Scrap metal arbitrage involves capitalizing on price differences of recyclable metals across regional markets to generate profit, leveraging fluctuations in supply and demand. Interest rate arbitrage exploits disparities in interest rates between countries or financial instruments to earn returns through borrowing at lower rates and investing in higher-yield assets. Explore the nuances of these arbitrage strategies to enhance your economic insights.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between scrap metal arbitrage and interest rate arbitrage is crucial because they involve distinct markets and risk factors, with scrap metal arbitrage focusing on physical commodity price discrepancies and interest rate arbitrage exploiting differences in borrowing costs across currencies. Scrap metal arbitrage requires knowledge of global supply chains, metal prices, and transportation costs, while interest rate arbitrage depends on monetary policies, exchange rates, and financial instruments. Mastering these concepts enables investors and businesses to optimize profits, manage risks, and make informed decisions in both commodity and financial markets. Failure to differentiate these arbitrage types can lead to misinformed strategies and significant financial losses.
Comparison Table
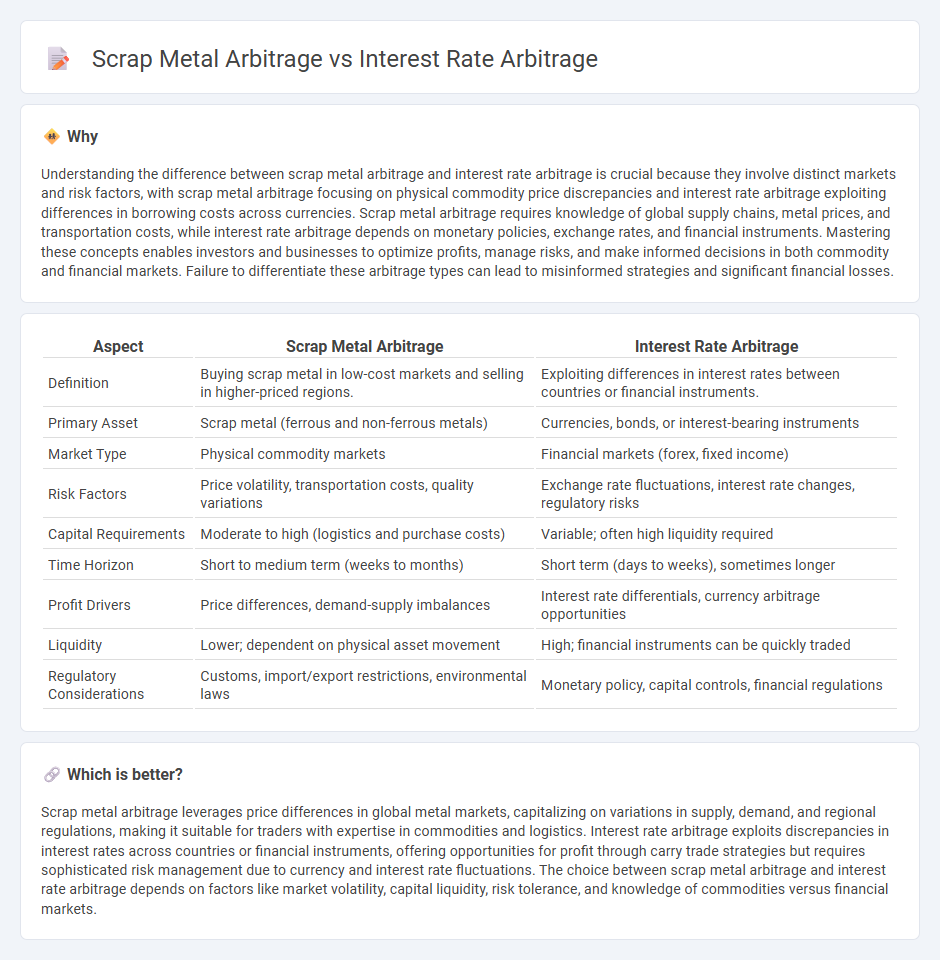
| Aspect | Scrap Metal Arbitrage | Interest Rate Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Buying scrap metal in low-cost markets and selling in higher-priced regions. | Exploiting differences in interest rates between countries or financial instruments. |
| Primary Asset | Scrap metal (ferrous and non-ferrous metals) | Currencies, bonds, or interest-bearing instruments |
| Market Type | Physical commodity markets | Financial markets (forex, fixed income) |
| Risk Factors | Price volatility, transportation costs, quality variations | Exchange rate fluctuations, interest rate changes, regulatory risks |
| Capital Requirements | Moderate to high (logistics and purchase costs) | Variable; often high liquidity required |
| Time Horizon | Short to medium term (weeks to months) | Short term (days to weeks), sometimes longer |
| Profit Drivers | Price differences, demand-supply imbalances | Interest rate differentials, currency arbitrage opportunities |
| Liquidity | Lower; dependent on physical asset movement | High; financial instruments can be quickly traded |
| Regulatory Considerations | Customs, import/export restrictions, environmental laws | Monetary policy, capital controls, financial regulations |
Which is better?
