Fragmented supply chains often lead to increased risks and inefficiencies due to reliance on multiple, distant suppliers, causing delays and higher costs. Regionalized supply chains focus on local sourcing and manufacturing, enhancing resilience, reducing transportation emissions, and improving responsiveness to market demands. Explore how shifting to regionalized supply networks can transform economic stability and sustainability.
Why it is important
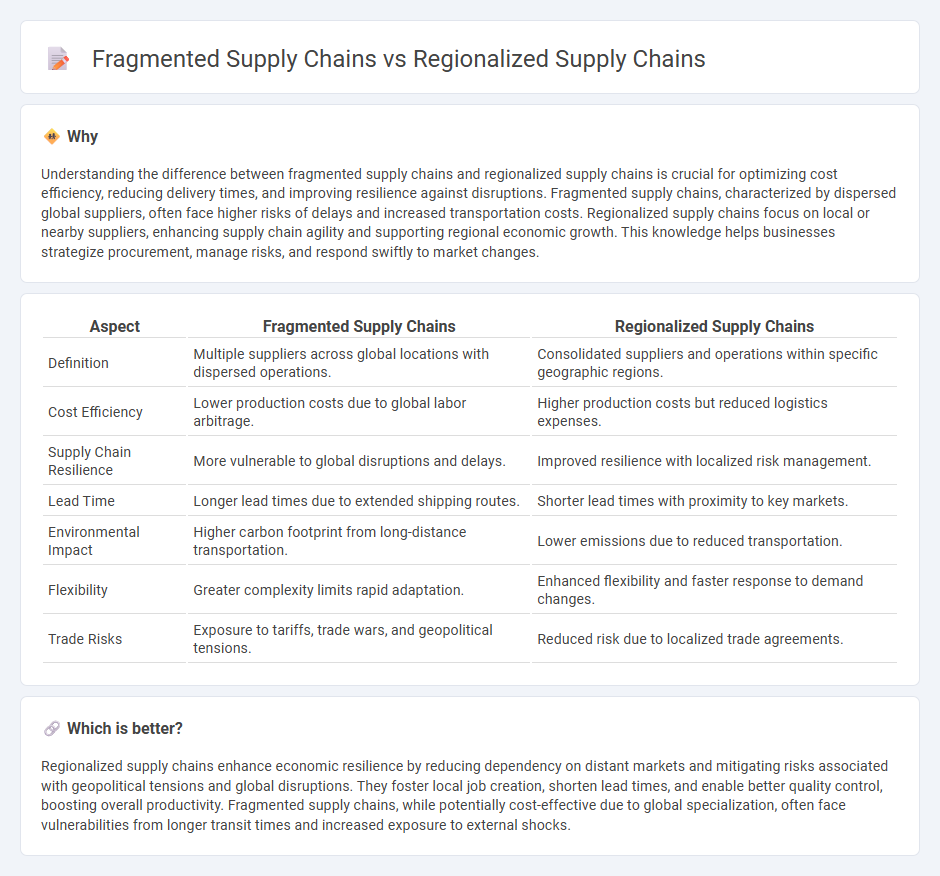
Understanding the difference between fragmented supply chains and regionalized supply chains is crucial for optimizing cost efficiency, reducing delivery times, and improving resilience against disruptions. Fragmented supply chains, characterized by dispersed global suppliers, often face higher risks of delays and increased transportation costs. Regionalized supply chains focus on local or nearby suppliers, enhancing supply chain agility and supporting regional economic growth. This knowledge helps businesses strategize procurement, manage risks, and respond swiftly to market changes.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Fragmented Supply Chains | Regionalized Supply Chains |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Multiple suppliers across global locations with dispersed operations. | Consolidated suppliers and operations within specific geographic regions. |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower production costs due to global labor arbitrage. | Higher production costs but reduced logistics expenses. |
| Supply Chain Resilience | More vulnerable to global disruptions and delays. | Improved resilience with localized risk management. |
| Lead Time | Longer lead times due to extended shipping routes. | Shorter lead times with proximity to key markets. |
| Environmental Impact | Higher carbon footprint from long-distance transportation. | Lower emissions due to reduced transportation. |
| Flexibility | Greater complexity limits rapid adaptation. | Enhanced flexibility and faster response to demand changes. |
| Trade Risks | Exposure to tariffs, trade wars, and geopolitical tensions. | Reduced risk due to localized trade agreements. |
Which is better?
Regionalized supply chains enhance economic resilience by reducing dependency on distant markets and mitigating risks associated with geopolitical tensions and global disruptions. They foster local job creation, shorten lead times, and enable better quality control, boosting overall productivity. Fragmented supply chains, while potentially cost-effective due to global specialization, often face vulnerabilities from longer transit times and increased exposure to external shocks.
Connection
Fragmented supply chains increase dependency on multiple decentralized suppliers, which drives the need for regionalized supply chains to enhance resilience and reduce transportation costs. Regionalized supply chains optimize local sourcing, aligning with fragmented structures by minimizing delays and risks associated with long-distance logistics. This interconnected dynamic supports economic stability by balancing diversification with proximity in supply chain management.
Key Terms
Resilience
Regionalized supply chains enhance resilience by shortening transportation routes, reducing dependency on distant suppliers, and enabling faster response to local disruptions. Fragmented supply chains, while offering cost advantages through global sourcing, often face increased vulnerability due to complex logistics and exposure to multiple geopolitical risks. Explore how optimizing supply chain design can boost resilience and safeguard business continuity.
Interdependence
Regionalized supply chains emphasize geographic proximity, enhancing interdependence through closer collaboration and faster response times between suppliers and manufacturers. Fragmented supply chains, spread across multiple distant locations, often face challenges in synchronization and communication, reducing overall interdependence and increasing vulnerability. Explore the benefits and risks of these structures to optimize supply chain resilience and efficiency.
Localization
Regionalized supply chains concentrate production and distribution within specific geographic areas, reducing transportation costs and enhancing responsiveness to local market demands. Fragmented supply chains, in contrast, involve dispersed operations across multiple regions or countries, increasing complexity and risks such as delays and tariff impacts. Explore how localization strategies can optimize supply chain efficiency and resilience in diverse industries.
Source and External Links
Regional Supply Chain Localizing & Minimizing Disruptions - GEP - Regionalized supply chains localize suppliers and vendors within a specific geographic area, offering advantages like lower costs, higher control, shorter delivery times, and better access to local expertise, while also requiring strategies to mitigate disruption risks.
Outpacing Disruption by Regionalizing Supply Chains - Regionalizing supply chains reduces the risk of disruption by shortening supply chain footprint and increasing resiliency, with many companies shifting to regionally diversified production to improve speed, service, and cost-effectiveness amid ongoing global uncertainties.
To regionalize or not? Optimizing North American supply chains - Regionalization in supply chains can improve profitability and resilience but depends on factors such as labor costs, supplier availability, infrastructure, and industry specifics, with more complex value chains potentially facing challenges in shifting production regionally.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com