Blockchain bookkeeping offers a decentralized, tamper-proof ledger that ensures enhanced transparency and real-time data verification compared to traditional ledger accounting, which relies on centralized, manual record-keeping prone to errors and fraud. Blockchain technology reduces reconciliation time and supports automated smart contracts, streamlining auditing processes and improving financial accuracy. Explore the benefits and challenges of integrating blockchain into accounting systems for a deeper understanding of this transformative innovation.
Why it is important
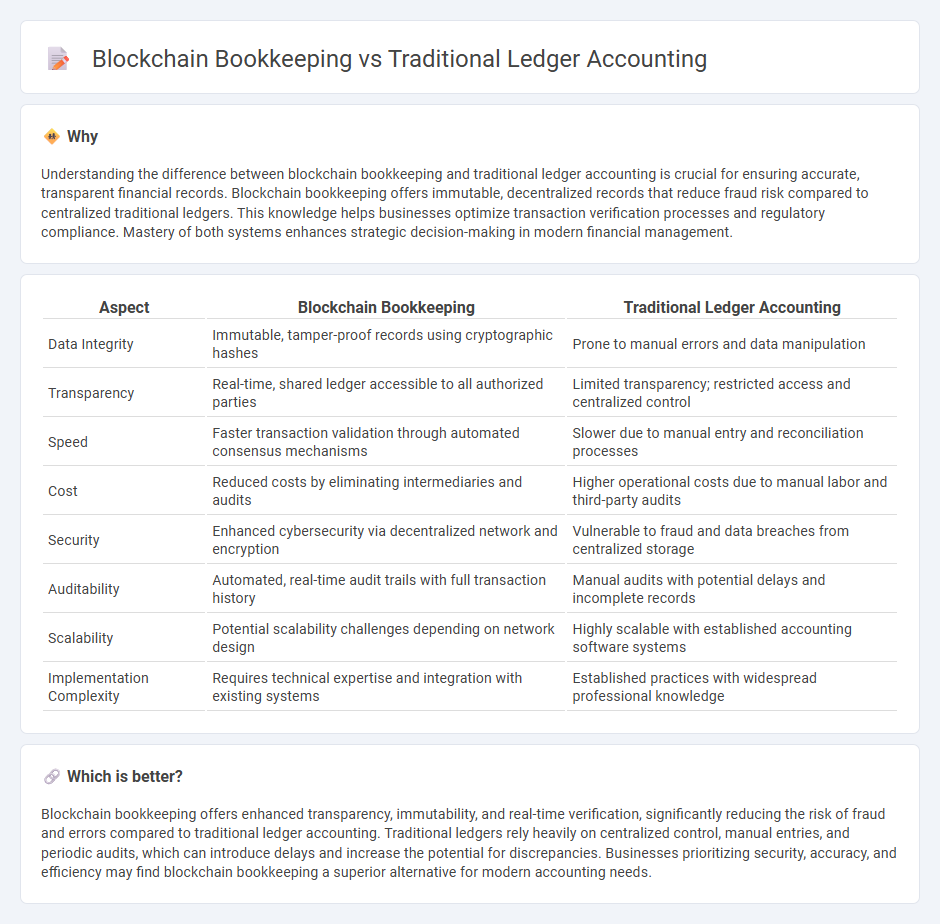
Understanding the difference between blockchain bookkeeping and traditional ledger accounting is crucial for ensuring accurate, transparent financial records. Blockchain bookkeeping offers immutable, decentralized records that reduce fraud risk compared to centralized traditional ledgers. This knowledge helps businesses optimize transaction verification processes and regulatory compliance. Mastery of both systems enhances strategic decision-making in modern financial management.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Blockchain Bookkeeping | Traditional Ledger Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Data Integrity | Immutable, tamper-proof records using cryptographic hashes | Prone to manual errors and data manipulation |
| Transparency | Real-time, shared ledger accessible to all authorized parties | Limited transparency; restricted access and centralized control |
| Speed | Faster transaction validation through automated consensus mechanisms | Slower due to manual entry and reconciliation processes |
| Cost | Reduced costs by eliminating intermediaries and audits | Higher operational costs due to manual labor and third-party audits |
| Security | Enhanced cybersecurity via decentralized network and encryption | Vulnerable to fraud and data breaches from centralized storage |
| Auditability | Automated, real-time audit trails with full transaction history | Manual audits with potential delays and incomplete records |
| Scalability | Potential scalability challenges depending on network design | Highly scalable with established accounting software systems |
| Implementation Complexity | Requires technical expertise and integration with existing systems | Established practices with widespread professional knowledge |
Which is better?
Blockchain bookkeeping offers enhanced transparency, immutability, and real-time verification, significantly reducing the risk of fraud and errors compared to traditional ledger accounting. Traditional ledgers rely heavily on centralized control, manual entries, and periodic audits, which can introduce delays and increase the potential for discrepancies. Businesses prioritizing security, accuracy, and efficiency may find blockchain bookkeeping a superior alternative for modern accounting needs.
Connection
Blockchain bookkeeping and traditional ledger accounting are connected through their core function of recording financial transactions to maintain accurate and transparent records. While traditional ledger accounting relies on centralized databases managed by trusted institutions, blockchain bookkeeping employs decentralized, immutable digital ledgers to enhance security and reduce fraud risks. Both systems aim to ensure data integrity, but blockchain's cryptographic validation provides an innovative layer of trust and verification beyond conventional methods.
Key Terms
Double-entry system
The traditional ledger accounting relies on a centralized double-entry bookkeeping system, ensuring accuracy through debit and credit entries managed by accountants. Blockchain bookkeeping innovates this by employing a decentralized ledger that records double-entry transactions across multiple nodes for enhanced transparency and fraud resistance. Explore the comparative advantages of these systems and how blockchain technology is reshaping financial record-keeping.
Decentralization
Traditional ledger accounting relies on centralized databases controlled by a single authority, which can lead to vulnerabilities in data integrity and limited transparency. Blockchain bookkeeping utilizes decentralized networks where multiple nodes validate transactions, enhancing security and ensuring a tamper-proof record accessible to all participants. Explore the advantages of decentralization in financial record-keeping to understand its impact on trust and efficiency.
Immutability
Traditional ledger accounting relies on centralized databases that can be altered or manipulated, posing risks to data integrity. Blockchain bookkeeping ensures immutability through cryptographic hashes and decentralized consensus mechanisms, making it nearly impossible to alter recorded transactions retroactively. Explore how blockchain technology enhances transparency and security in financial record-keeping.
Source and External Links
What does Ledger mean? - Describes traditional ledger books where debit transactions are entered into the left-hand column and credit transactions into the right-hand column.
Ledgers - Financial Accounting - Explains how a general ledger is the complete collection of all accounts and transactions of a company, often organized by account.
A Beginners Guide to Accounting Ledgers - Provides an introduction to accounting ledgers as the primary repository for a business's financial position, including debits, credits, and balances.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com