Greenwashing detection focuses on identifying deceptive claims by companies that exaggerate environmental responsibility, contrasting with creative accounting, which manipulates financial statements to present a misleading economic reality. Both practices undermine transparency and trust, yet each targets different aspects of corporate reporting--environmental impact versus financial performance. Discover more about distinguishing these tactics to ensure accurate and ethical corporate disclosures.
Why it is important
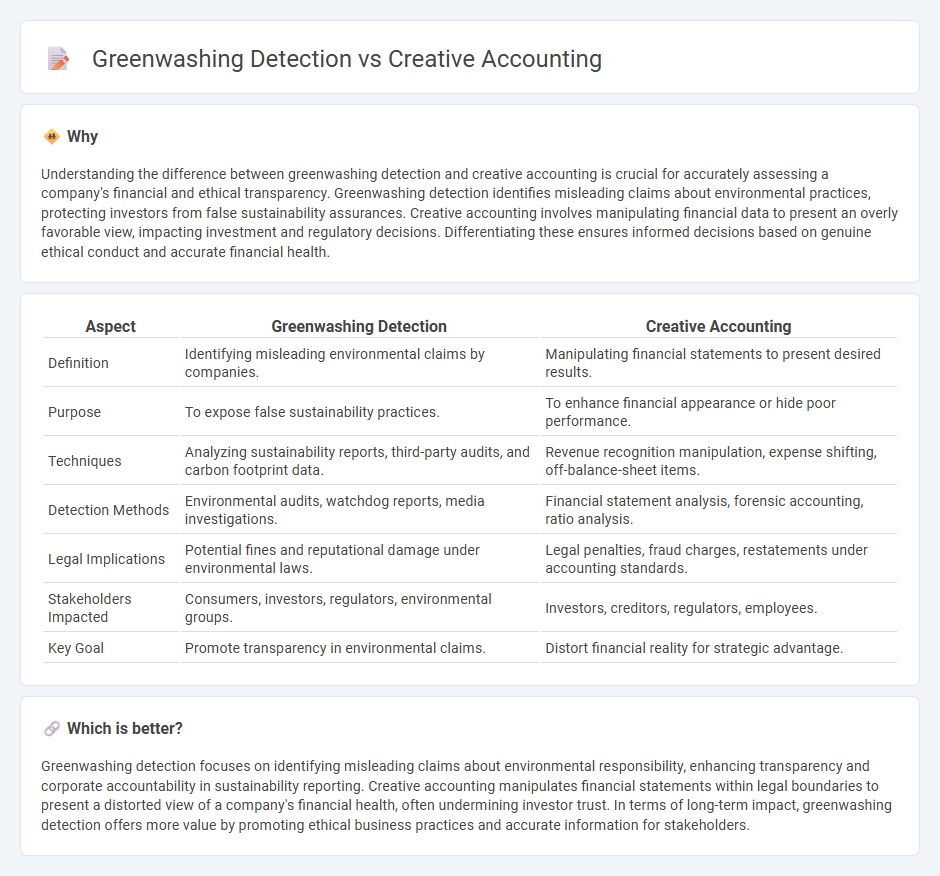
Understanding the difference between greenwashing detection and creative accounting is crucial for accurately assessing a company's financial and ethical transparency. Greenwashing detection identifies misleading claims about environmental practices, protecting investors from false sustainability assurances. Creative accounting involves manipulating financial data to present an overly favorable view, impacting investment and regulatory decisions. Differentiating these ensures informed decisions based on genuine ethical conduct and accurate financial health.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Greenwashing Detection | Creative Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Identifying misleading environmental claims by companies. | Manipulating financial statements to present desired results. |
| Purpose | To expose false sustainability practices. | To enhance financial appearance or hide poor performance. |
| Techniques | Analyzing sustainability reports, third-party audits, and carbon footprint data. | Revenue recognition manipulation, expense shifting, off-balance-sheet items. |
| Detection Methods | Environmental audits, watchdog reports, media investigations. | Financial statement analysis, forensic accounting, ratio analysis. |
| Legal Implications | Potential fines and reputational damage under environmental laws. | Legal penalties, fraud charges, restatements under accounting standards. |
| Stakeholders Impacted | Consumers, investors, regulators, environmental groups. | Investors, creditors, regulators, employees. |
| Key Goal | Promote transparency in environmental claims. | Distort financial reality for strategic advantage. |
Which is better?
Greenwashing detection focuses on identifying misleading claims about environmental responsibility, enhancing transparency and corporate accountability in sustainability reporting. Creative accounting manipulates financial statements within legal boundaries to present a distorted view of a company's financial health, often undermining investor trust. In terms of long-term impact, greenwashing detection offers more value by promoting ethical business practices and accurate information for stakeholders.
Connection
Greenwashing detection and creative accounting intersect in their focus on uncovering deceptive financial practices used to manipulate perceptions of corporate responsibility and performance. Creative accounting techniques often involve misrepresenting financial data, which can mask unethical environmental practices, making greenwashing detection crucial for ensuring transparency and accurate sustainability reporting. Regulatory frameworks and forensic accounting tools play a vital role in identifying these manipulative strategies to protect investors and stakeholders from false claims.
Key Terms
Financial Statement Analysis
Financial statement analysis plays a crucial role in detecting both creative accounting and greenwashing by scrutinizing discrepancies in reported numbers and sustainability claims. Techniques such as ratio analysis, cash flow examination, and comparison of disclosed information with industry benchmarks reveal manipulative financial practices and misleading environmental assertions. Explore further to understand the tools and frameworks that enhance transparency and accountability in corporate reporting.
ESG Reporting
Creative accounting techniques often manipulate financial statements to mask true company performance, complicating the assessment of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) metrics. Greenwashing detection centers on identifying misleading claims about sustainability practices, ensuring transparency and integrity in ESG reporting. Explore advanced methodologies and tools to enhance accuracy and trust in ESG disclosures.
Forensic Audit
Forensic audits play a crucial role in detecting creative accounting by meticulously examining financial records for manipulations aimed at misleading stakeholders. They also identify greenwashing practices by verifying the authenticity of sustainability claims against actual environmental performance data. Explore forensic audit techniques to understand how organizations ensure transparency and accountability in financial and ESG reporting.
Source and External Links
Creative Accounting: What it is, Types, and Methods - Creative accounting refers to the manipulation of financial records using accounting loopholes or grey areas, allowing companies to present a more favorable financial picture without breaking the law.
Creative Accounting: Definition, Types & Methods - FreshBooks - Creative accounting is a practice where financial statements are reported in a less-than-transparent way by exploiting ambiguities in accounting standards, often to make a company appear healthier than it truly is.
Creative accounting - Wikipedia - Creative accounting uses legal accounting practices to manage or alter financial reports, sometimes to mislead stakeholders about a company's true economic performance or influence contractual outcomes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com