Neobanks operate exclusively online without physical branches, offering streamlined digital banking services such as savings accounts, loans, and payments. Payment banks focus primarily on high-volume transactional services like remittances, deposits, and bill payments, often with restrictions on lending activities. Explore the key differences, advantages, and use cases of neobanks versus payment banks to optimize your financial strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between neobanks and payment banks is crucial for selecting the right financial service tailored to your needs. Neobanks operate entirely online, offering a range of banking services without physical branches, while payment banks focus on payments and remittances with limited deposit capabilities. Choosing correctly impacts transaction fees, interest rates, and regulatory protections. This knowledge ensures optimized financial management and security in digital banking.
Comparison Table
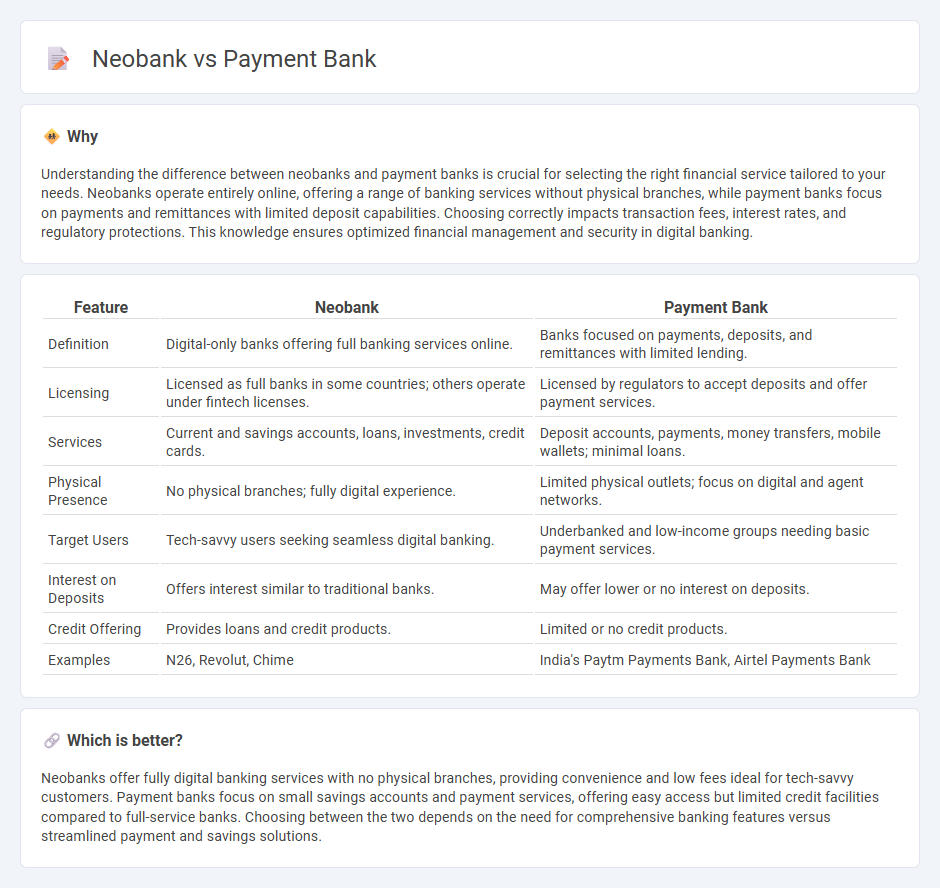
| Feature | Neobank | Payment Bank |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digital-only banks offering full banking services online. | Banks focused on payments, deposits, and remittances with limited lending. |
| Licensing | Licensed as full banks in some countries; others operate under fintech licenses. | Licensed by regulators to accept deposits and offer payment services. |
| Services | Current and savings accounts, loans, investments, credit cards. | Deposit accounts, payments, money transfers, mobile wallets; minimal loans. |
| Physical Presence | No physical branches; fully digital experience. | Limited physical outlets; focus on digital and agent networks. |
| Target Users | Tech-savvy users seeking seamless digital banking. | Underbanked and low-income groups needing basic payment services. |
| Interest on Deposits | Offers interest similar to traditional banks. | May offer lower or no interest on deposits. |
| Credit Offering | Provides loans and credit products. | Limited or no credit products. |
| Examples | N26, Revolut, Chime | India's Paytm Payments Bank, Airtel Payments Bank |
Which is better?
Neobanks offer fully digital banking services with no physical branches, providing convenience and low fees ideal for tech-savvy customers. Payment banks focus on small savings accounts and payment services, offering easy access but limited credit facilities compared to full-service banks. Choosing between the two depends on the need for comprehensive banking features versus streamlined payment and savings solutions.
Connection
Neobanks and payment banks both operate primarily in the digital financial services domain, leveraging technology to provide seamless banking experiences without traditional brick-and-mortar branches. Neobanks focus on offering comprehensive banking services through mobile applications, while payment banks specialize in digital payments, remittances, and deposit acceptance with limited lending capabilities. Their connection lies in complementing each other's services to enhance financial inclusion and streamline digital transactions for consumers and businesses.
Key Terms
Digital-Only Operations
Payment banks offer limited banking services such as deposits and remittances, primarily targeting unbanked populations through digital platforms but often require physical branches for full functionality. Neobanks operate entirely online without physical branches, providing a comprehensive suite of banking services including savings, payments, and credit products designed for tech-savvy customers seeking seamless digital experiences. Explore key differences and benefits to determine which digital-only banking solution best fits your financial needs.
Regulatory License
Payment banks in India operate under licensing from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), which mandates stringent regulatory compliance, including restrictions on lending activities and deposit limits capped at Rs2 lakh per customer. Neobanks, while offering digital banking services, typically do not hold a banking license themselves and instead partner with traditional banks to provide regulated financial products. Explore more about how regulatory frameworks shape the operational scope of payment banks and neobanks.
Financial Services Scope
Payment banks primarily offer limited financial services such as deposits, withdrawals, and remittances without loan or credit facilities, focusing on basic banking accessibility. Neobanks provide a broader range of financial products including digital payments, savings accounts, personal loans, and investment options through a fully digital interface. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which model best fits evolving consumer financial needs.
Source and External Links
Payments bank - Wikipedia - Payments banks in India are a new model conceptualized by the Reserve Bank of India that can accept deposits but cannot issue credit, with key players like Airtel Payments Bank, India Post Payments Bank, and Jio Payments Bank operating under this model.
Pay by bank - bank payment API solution - Plaid - Plaid offers a pay by bank solution enabling faster, more reliable payments directly from bank accounts with lower transaction fees, real-time risk tools, and a seamless checkout experience without relying on cards.
Paymentbanc: Home - PaymentBanc provides payment management tools for the patient financial lifecycle, including risk assessment and point-of-care payment acceptance, focusing on ethical service and patient support.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com