Pay by bank enables customers to make real-time, secure payments directly from their bank accounts, leveraging open banking APIs for instant fund transfers without intermediaries. Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT) processes payments through batch clearing systems such as ACH, which may involve delays of one to three business days depending on the financial institution. Discover the distinct advantages of pay by bank and EFT to optimize your payment strategy.
Why it is important
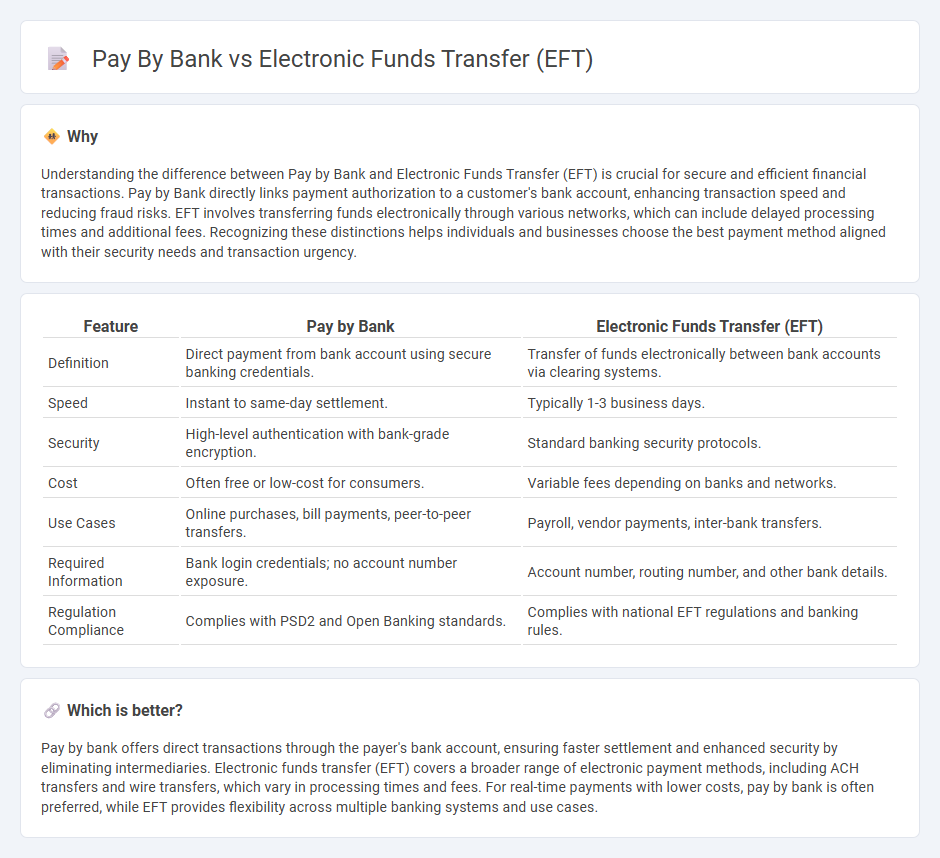
Understanding the difference between Pay by Bank and Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT) is crucial for secure and efficient financial transactions. Pay by Bank directly links payment authorization to a customer's bank account, enhancing transaction speed and reducing fraud risks. EFT involves transferring funds electronically through various networks, which can include delayed processing times and additional fees. Recognizing these distinctions helps individuals and businesses choose the best payment method aligned with their security needs and transaction urgency.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Pay by Bank | Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Direct payment from bank account using secure banking credentials. | Transfer of funds electronically between bank accounts via clearing systems. |
| Speed | Instant to same-day settlement. | Typically 1-3 business days. |
| Security | High-level authentication with bank-grade encryption. | Standard banking security protocols. |
| Cost | Often free or low-cost for consumers. | Variable fees depending on banks and networks. |
| Use Cases | Online purchases, bill payments, peer-to-peer transfers. | Payroll, vendor payments, inter-bank transfers. |
| Required Information | Bank login credentials; no account number exposure. | Account number, routing number, and other bank details. |
| Regulation Compliance | Complies with PSD2 and Open Banking standards. | Complies with national EFT regulations and banking rules. |
Which is better?
Pay by bank offers direct transactions through the payer's bank account, ensuring faster settlement and enhanced security by eliminating intermediaries. Electronic funds transfer (EFT) covers a broader range of electronic payment methods, including ACH transfers and wire transfers, which vary in processing times and fees. For real-time payments with lower costs, pay by bank is often preferred, while EFT provides flexibility across multiple banking systems and use cases.
Connection
Pay by bank and electronic funds transfer (EFT) are interconnected as both facilitate direct, secure transactions between bank accounts without using physical cash or checks. Pay by bank leverages EFT protocols such as ACH or wire transfers to instantly move funds between accounts, enhancing transaction speed and reducing processing costs. Electronic funds transfer systems provide the infrastructure that enables seamless real-time payments, making pay by bank a reliable method for e-commerce and bill payments.
Key Terms
Payment Network
Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT) transactions typically utilize established payment networks like ACH, SWIFT, or wire transfer systems to move money securely between bank accounts. In contrast, Pay By Bank relies on direct bank-to-bank connections or emerging faster payment infrastructures, enabling real-time authorization and settlement without intermediaries. Explore more to understand how each network impacts transaction speed, cost, and security.
Authentication
Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT) typically relies on Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) methods such as OTPs, PINs, or biometric verification to secure transactions, ensuring compliance with financial regulations like PSD2. Pay by Bank leverages direct bank authentication protocols, often using Open Banking APIs to connect users' bank accounts securely without exposing sensitive data, enhancing transaction transparency and reducing fraud risk. Explore the nuances of authentication in these payment methods to optimize your financial security practices.
Settlement Speed
Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT) typically processes transactions within one to three business days, depending on the banks involved and operational hours. Pay by bank solutions offer near-instant settlement speed by directly debiting funds from the payer's bank account and crediting the payee in real-time or within minutes. Explore more to understand the comparative benefits and implications of settlement speed in EFT versus pay by bank systems.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com