Carbon border adjustment mechanisms impose tariffs on imported goods based on their carbon emissions to level the playing field for domestic producers adhering to strict environmental standards. These policies aim to prevent carbon leakage and promote global climate action by encouraging cleaner production methods worldwide. Explore the distinctions and economic impacts of carbon border adjustments versus traditional environmental standards to understand their roles in sustainable trade.
Why it is important
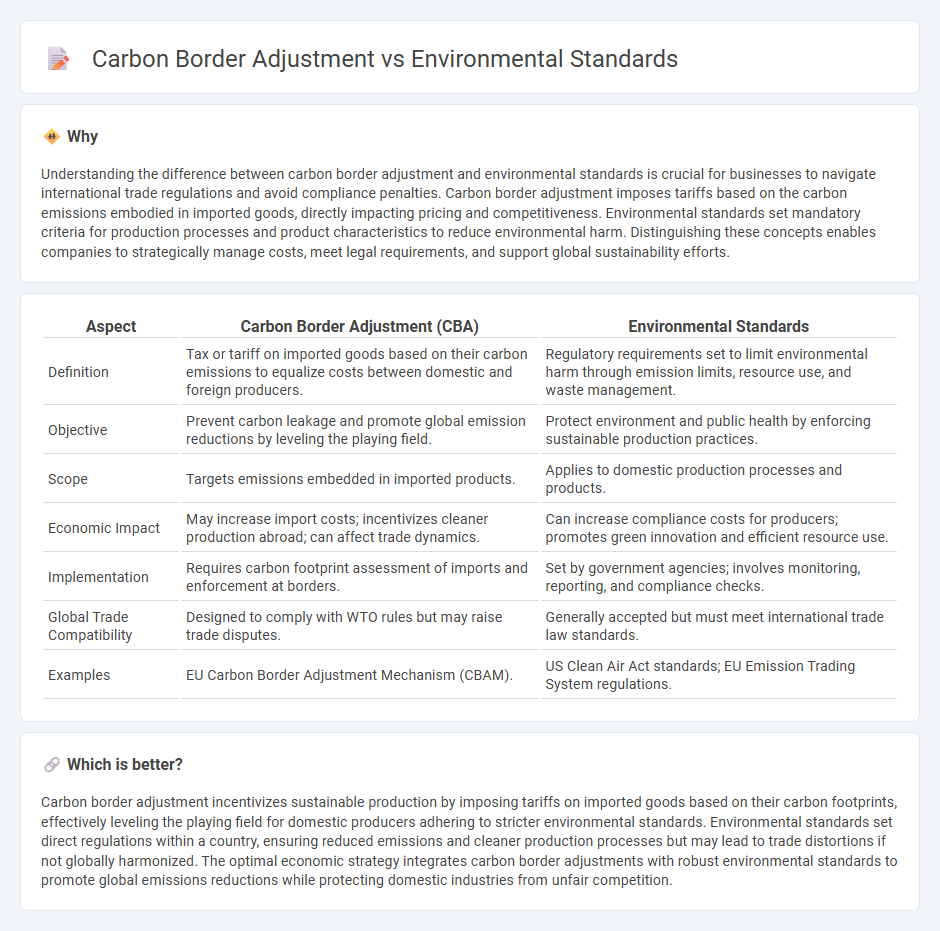
Understanding the difference between carbon border adjustment and environmental standards is crucial for businesses to navigate international trade regulations and avoid compliance penalties. Carbon border adjustment imposes tariffs based on the carbon emissions embodied in imported goods, directly impacting pricing and competitiveness. Environmental standards set mandatory criteria for production processes and product characteristics to reduce environmental harm. Distinguishing these concepts enables companies to strategically manage costs, meet legal requirements, and support global sustainability efforts.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Carbon Border Adjustment (CBA) | Environmental Standards |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tax or tariff on imported goods based on their carbon emissions to equalize costs between domestic and foreign producers. | Regulatory requirements set to limit environmental harm through emission limits, resource use, and waste management. |
| Objective | Prevent carbon leakage and promote global emission reductions by leveling the playing field. | Protect environment and public health by enforcing sustainable production practices. |
| Scope | Targets emissions embedded in imported products. | Applies to domestic production processes and products. |
| Economic Impact | May increase import costs; incentivizes cleaner production abroad; can affect trade dynamics. | Can increase compliance costs for producers; promotes green innovation and efficient resource use. |
| Implementation | Requires carbon footprint assessment of imports and enforcement at borders. | Set by government agencies; involves monitoring, reporting, and compliance checks. |
| Global Trade Compatibility | Designed to comply with WTO rules but may raise trade disputes. | Generally accepted but must meet international trade law standards. |
| Examples | EU Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM). | US Clean Air Act standards; EU Emission Trading System regulations. |
Which is better?
Carbon border adjustment incentivizes sustainable production by imposing tariffs on imported goods based on their carbon footprints, effectively leveling the playing field for domestic producers adhering to stricter environmental standards. Environmental standards set direct regulations within a country, ensuring reduced emissions and cleaner production processes but may lead to trade distortions if not globally harmonized. The optimal economic strategy integrates carbon border adjustments with robust environmental standards to promote global emissions reductions while protecting domestic industries from unfair competition.
Connection
Carbon border adjustment mechanisms align international trade with environmental standards by imposing tariffs on imported goods based on their carbon emissions. This approach incentivizes global manufacturers to adopt cleaner production processes to remain competitive in markets with stringent climate policies. Integrating these measures supports economic decarbonization while preventing carbon leakage across borders.
Key Terms
Emissions Regulation
Environmental standards regulate emissions through specific limits and compliance requirements to reduce pollutants and mitigate climate impact. Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanisms (CBAM) impose tariffs on imported goods based on their carbon footprint, aiming to level the playing field and prevent carbon leakage in international trade. Explore how these approaches interact and shape global emissions regulation by learning more.
Trade Competitiveness
Environmental standards impose regulations on emissions and resource use, influencing production costs and trade patterns by requiring businesses to adopt cleaner technologies. Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanisms (CBAM) impose tariffs on imported goods based on their carbon footprint, aiming to level the playing field and prevent carbon leakage in international trade. Explore the implications of these mechanisms on trade competitiveness and global market dynamics.
Carbon Leakage
Environmental standards regulate pollutant emissions and resource use to minimize ecological harm, while carbon border adjustment mechanisms (CBAM) impose fees on imports based on their carbon footprint to prevent carbon leakage. Carbon leakage occurs when businesses relocate production to countries with laxer environmental rules, undermining global emission reduction efforts. Explore how integrating environmental standards with CBAM can effectively combat carbon leakage and promote sustainable trade.
Source and External Links
Environmental standard - Environmental standards are administrative regulations or legal rules set by governments to protect and maintain the environment, covering activities such as pollution control and resource use, based on scientific, social, and legal considerations.
ISO 14000 family -- Environmental management - The ISO 14000 family provides international standards like ISO 14001 for organizations to manage environmental responsibilities systematically and improve environmental performance through certified management systems.
Laws & Regulations | US EPA - The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency codifies environmental rules under Title 40 of the Code of Federal Regulations and enforces compliance with laws designed to protect the environment.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com