patterns, influencing GDP growth and inflation rates.
Key Terms
Consumer Confidence
Consumer confidence fluctuates significantly between doom saving and doom spending behaviors, influenced by economic uncertainty and market volatility. During periods of heightened concern, consumers tend to prioritize saving to buffer against potential financial downturns, whereas optimistic outlooks boost spending and drive economic growth. Explore further to understand how shifts in consumer sentiment impact broader economic trends and personal financial decisions.
Liquidity Trap
Doom saving refers to excessive saving behavior driven by fear and economic uncertainty, leading to reduced consumer spending and demand. Doom spending, on the other hand, involves increased consumption and expenditure as a reaction to perceived future economic instability, often aimed at securing goods before prices rise or supply diminishes. Understanding the dynamics of doom saving and doom spending is crucial for grasping liquidity trap scenarios where conventional monetary policy fails to stimulate economic growth; explore more to deepen your insight into these behavioral economic patterns.
Inflation Expectations
Doom saving refers to the tendency of consumers to aggressively save in anticipation of future economic downturns or high inflation, while doom spending involves increased consumption driven by fears of rising prices eroding purchasing power. Inflation expectations significantly influence consumer behavior, with elevated expectations often triggering either sharp reductions in current spending or accelerated purchases depending on individual confidence levels and financial resilience. Explore how these contrasting behaviors shape economic cycles and policy responses amid fluctuating inflation trends.
Source and External Links
Americans Are Doom Saving, Too - Business Insider - In response to economic uncertainty, some Americans are "doom saving," meaning they are prioritizing saving money even if it might slow down spending in the broader economy.
Save game - The Doom Wiki at DoomWiki.org - In the Doom video game series, a save game records the player's current state to file, allowing them to resume from that point, but these files are generally not transferable between different versions or systems.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com