Scrap metal arbitrage leverages price differences in global metal markets, capitalizing on variations in supply, demand, and regional regulations, making it suitable for traders with expertise in commodities and logistics. Interest rate arbitrage exploits discrepancies in interest rates across countries or financial instruments, offering opportunities for profit through carry trade strategies but requires sophisticated risk management due to currency and interest rate fluctuations. The choice between scrap metal arbitrage and interest rate arbitrage depends on factors like market volatility, capital liquidity, risk tolerance, and knowledge of commodities versus financial markets.
Connection
Scrap metal arbitrage and interest rate arbitrage are connected through their reliance on market inefficiencies and capital flow optimization to generate profits. Investors exploit price differences in scrap metal markets by buying low and selling high across regions, while interest rate arbitrage capitalizes on disparities in borrowing costs between different countries or financial instruments. Both strategies require precise timing, adequate liquidity, and an understanding of global economic conditions affecting supply chains and monetary policies.
Key Terms
Capital flows
Interest rate arbitrage involves exploiting differences in interest rates across countries to optimize capital flows and maximize returns on investments, often through currency trading and banking activities. Scrap metal arbitrage focuses on capitalizing on price disparities in the global scrap metal markets, driving trade flows between regions with surplus materials and those with high demand for raw metal inputs. Discover how these distinct arbitrage strategies influence capital allocation and market dynamics in greater detail.
Price differentials
Interest rate arbitrage exploits discrepancies in borrowing costs across different financial markets to generate profit, relying heavily on interest rate differentials between countries or institutions. Scrap metal arbitrage capitalizes on price differentials in various geographic locations or between market segments by buying low-cost scrap metals and selling them where prices are higher. Explore deeper insights into these arbitrage strategies and their practical applications to understand their unique market dynamics.
Asset valuation
Interest rate arbitrage leverages differences in interest rates between countries to exploit gains from currency value fluctuations, focusing primarily on financial asset valuation through yield differentials and exchange rates. Scrap metal arbitrage involves capitalizing on price discrepancies in metals markets, with asset valuation centered around physical commodity prices influenced by supply-demand dynamics and global industrial demand. Explore the detailed mechanisms and valuation strategies behind these arbitrage types to understand their distinct financial and tangible asset implications.
Source and External Links
Exploit Profits with Interest Rate Arbitrage - MarketBulls - Interest rate arbitrage is a strategy where investors borrow money in markets with low interest rates and invest in markets with higher rates to earn risk-free profits by exploiting interest rate differences; key methods include currency carry trades and covered interest arbitrage, which uses forward contracts to avoid currency risk.
Covered interest arbitrage - Wikipedia - Covered interest arbitrage involves converting domestic currency to foreign currency, investing at the foreign interest rate, and simultaneously entering a forward contract to convert the investment back to domestic currency at a set rate, thus locking in profits from the interest rate differential without currency risk.
Interest Rate Arbitrage in Negative Yielding Currencies - The Hedge Fund Journal - Interest rate arbitrage can also be applied in negative-yield environments where investors borrow at negative rates against collateral and invest in higher-yielding instruments, exploiting the rate spreads.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com