Alternative credit data includes non-traditional financial information such as rental payments, utility bills, and telecom history, which can enhance credit scoring for underbanked individuals. Open banking data provides real-time access to consumer transaction records and account balances through secure APIs authorized by customers, enabling more precise credit risk analysis. Discover how integrating alternative credit data with open banking can revolutionize lending decisions and financial inclusion.
Why it is important
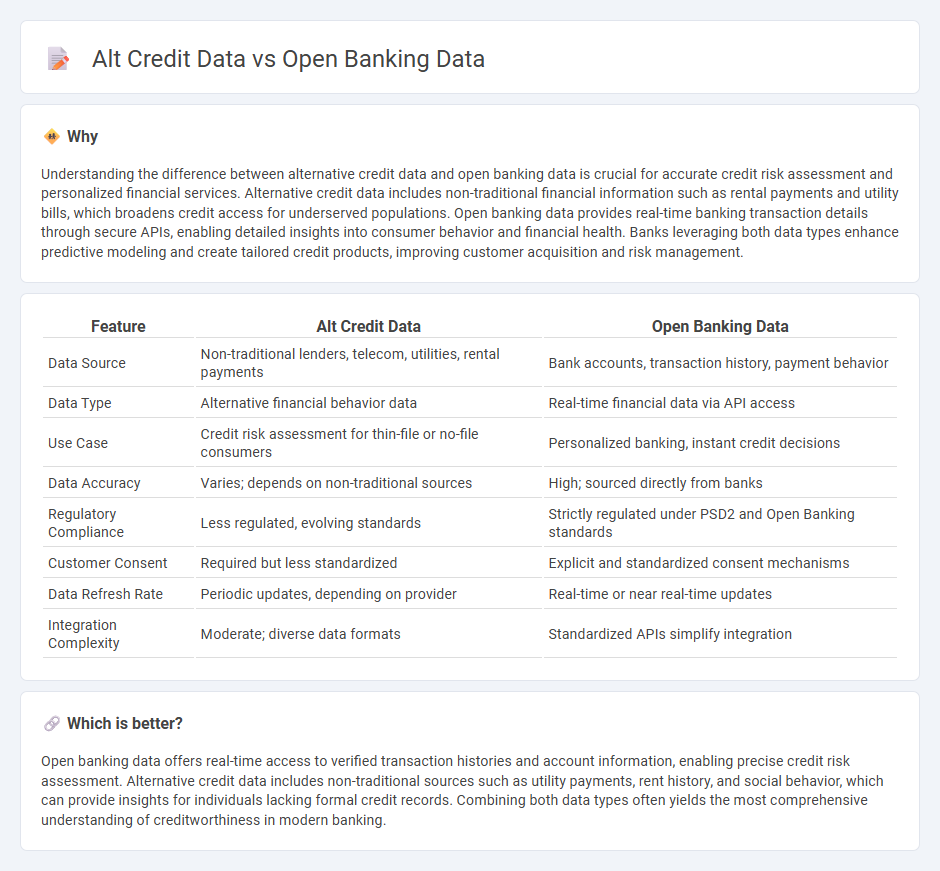
Understanding the difference between alternative credit data and open banking data is crucial for accurate credit risk assessment and personalized financial services. Alternative credit data includes non-traditional financial information such as rental payments and utility bills, which broadens credit access for underserved populations. Open banking data provides real-time banking transaction details through secure APIs, enabling detailed insights into consumer behavior and financial health. Banks leveraging both data types enhance predictive modeling and create tailored credit products, improving customer acquisition and risk management.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Alt Credit Data | Open Banking Data |
|---|---|---|
| Data Source | Non-traditional lenders, telecom, utilities, rental payments | Bank accounts, transaction history, payment behavior |
| Data Type | Alternative financial behavior data | Real-time financial data via API access |
| Use Case | Credit risk assessment for thin-file or no-file consumers | Personalized banking, instant credit decisions |
| Data Accuracy | Varies; depends on non-traditional sources | High; sourced directly from banks |
| Regulatory Compliance | Less regulated, evolving standards | Strictly regulated under PSD2 and Open Banking standards |
| Customer Consent | Required but less standardized | Explicit and standardized consent mechanisms |
| Data Refresh Rate | Periodic updates, depending on provider | Real-time or near real-time updates |
| Integration Complexity | Moderate; diverse data formats | Standardized APIs simplify integration |
Which is better?
Open banking data offers real-time access to verified transaction histories and account information, enabling precise credit risk assessment. Alternative credit data includes non-traditional sources such as utility payments, rent history, and social behavior, which can provide insights for individuals lacking formal credit records. Combining both data types often yields the most comprehensive understanding of creditworthiness in modern banking.
Connection
Alt credit data and Open banking data are interconnected through their shared ability to enhance credit risk assessment using alternative financial information. Open banking data provides real-time access to transactional and account information, while alt credit data aggregates non-traditional financial behaviors such as utility payments or rental history, expanding the credit profile beyond conventional reports. Leveraging both datasets improves lending decisions, promotes financial inclusion, and reduces default risks by delivering a more comprehensive view of a borrower's creditworthiness.
Key Terms
API Integration
Open banking data leverages API integration to securely access real-time financial information from multiple banks, enhancing credit decision accuracy by providing a comprehensive view of customers' financial behavior. Alternative credit data, sourced from non-traditional entities via APIs, captures payment histories and utility bills, expanding credit access for underbanked populations. Explore how API integration bridges open banking and alternative credit data to revolutionize lending strategies and risk assessment.
Consent Management
Open banking data leverages real-time financial information obtained with explicit user consent, enabling secure access to transaction histories and account details through APIs, while alternative credit data encompasses non-traditional financial behaviors such as rental payments, utility bills, and social media activity. Consent management is critical in both frameworks to ensure data privacy, regulatory compliance with GDPR or PSD2, and user control over data sharing preferences. Explore more about the evolving landscape of consent management in open banking and alternative credit data usage.
Alternative Data Sources
Open banking data leverages real-time financial transaction information directly from bank accounts, providing granular insights into cash flow and spending behaviors, while alternative credit data incorporates broader, non-traditional sources such as utility payments, rental history, and social media activity to assess creditworthiness. These alternative data sources enhance credit scoring models by capturing financial behaviors outside conventional credit reports, enabling lenders to better evaluate thin-file or underbanked consumers. Explore more about how integrating open banking and alternative credit data is transforming credit risk assessment and financial inclusion.
Source and External Links
Open banking data: what is it and what is it good for? - GoCardless - Open banking data enables consumers to securely share their financial data with accredited third-party providers via APIs, under strict government regulations to ensure transparency and data security.
Open banking - Wikipedia - Open banking allows customers to electronically share their financial information securely with authorized entities, with the UK having mandated its biggest banks to provide such data access to licensed startups starting in 2018.
What is open banking? A guide to the future of finance - Plaid - Open banking is a system where consumers permit third-party providers to access their banking and transaction data via standardized APIs, enabling real-time data sharing that improves transparency, innovation, and financial service personalization.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com