Liquidity crunch occurs when financial institutions face a shortage of cash or liquid assets to meet immediate demands, restricting day-to-day transactions and operational flow. Credit crunch involves a significant reduction in the availability of loans or credit from banks, leading to decreased borrowing and investment. Explore the key differences and impacts of liquidity and credit crunches on the economy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between a liquidity crunch and a credit crunch is crucial for effective economic policy and financial decision-making, as a liquidity crunch involves a shortage of cash or liquid assets affecting market transactions, while a credit crunch signifies a reduction in the availability of loans or credit from banks to businesses and consumers. Misinterpreting these conditions can lead to inappropriate interventions that may worsen economic instability, such as tightening money supply during a liquidity crunch or relaxing lending standards during a credit crunch. Accurate identification helps governments and central banks tailor monetary policy tools like interest rates and reserve requirements to stabilize financial markets and support economic growth. This knowledge is essential for investors, policymakers, and businesses to navigate risks and maintain economic resilience during financial crises.
Comparison Table
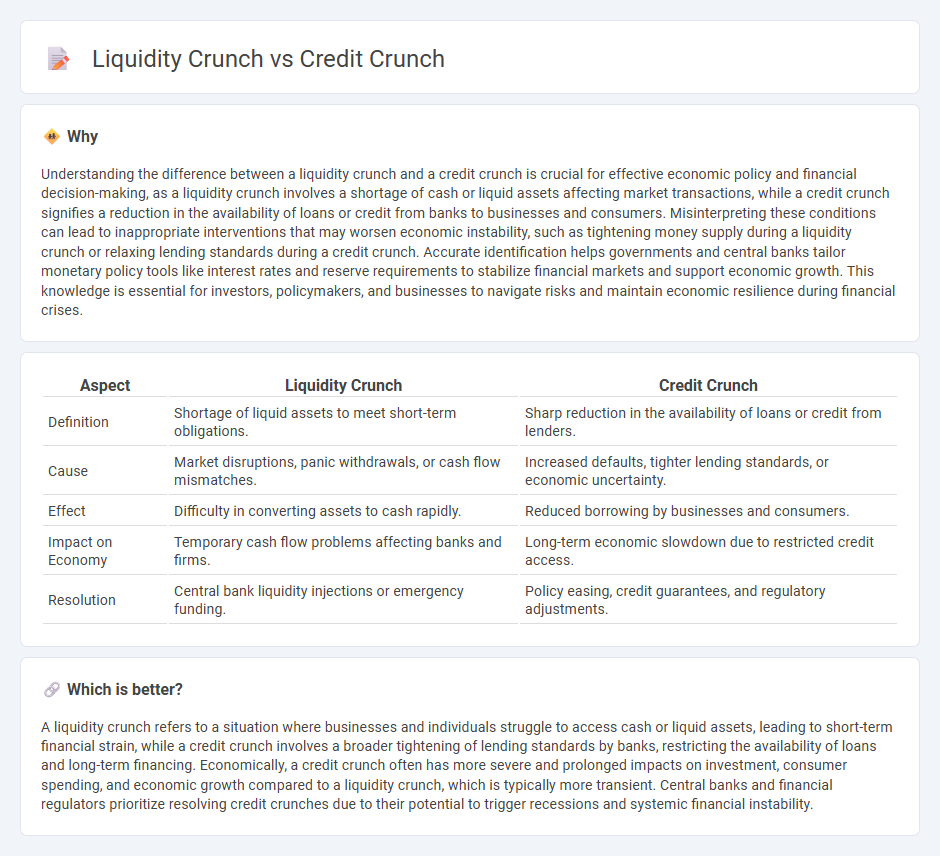
| Aspect | Liquidity Crunch | Credit Crunch |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shortage of liquid assets to meet short-term obligations. | Sharp reduction in the availability of loans or credit from lenders. |
| Cause | Market disruptions, panic withdrawals, or cash flow mismatches. | Increased defaults, tighter lending standards, or economic uncertainty. |
| Effect | Difficulty in converting assets to cash rapidly. | Reduced borrowing by businesses and consumers. |
| Impact on Economy | Temporary cash flow problems affecting banks and firms. | Long-term economic slowdown due to restricted credit access. |
| Resolution | Central bank liquidity injections or emergency funding. | Policy easing, credit guarantees, and regulatory adjustments. |
Which is better?
A liquidity crunch refers to a situation where businesses and individuals struggle to access cash or liquid assets, leading to short-term financial strain, while a credit crunch involves a broader tightening of lending standards by banks, restricting the availability of loans and long-term financing. Economically, a credit crunch often has more severe and prolonged impacts on investment, consumer spending, and economic growth compared to a liquidity crunch, which is typically more transient. Central banks and financial regulators prioritize resolving credit crunches due to their potential to trigger recessions and systemic financial instability.
Connection
A liquidity crunch occurs when financial institutions and businesses face a shortage of cash or easily convertible assets, limiting their ability to meet short-term obligations. This situation often triggers a credit crunch, where lenders tighten borrowing standards and reduce loan availability due to increased risk and lack of liquid funds. The interplay between liquidity constraints and credit tightening can exacerbate economic slowdowns by restricting investment, consumer spending, and overall financial market stability.
Key Terms
Credit Availability
Credit crunch refers to a significant reduction in the availability of loans or credit from financial institutions, often caused by tighter lending standards or increased risk aversion. Liquidity crunch involves a shortage of liquid assets in the financial system, making it difficult for businesses and individuals to access cash quickly, though credit lines may still technically be available. Explore more to understand how credit and liquidity crunches impact economic stability and financial markets.
Solvency
A credit crunch occurs when lenders significantly reduce the availability of loans, impacting borrowers' ability to access credit, whereas a liquidity crunch involves a shortage of liquid assets despite solvency, hindering a company's ability to meet short-term obligations. Solvency remains a critical factor, as credit crunches often escalate into liquidity crises, threatening long-term financial stability and risking insolvency if not addressed promptly. Explore the nuances between credit and liquidity crunches to better understand their effects on solvency and financial health.
Market Liquidity
A credit crunch occurs when banks and lenders sharply reduce the availability of loans, causing a significant drop in credit supply to borrowers, while a liquidity crunch specifically refers to a shortage of liquid assets within the financial system, limiting the ease with which assets can be bought or sold without price disruption. Market liquidity, focused on the ability to quickly trade assets at stable prices, is severely impaired during a liquidity crunch as investors struggle to convert assets into cash without significant losses. Explore further how these financial conditions impact investment strategies and market stability.
Source and External Links
Credit crunch - Wikipedia - A credit crunch is a sudden reduction in the general availability of loans, often independent of a rise in official interest rates, leading to tighter lending standards and credit rationing.
Credit Crunch Definition, Causes & Consequences - Study.com - A credit crunch occurs when banks become reluctant to lend, usually during economic downturns, due to factors like rising defaults, loss of confidence in the financial system, or external shocks, resulting in higher borrowing costs and broader economic stress.
What happens during a credit crunch and what that could mean for you - During a credit crunch, loans become harder to obtain for both individuals and businesses, as banks tighten lending standards, potentially affecting those with little savings or high debt more severely.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com