Girl math simplifies personal finance by turning everyday purchases into manageable, guilt-free calculations, while investor math focuses on data-driven analysis and long-term portfolio growth strategies. Understanding the differences between these approaches reveals how emotional versus analytical thinking impacts money management and wealth accumulation. Explore how blending girl math intuition with investor math precision can optimize your financial decisions.
Why it is important
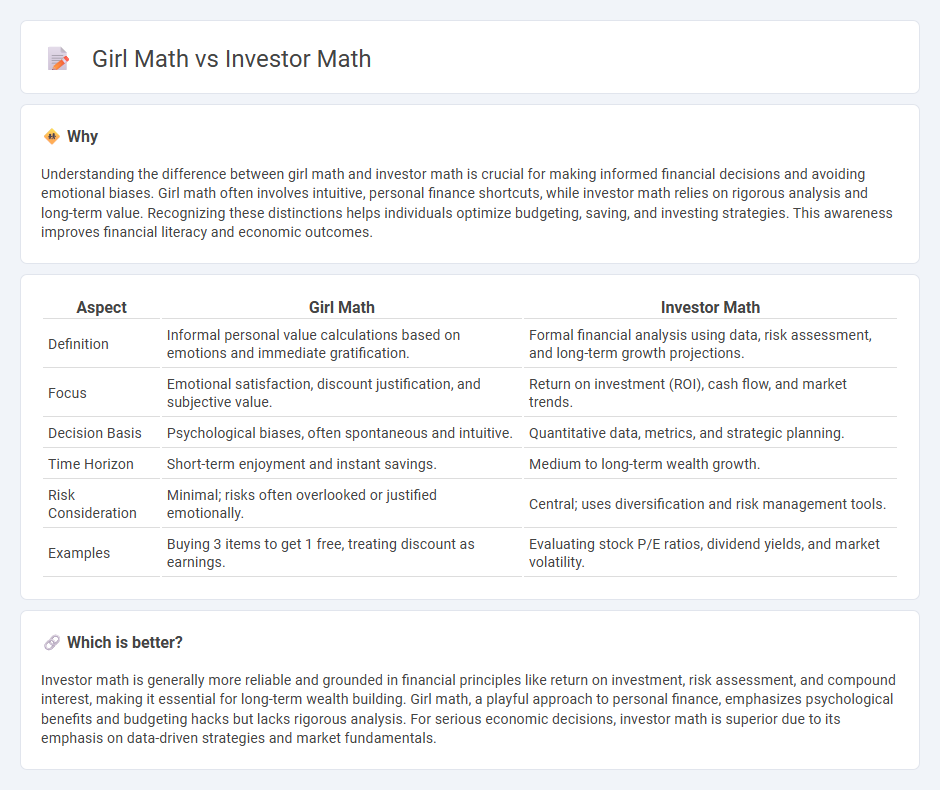
Understanding the difference between girl math and investor math is crucial for making informed financial decisions and avoiding emotional biases. Girl math often involves intuitive, personal finance shortcuts, while investor math relies on rigorous analysis and long-term value. Recognizing these distinctions helps individuals optimize budgeting, saving, and investing strategies. This awareness improves financial literacy and economic outcomes.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Girl Math | Investor Math |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Informal personal value calculations based on emotions and immediate gratification. | Formal financial analysis using data, risk assessment, and long-term growth projections. |
| Focus | Emotional satisfaction, discount justification, and subjective value. | Return on investment (ROI), cash flow, and market trends. |
| Decision Basis | Psychological biases, often spontaneous and intuitive. | Quantitative data, metrics, and strategic planning. |
| Time Horizon | Short-term enjoyment and instant savings. | Medium to long-term wealth growth. |
| Risk Consideration | Minimal; risks often overlooked or justified emotionally. | Central; uses diversification and risk management tools. |
| Examples | Buying 3 items to get 1 free, treating discount as earnings. | Evaluating stock P/E ratios, dividend yields, and market volatility. |
Which is better?
Investor math is generally more reliable and grounded in financial principles like return on investment, risk assessment, and compound interest, making it essential for long-term wealth building. Girl math, a playful approach to personal finance, emphasizes psychological benefits and budgeting hacks but lacks rigorous analysis. For serious economic decisions, investor math is superior due to its emphasis on data-driven strategies and market fundamentals.
Connection
Girl math and investor math both use psychological shortcuts to simplify complex financial decisions, focusing on perceived value and emotional impact rather than strict numerical accuracy. These informal cognitive frameworks influence spending and investing behavior by framing costs and returns in more relatable or motivational terms. Understanding this connection helps economists and financial advisors predict consumer and investor choices driven by mental accounting and subjective valuation.
Key Terms
**Investor Math:**
Investor math involves analyzing financial metrics such as compound interest, return on investment (ROI), and risk-adjusted returns to make informed decisions that maximize wealth growth over time. It relies heavily on data-driven calculations, including cash flow projections, net present value (NPV), and portfolio diversification principles to optimize investment strategies. Explore further to deepen your understanding of effective investor math techniques.
Compound Interest
Investor math emphasizes compound interest as a powerful tool for wealth growth, where interest earned is reinvested, generating exponential returns over time. Girl math, a playful term used to highlight practical and relatable financial hacks, might focus more on everyday savings and budgeting techniques rather than long-term investment concepts. Explore deeper insights into how mastering compound interest can transform your financial future.
Risk-Return Tradeoff
Investor math revolves around the risk-return tradeoff, emphasizing the balance between potential gains and the probability of loss in financial decisions. Girl math, a playful social media concept, often frames spending or saving habits through relatable, emotion-driven logic rather than strict financial principles. Explore deeper insights into how risk perception shapes diverse financial behaviors and decision-making strategies.
Source and External Links
Essential Mathematics You Must Know for Investing in the Stock ... - Learn key formulas like Future Value (\(F = P \times (1 + R)^t\)) and Total Return (including dividends) to estimate growth and actual returns on investments.
The Rule of 72: A Simple Formula for Smart Investing - Use the Rule of 72 (divide 72 by your annual rate of return) to quickly estimate how many years it will take for your investment to double.
Investment Math - Understand that compounding means returns build on previous gains, losses require larger percentage gains to recover, and large percentage changes (e.g., 100%, 200%) have clear multiplicative effects on your wealth.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com