Unretirement reflects a growing economic trend where older adults re-enter the workforce to supplement income, maintain social engagement, and leverage their expertise. Flexible work arrangements provide adaptability in hours and location, promoting work-life balance and increasing productivity across diverse industries. Discover more about how these shifts are reshaping economic participation in modern labor markets.
Why it is important
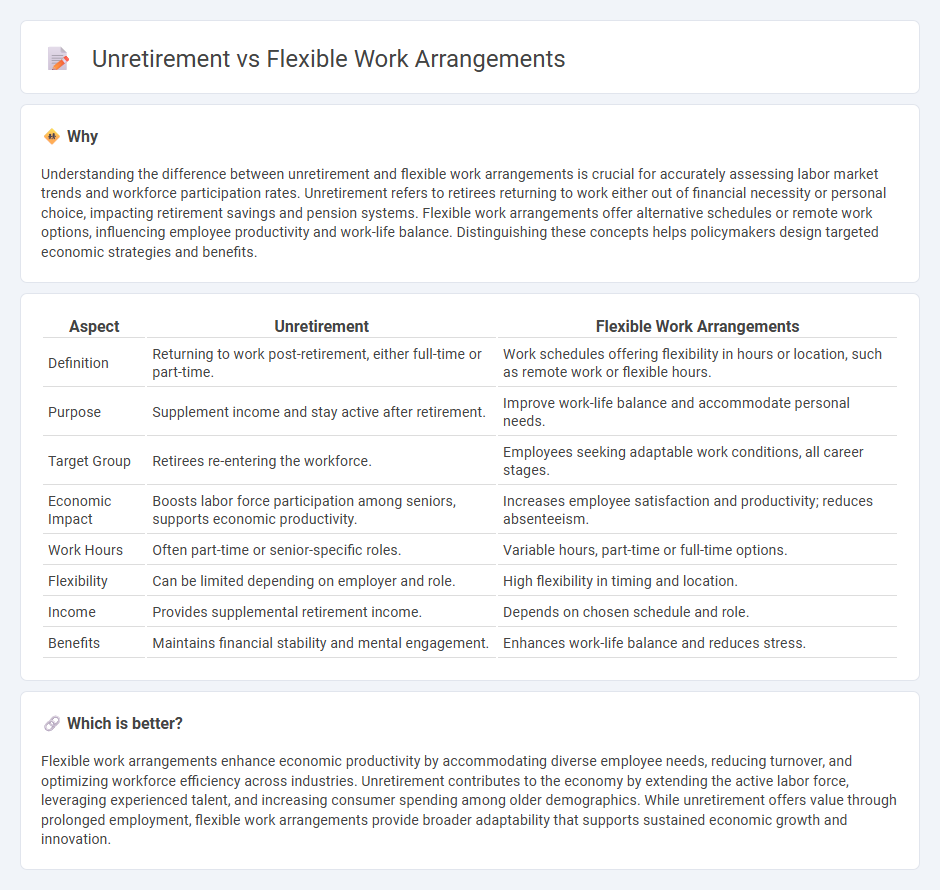
Understanding the difference between unretirement and flexible work arrangements is crucial for accurately assessing labor market trends and workforce participation rates. Unretirement refers to retirees returning to work either out of financial necessity or personal choice, impacting retirement savings and pension systems. Flexible work arrangements offer alternative schedules or remote work options, influencing employee productivity and work-life balance. Distinguishing these concepts helps policymakers design targeted economic strategies and benefits.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Unretirement | Flexible Work Arrangements |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Returning to work post-retirement, either full-time or part-time. | Work schedules offering flexibility in hours or location, such as remote work or flexible hours. |
| Purpose | Supplement income and stay active after retirement. | Improve work-life balance and accommodate personal needs. |
| Target Group | Retirees re-entering the workforce. | Employees seeking adaptable work conditions, all career stages. |
| Economic Impact | Boosts labor force participation among seniors, supports economic productivity. | Increases employee satisfaction and productivity; reduces absenteeism. |
| Work Hours | Often part-time or senior-specific roles. | Variable hours, part-time or full-time options. |
| Flexibility | Can be limited depending on employer and role. | High flexibility in timing and location. |
| Income | Provides supplemental retirement income. | Depends on chosen schedule and role. |
| Benefits | Maintains financial stability and mental engagement. | Enhances work-life balance and reduces stress. |
Which is better?
Flexible work arrangements enhance economic productivity by accommodating diverse employee needs, reducing turnover, and optimizing workforce efficiency across industries. Unretirement contributes to the economy by extending the active labor force, leveraging experienced talent, and increasing consumer spending among older demographics. While unretirement offers value through prolonged employment, flexible work arrangements provide broader adaptability that supports sustained economic growth and innovation.
Connection
Unretirement is driven by flexible work arrangements that allow older adults to re-enter the workforce without committing to full-time roles, enhancing economic participation and income stability. Flexible schedules, remote work, and part-time options cater to retirees seeking supplemental earnings, contributing to a dynamic labor market and reducing retirement income gaps. This trend supports economic growth by leveraging experienced talent and addressing labor shortages across various industries.
Key Terms
Labor Force Participation
Flexible work arrangements significantly boost labor force participation by enabling employees to balance professional and personal commitments effectively. Unretirement, characterized by retirees re-entering the workforce, contributes to sustained economic engagement and addresses labor shortages, especially among experienced professionals. Explore how these trends reshape workforce demographics and economic productivity.
Gig Economy
Flexible work arrangements in the gig economy offer unparalleled autonomy, allowing workers to choose projects and hours that suit their lifestyles, contrasting with traditional unretirement paths where older adults return to conventional employment. Gig economy platforms like Uber, Upwork, and Fiverr cater heavily to retirees seeking supplemental income without long-term commitments, leveraging their experience while maintaining flexibility. Explore how these evolving work models empower a diverse workforce by visiting our detailed analysis.
Retirement Age
Flexible work arrangements extend career longevity by allowing retirees to adjust hours or roles beyond traditional retirement age, enhancing financial stability and personal satisfaction. Unretirement involves returning to work full-time or part-time after officially retiring, often driven by financial necessity or the desire to stay engaged. Explore the evolving trends in retirement age and how they impact workforce participation for valuable insights.
Source and External Links
6 Types of Flexible Work Arrangements with Examples - ActivTrak - Flexible work arrangements are business policies allowing employees to choose how, when, and where they work, including remote work, hybrid work, compressed workweeks, job sharing, and flextime, with examples from companies like LinkedIn, Amazon, and Salesforce.
Flexible Work Arrangements: Types and Benefits - Upwork - Flexible work arrangements give employees significant leeway in fulfilling their responsibilities, common types being flextime (choosing start and finish times), part-time roles, remote work, and others designed to improve work-life balance.
6 Flexible Work Arrangement Trends and Examples for 2025 - In 2025, hybrid work models, compressed workweeks, flextime, and part-time roles continue to grow in popularity, improving employee autonomy, reducing burnout, and boosting productivity while requiring clear policies and communication from employers.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com