Reshoring involves bringing manufacturing and production processes back to a company's original country, while insourcing refers to handling business functions internally rather than outsourcing them to third parties. Both strategies aim to enhance control over quality, reduce lead times, and improve supply chain resilience in response to global economic shifts. Explore the benefits and challenges of reshoring and insourcing to understand their impact on modern economies.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between reshoring and insourcing is crucial for businesses to optimize supply chain management and reduce costs effectively. Reshoring involves bringing manufacturing back to the company's home country, enhancing local job creation and reducing transportation risks. Insourcing means using the company's own resources to perform tasks previously outsourced, improving control over quality and efficiency. Accurate knowledge of these concepts enables strategic decisions that boost competitiveness and economic growth.
Comparison Table
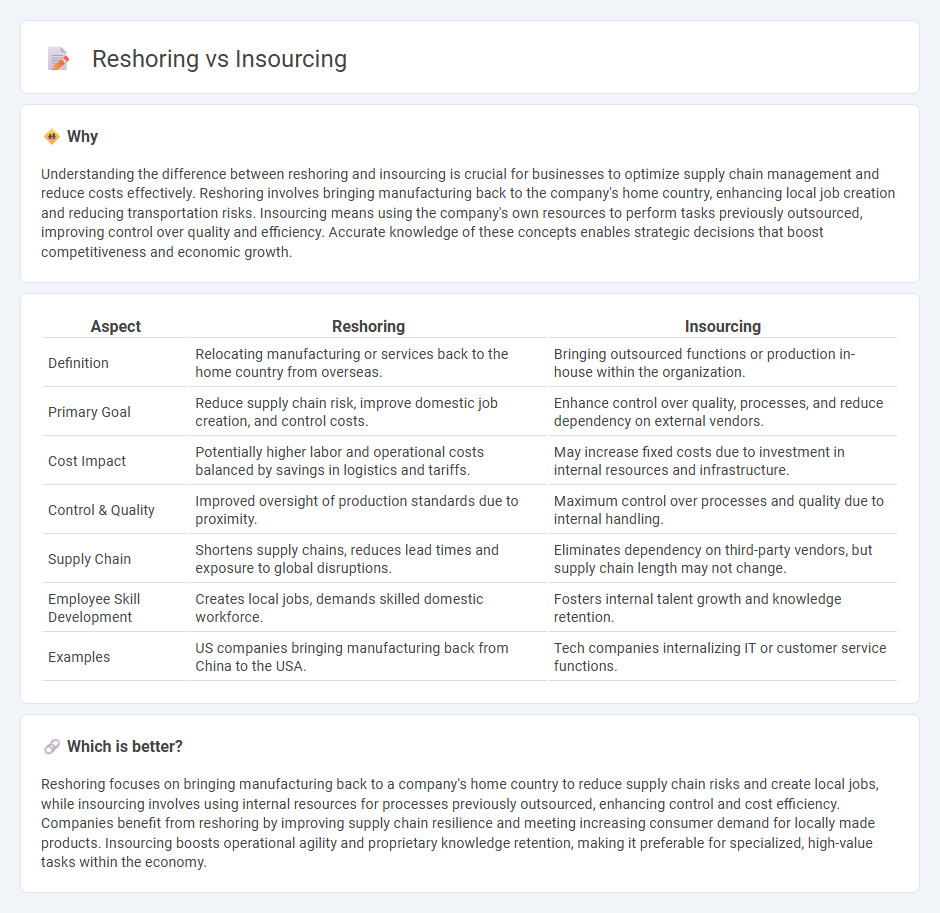
| Aspect | Reshoring | Insourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Relocating manufacturing or services back to the home country from overseas. | Bringing outsourced functions or production in-house within the organization. |
| Primary Goal | Reduce supply chain risk, improve domestic job creation, and control costs. | Enhance control over quality, processes, and reduce dependency on external vendors. |
| Cost Impact | Potentially higher labor and operational costs balanced by savings in logistics and tariffs. | May increase fixed costs due to investment in internal resources and infrastructure. |
| Control & Quality | Improved oversight of production standards due to proximity. | Maximum control over processes and quality due to internal handling. |
| Supply Chain | Shortens supply chains, reduces lead times and exposure to global disruptions. | Eliminates dependency on third-party vendors, but supply chain length may not change. |
| Employee Skill Development | Creates local jobs, demands skilled domestic workforce. | Fosters internal talent growth and knowledge retention. |
| Examples | US companies bringing manufacturing back from China to the USA. | Tech companies internalizing IT or customer service functions. |
Which is better?
Reshoring focuses on bringing manufacturing back to a company's home country to reduce supply chain risks and create local jobs, while insourcing involves using internal resources for processes previously outsourced, enhancing control and cost efficiency. Companies benefit from reshoring by improving supply chain resilience and meeting increasing consumer demand for locally made products. Insourcing boosts operational agility and proprietary knowledge retention, making it preferable for specialized, high-value tasks within the economy.
Connection
Reshoring involves bringing manufacturing and services back to the home country to boost local economies and reduce reliance on foreign suppliers. Insourcing complements reshoring by reallocating previously outsourced tasks to in-house teams, enhancing control over quality and efficiency. Together, these strategies drive economic growth by creating domestic jobs and strengthening supply chain resilience.
Key Terms
Supply Chain
Insourcing centralizes production within a company's existing facilities to enhance supply chain control, reduce lead times, and improve quality assurance. Reshoring involves relocating manufacturing operations back to the home country, aiming to mitigate risks from global disruptions and lower transportation costs. Explore the distinct supply chain benefits of insourcing versus reshoring to optimize your operational strategy.
Labor Costs
Labor costs play a critical role in insourcing and reshoring decisions as companies evaluate wage differences and productivity levels between domestic and offshore locations. Insourcing often leverages existing in-house labor to reduce reliance on external vendors, while reshoring aims to bring jobs back to higher-wage domestic markets to improve quality control and reduce supply chain risks. Explore a deeper analysis of labor cost impacts to optimize your strategic production choices.
Domestic Production
Insourcing and reshoring both emphasize strengthening domestic production by relocating manufacturing processes and operations within a country's borders to enhance control, reduce costs, and improve supply chain reliability. Insourcing involves companies bringing previously outsourced activities back in-house, while reshoring refers to moving entire production facilities or services from overseas back to the home country. Discover how these strategies can optimize your business's operational efficiency and competitiveness by exploring their distinct advantages and implementation challenges.
Source and External Links
What Is Insourcing and How It Works (With Examples) - Insourcing is the process where a company brings individuals in from other companies or locations to complete tasks internally, offering better efficiency, quality, and control compared to outsourcing.
What Is Insourcing? Definition, Benefits, And Examples - Insourcing involves using a company's own resources and employees to handle tasks internally, often through staff augmentation and training, which improves quality control and collaboration.
Insourcing - Definition, Examples & FAQ - Insourcing means performing tasks within the organization by leveraging existing talent and resources, providing advantages such as quicker responses, better process control, enhanced collaboration, and employee development.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com