Deglobalization involves the reduction of global interdependence by limiting trade, investment, and cross-border economic activities, often driven by protectionist policies and national interests. Economic integration refers to the process where countries reduce barriers to trade and investment to create a more unified market, promoting economic growth through cooperation and shared regulations. Discover how these opposing trends are shaping the future of global markets and international relations.
Why it is important
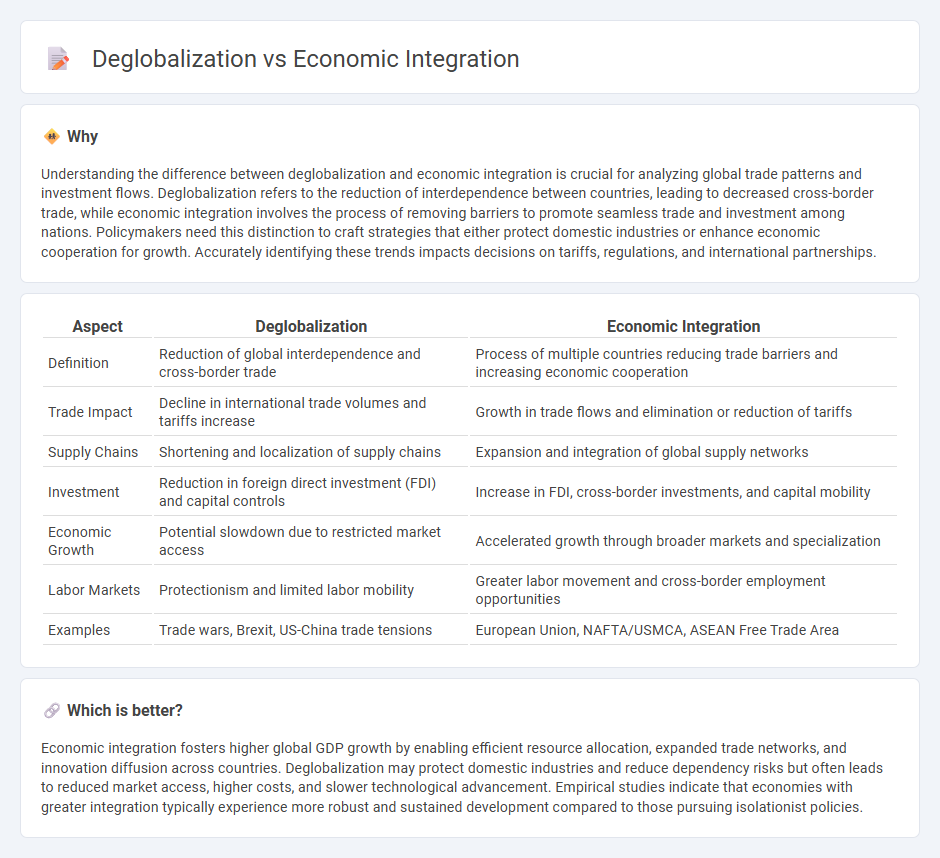
Understanding the difference between deglobalization and economic integration is crucial for analyzing global trade patterns and investment flows. Deglobalization refers to the reduction of interdependence between countries, leading to decreased cross-border trade, while economic integration involves the process of removing barriers to promote seamless trade and investment among nations. Policymakers need this distinction to craft strategies that either protect domestic industries or enhance economic cooperation for growth. Accurately identifying these trends impacts decisions on tariffs, regulations, and international partnerships.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Deglobalization | Economic Integration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reduction of global interdependence and cross-border trade | Process of multiple countries reducing trade barriers and increasing economic cooperation |
| Trade Impact | Decline in international trade volumes and tariffs increase | Growth in trade flows and elimination or reduction of tariffs |
| Supply Chains | Shortening and localization of supply chains | Expansion and integration of global supply networks |
| Investment | Reduction in foreign direct investment (FDI) and capital controls | Increase in FDI, cross-border investments, and capital mobility |
| Economic Growth | Potential slowdown due to restricted market access | Accelerated growth through broader markets and specialization |
| Labor Markets | Protectionism and limited labor mobility | Greater labor movement and cross-border employment opportunities |
| Examples | Trade wars, Brexit, US-China trade tensions | European Union, NAFTA/USMCA, ASEAN Free Trade Area |
Which is better?
Economic integration fosters higher global GDP growth by enabling efficient resource allocation, expanded trade networks, and innovation diffusion across countries. Deglobalization may protect domestic industries and reduce dependency risks but often leads to reduced market access, higher costs, and slower technological advancement. Empirical studies indicate that economies with greater integration typically experience more robust and sustained development compared to those pursuing isolationist policies.
Connection
Deglobalization and economic integration are interconnected through the shifting dynamics of international trade and investment patterns, where deglobalization trends lead to the restructuring of supply chains and selective regional cooperation frameworks. Economic integration often emerges as a strategic response to deglobalization, fostering closer cooperation among neighboring countries to enhance market access, reduce trade barriers, and stabilize regional economies. This interplay shapes global economic policies and influences the balance between global connectivity and regional consolidation.
Key Terms
Trade Liberalization
Economic integration emphasizes reducing trade barriers through agreements like NAFTA and the EU Single Market, promoting efficient allocation of resources and increased cross-border trade. Deglobalization, characterized by rising tariffs, trade restrictions, and the reshoring of supply chains, challenges free trade principles and often leads to fragmented markets. Explore how these opposing trends impact global trade liberalization strategies and economic growth.
Protectionism
Economic integration fosters global trade by reducing tariffs and barriers, promoting cooperative policies that enhance market access and supply chain efficiency. Deglobalization, driven by protectionism, emphasizes national sovereignty through increased tariffs, import restrictions, and trade barriers to safeguard domestic industries and jobs. Explore how these contrasting approaches impact global economic stability and international relations.
Regional Blocs
Economic integration in regional blocs like the European Union and ASEAN enhances trade liberalization, regulatory alignment, and investment flows among member countries, creating robust interconnected markets. Deglobalization trends, driven by protectionism and supply chain reconfiguration, challenge these blocs by emphasizing national sovereignty and reduced cross-border dependencies. Explore the evolving dynamics between regional economic integration and deglobalization to understand their impacts on global trade networks.
Source and External Links
Economic integration | EBSCO Research Starters - Economic integration is the process where multiple countries combine their economic policies to enhance trade and cooperation by reducing tariffs and trade barriers, fostering regional cooperation and boosting economic growth.
Economic Integration Definition, stages, and its advantages - Economic integration facilitates economies of scale, specialization, enhanced competition, increased foreign direct investment, job creation, consumer benefits, and political cooperation among member countries.
Economic integration | Trade, Investment & Growth - Economic integration involves reducing trade barriers and harmonizing regulations among countries to create a free-flowing regional economic space, including free movement of goods, services, and labor.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com