Continuous auditing employs automated tools and real-time data analysis to provide ongoing assurance and immediate detection of anomalies, enhancing risk management and operational efficiency. Internal auditing, conducted periodically, evaluates organizational processes, internal controls, and compliance to ensure financial accuracy and regulatory adherence. Explore the key differences and benefits of continuous versus internal auditing to optimize your financial oversight strategies.
Why it is important
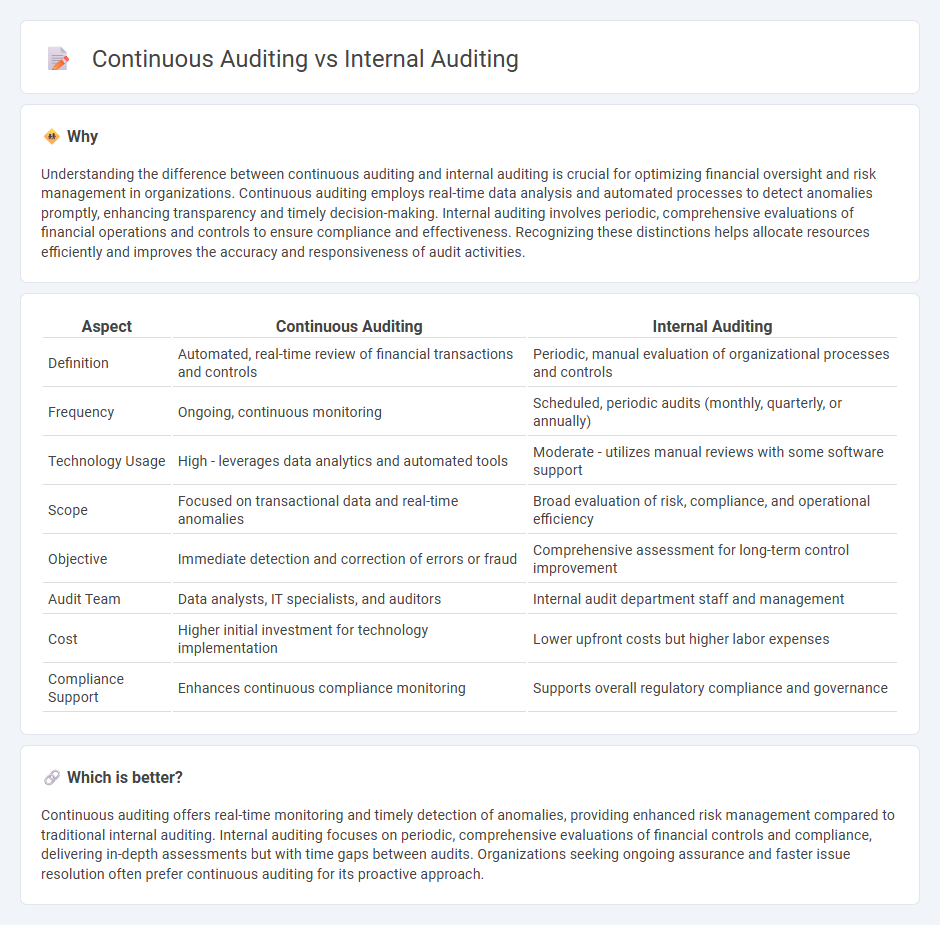
Understanding the difference between continuous auditing and internal auditing is crucial for optimizing financial oversight and risk management in organizations. Continuous auditing employs real-time data analysis and automated processes to detect anomalies promptly, enhancing transparency and timely decision-making. Internal auditing involves periodic, comprehensive evaluations of financial operations and controls to ensure compliance and effectiveness. Recognizing these distinctions helps allocate resources efficiently and improves the accuracy and responsiveness of audit activities.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Continuous Auditing | Internal Auditing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated, real-time review of financial transactions and controls | Periodic, manual evaluation of organizational processes and controls |
| Frequency | Ongoing, continuous monitoring | Scheduled, periodic audits (monthly, quarterly, or annually) |
| Technology Usage | High - leverages data analytics and automated tools | Moderate - utilizes manual reviews with some software support |
| Scope | Focused on transactional data and real-time anomalies | Broad evaluation of risk, compliance, and operational efficiency |
| Objective | Immediate detection and correction of errors or fraud | Comprehensive assessment for long-term control improvement |
| Audit Team | Data analysts, IT specialists, and auditors | Internal audit department staff and management |
| Cost | Higher initial investment for technology implementation | Lower upfront costs but higher labor expenses |
| Compliance Support | Enhances continuous compliance monitoring | Supports overall regulatory compliance and governance |
Which is better?
Continuous auditing offers real-time monitoring and timely detection of anomalies, providing enhanced risk management compared to traditional internal auditing. Internal auditing focuses on periodic, comprehensive evaluations of financial controls and compliance, delivering in-depth assessments but with time gaps between audits. Organizations seeking ongoing assurance and faster issue resolution often prefer continuous auditing for its proactive approach.
Connection
Continuous auditing enhances internal auditing by providing real-time data analysis and ongoing risk assessment, enabling auditors to identify discrepancies promptly. Internal auditing relies on continuous auditing techniques to improve the accuracy and efficiency of control evaluations, ensuring regulatory compliance. Integration of both practices leads to a more proactive and dynamic audit environment, supporting better governance and financial transparency.
Key Terms
Internal Auditing:
Internal auditing systematically evaluates an organization's internal controls, risk management, and governance processes to ensure compliance and operational efficiency. It is typically periodic, offering a comprehensive overview of financial and operational activities at scheduled intervals. Explore more to understand how internal auditing strengthens organizational accountability and decision-making.
Risk Assessment
Internal auditing traditionally involves periodic risk assessments to evaluate an organization's control environment, ensuring compliance and identifying potential vulnerabilities. Continuous auditing integrates real-time data analysis and automated monitoring tools, enabling ongoing risk assessment and quicker detection of anomalies. Explore more to understand how continuous auditing transforms risk management strategies.
Compliance
Internal auditing focuses on periodic reviews to ensure organizational compliance with regulations, policies, and standards through comprehensive assessments and documentation. Continuous auditing employs real-time data analysis and automated monitoring systems to detect compliance deviations promptly, enhancing risk management and operational efficiency. Explore how integrating both approaches can strengthen your regulatory adherence and control processes.
Source and External Links
Internal Audit 101: Everything You Need to Know - Internal auditing is an independent, objective review of a company's internal systems and processes designed to provide assurance on risk management, controls, and compliance to improve operations and achieve company goals.
What is Internal Auditing? - Internal auditing is an independent assurance and consulting activity aimed at adding value by assessing and improving the effectiveness of risk management, control, and governance within an organization.
What is Internal Audit? Types, Value, Process & Standards - Internal audits include various types such as compliance, environmental, financial, IT, operational, and performance audits, all focused on evaluating and improving different aspects of an organization's controls and efficiency.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com