Deferred revenue recognition occurs when a company receives payment before delivering goods or services, creating a liability on the balance sheet. Earned revenue reflects the fulfillment of performance obligations, allowing the company to recognize income according to revenue recognition principles under GAAP or IFRS. Discover how proper revenue recognition impacts financial reporting and business valuation.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between deferred revenue recognition and earned revenue is crucial for accurate financial reporting and compliance with accounting standards such as GAAP and IFRS. Deferred revenue represents cash received before delivering goods or services, while earned revenue reflects completed obligations, ensuring correct matching of revenue and expenses. Accurate distinction prevents misleading financial statements and supports effective business decision-making and cash flow management. Proper revenue recognition impacts tax liabilities and investor confidence by presenting a true financial position.
Comparison Table
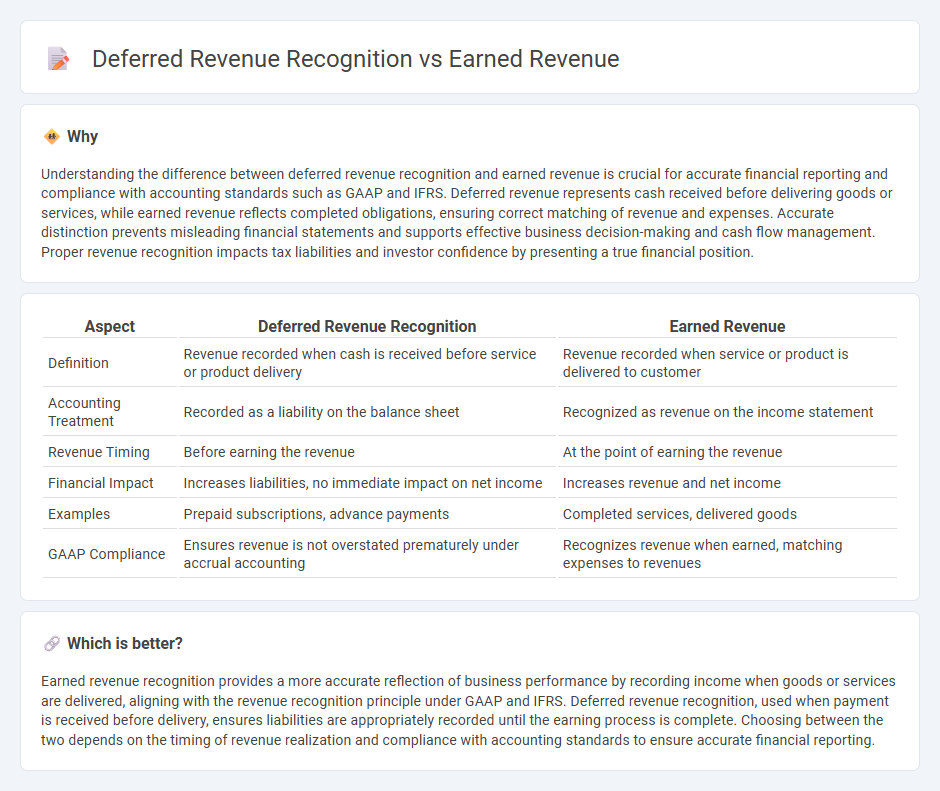
| Aspect | Deferred Revenue Recognition | Earned Revenue |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Revenue recorded when cash is received before service or product delivery | Revenue recorded when service or product is delivered to customer |
| Accounting Treatment | Recorded as a liability on the balance sheet | Recognized as revenue on the income statement |
| Revenue Timing | Before earning the revenue | At the point of earning the revenue |
| Financial Impact | Increases liabilities, no immediate impact on net income | Increases revenue and net income |
| Examples | Prepaid subscriptions, advance payments | Completed services, delivered goods |
| GAAP Compliance | Ensures revenue is not overstated prematurely under accrual accounting | Recognizes revenue when earned, matching expenses to revenues |
Which is better?
Earned revenue recognition provides a more accurate reflection of business performance by recording income when goods or services are delivered, aligning with the revenue recognition principle under GAAP and IFRS. Deferred revenue recognition, used when payment is received before delivery, ensures liabilities are appropriately recorded until the earning process is complete. Choosing between the two depends on the timing of revenue realization and compliance with accounting standards to ensure accurate financial reporting.
Connection
Deferred revenue recognition and earned revenue are linked through the matching principle in accounting, where deferred revenue represents cash received for goods or services not yet delivered. As the company fulfills its performance obligations, deferred revenue gradually converts to earned revenue in the income statement. This process ensures accurate revenue reporting aligned with the timing of service delivery or product transfer.
Key Terms
Accrual Basis
Earned revenue refers to income that a company has realized by delivering goods or services, while deferred revenue represents payments received before the performance obligations are fulfilled, recorded as a liability under the accrual basis of accounting. Recognizing earned revenue aligns with matching income to the period in which related expenses are incurred, ensuring accurate financial reporting and compliance with GAAP or IFRS standards. Explore detailed guidelines and examples to understand revenue recognition principles on an accrual basis fully.
Unearned Revenue
Unearned revenue, also known as deferred revenue, represents payments received by a company before delivering goods or services, and it is recorded as a liability on the balance sheet until earned. Earned revenue recognition occurs when the company fulfills its obligation, transferring the amount from unearned revenue to recognized income in accordance with revenue recognition principles like ASC 606 or IFRS 15. Explore detailed guidelines on managing unearned revenue timing and compliance for accurate financial reporting.
Performance Obligation
Earned revenue is recognized when a company's performance obligation is fully satisfied by transferring goods or services to the customer, reflecting that the earnings process is complete. Deferred revenue, also known as unearned revenue, represents cash received before the performance obligation is met and is recorded as a liability until the service or product is delivered. Explore more about how performance obligations impact revenue recognition in different industries and accounting standards.
Source and External Links
Earned revenue - (Financial Accounting II) - Fiveable - Earned revenue is income a company recognizes when it has provided goods or services to customers, indicating the earning process is complete.
At what point are revenues considered to be earned? - Revenues are considered earned when the earning process has been substantially completed, such as when goods have been delivered or services performed, regardless of whether payment has been received.
Earned vs. Contributed Revenue - Fractured Atlas - Earned revenue refers to funds received in exchange for goods or services, such as ticket sales, payment for services, or merchandise fees, where the payer receives something of value in return.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com