Tipflation and deflation represent contrasting economic phenomena impacting consumer prices and market stability; tipflation involves rising service costs due to increased tipping habits, while deflation refers to a sustained decrease in the general price level of goods and services, often signaling reduced demand. Both concepts influence purchasing power, wage dynamics, and monetary policy decisions, affecting overall economic growth and inflation control. Explore further to understand how tipflation and deflation shape financial strategies and economic forecasts.
Why it is important
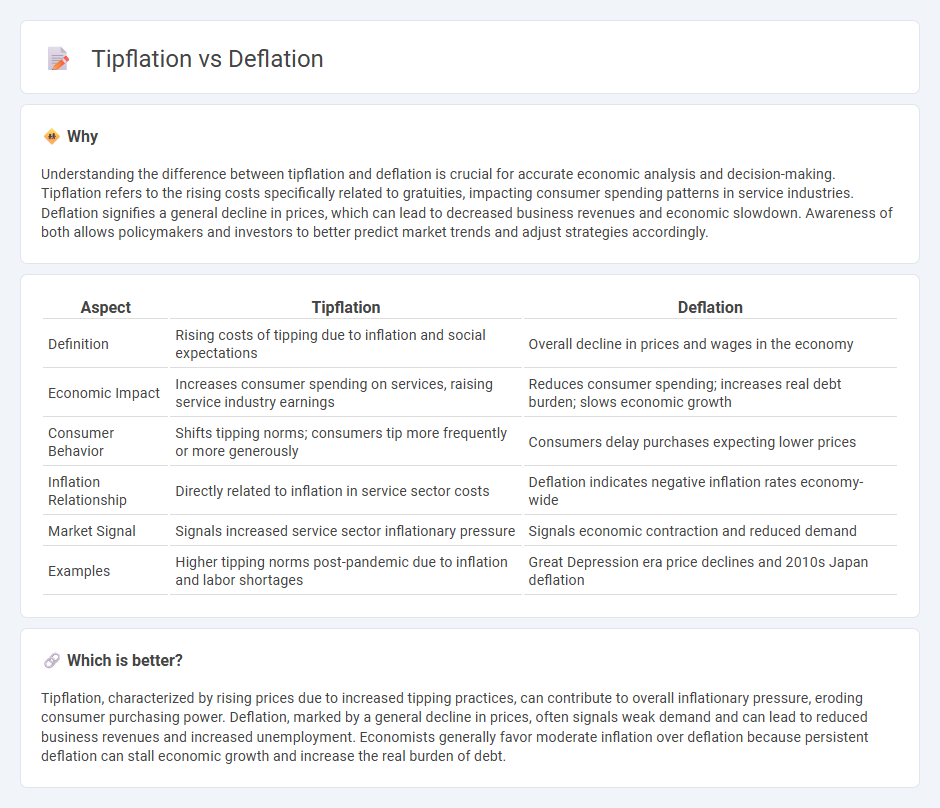
Understanding the difference between tipflation and deflation is crucial for accurate economic analysis and decision-making. Tipflation refers to the rising costs specifically related to gratuities, impacting consumer spending patterns in service industries. Deflation signifies a general decline in prices, which can lead to decreased business revenues and economic slowdown. Awareness of both allows policymakers and investors to better predict market trends and adjust strategies accordingly.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Tipflation | Deflation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rising costs of tipping due to inflation and social expectations | Overall decline in prices and wages in the economy |
| Economic Impact | Increases consumer spending on services, raising service industry earnings | Reduces consumer spending; increases real debt burden; slows economic growth |
| Consumer Behavior | Shifts tipping norms; consumers tip more frequently or more generously | Consumers delay purchases expecting lower prices |
| Inflation Relationship | Directly related to inflation in service sector costs | Deflation indicates negative inflation rates economy-wide |
| Market Signal | Signals increased service sector inflationary pressure | Signals economic contraction and reduced demand |
| Examples | Higher tipping norms post-pandemic due to inflation and labor shortages | Great Depression era price declines and 2010s Japan deflation |
Which is better?
Tipflation, characterized by rising prices due to increased tipping practices, can contribute to overall inflationary pressure, eroding consumer purchasing power. Deflation, marked by a general decline in prices, often signals weak demand and can lead to reduced business revenues and increased unemployment. Economists generally favor moderate inflation over deflation because persistent deflation can stall economic growth and increase the real burden of debt.
Connection
Tipflation and deflation intersect through their impact on consumer spending behavior and perceived cost of goods and services. Tipflation, where tipping amounts increase disproportionately, can mimic inflation by raising overall expenses despite stable prices, potentially reducing discretionary spending. Deflation, characterized by falling prices, may intensify the psychological effects of tipflation as consumers adjust tipping habits amid declining product and service costs, influencing economic demand.
Key Terms
Purchasing Power
Deflation increases purchasing power by reducing prices across goods and services, enabling consumers to buy more with the same amount of money. In contrast, tipflation raises the effective cost of dining out or services by increasing tipping expectations, which erodes purchasing power without altering listed prices. Explore how these economic phenomena uniquely impact consumer spending and financial strategies.
Price Levels
Deflation occurs when the general price level of goods and services decreases over time, increasing purchasing power and often signaling reduced consumer demand. Tipflation refers to rising tip amounts contributing to an overall increase in service costs, impacting the effective price consumers pay despite stable base prices. Explore further to understand how these phenomena influence economic behavior and pricing strategies.
Gratuity Practices
Deflation refers to the general decline in prices, reducing the purchasing power of money, whereas tipflation specifically pertains to the rising expectations and amounts in gratuity practices, often driven by inflation and changing social norms. Gratuity trends show increased tipping percentages in restaurants and service sectors, impacting consumer budgets despite broader economic deflation. Explore how evolving gratuity norms affect economic behavior and service industry sustainability.
Source and External Links
Deflation | EBSCO Research Starters - Deflation is an economic phenomenon marked by a decrease in the money supply or credit that causes prices of goods and services to decline, often signaling deeper economic problems like recessions or depressions.
Deflation - Definition, Causes, Effects, Impact - Deflation is the general decline in prices, or negative inflation, caused primarily by a fall in aggregate demand or an increase in aggregate supply, which can intensify recessions or lead to deflationary spirals.
Deflation - Wikipedia - Deflation occurs when inflation falls below zero, increasing currency value and allowing more purchasing power, but it can raise the real value of debt and worsen recessions through deflationary spirals.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com