Algorithmic compliance leverages automated systems to ensure adherence to regulatory standards by analyzing large datasets and detecting anomalies in financial transactions. Materiality assessment evaluates the significance of financial information to determine its impact on decision-making and reporting accuracy. Explore the differences and practical applications of these approaches to enhance accounting accuracy and regulatory compliance.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Algorithmic Compliance and Materiality Assessment is crucial in accounting to ensure accurate financial reporting and regulatory adherence. Algorithmic Compliance focuses on meeting strict rules and automated procedures to avoid errors and penalties, while Materiality Assessment evaluates the significance of financial information to stakeholders for informed decision-making. Proper knowledge of both concepts helps accountants prioritize relevant data and maintain ethical standards. This distinction enhances audit quality and supports transparency in financial statements.
Comparison Table
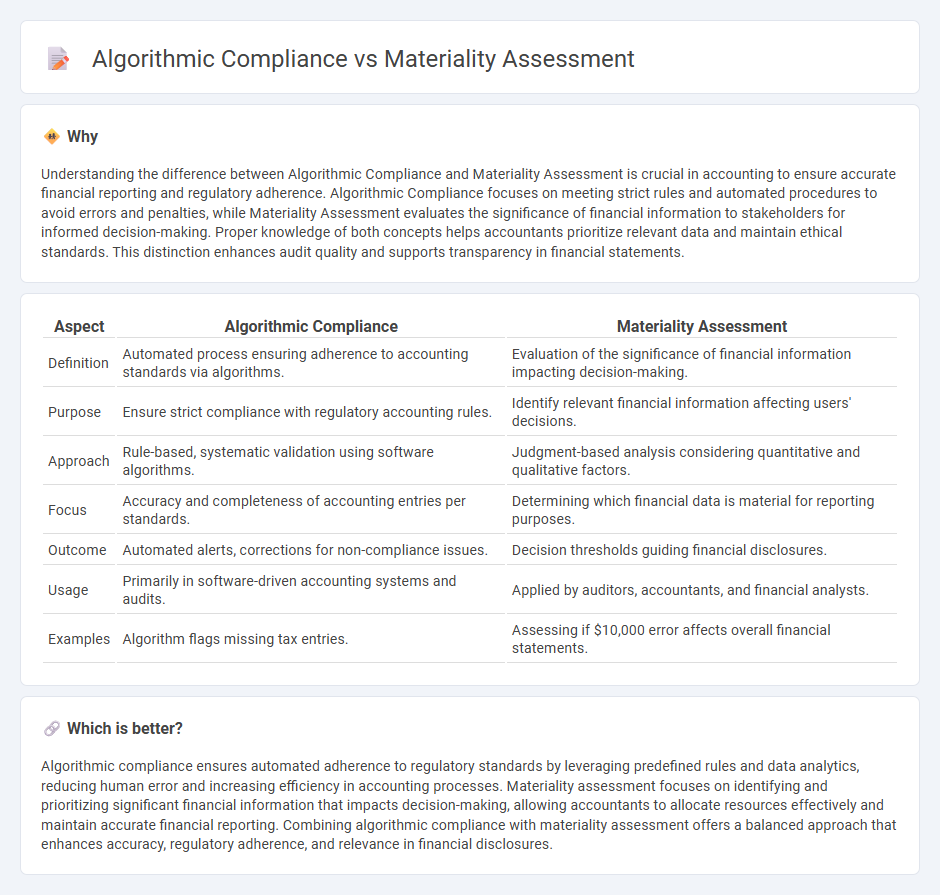
| Aspect | Algorithmic Compliance | Materiality Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated process ensuring adherence to accounting standards via algorithms. | Evaluation of the significance of financial information impacting decision-making. |
| Purpose | Ensure strict compliance with regulatory accounting rules. | Identify relevant financial information affecting users' decisions. |
| Approach | Rule-based, systematic validation using software algorithms. | Judgment-based analysis considering quantitative and qualitative factors. |
| Focus | Accuracy and completeness of accounting entries per standards. | Determining which financial data is material for reporting purposes. |
| Outcome | Automated alerts, corrections for non-compliance issues. | Decision thresholds guiding financial disclosures. |
| Usage | Primarily in software-driven accounting systems and audits. | Applied by auditors, accountants, and financial analysts. |
| Examples | Algorithm flags missing tax entries. | Assessing if $10,000 error affects overall financial statements. |
Which is better?
Algorithmic compliance ensures automated adherence to regulatory standards by leveraging predefined rules and data analytics, reducing human error and increasing efficiency in accounting processes. Materiality assessment focuses on identifying and prioritizing significant financial information that impacts decision-making, allowing accountants to allocate resources effectively and maintain accurate financial reporting. Combining algorithmic compliance with materiality assessment offers a balanced approach that enhances accuracy, regulatory adherence, and relevance in financial disclosures.
Connection
Algorithmic compliance enhances accounting accuracy by automating regulatory adherence, reducing human error in financial reporting. Materiality assessment focuses on identifying significant financial information that influences decision-making, guiding the threshold for data inclusion. Integrating algorithmic compliance with materiality assessment ensures efficient evaluation of material facts in accordance with accounting standards, improving audit quality and regulatory transparency.
Key Terms
Materiality assessment:
Materiality assessment evaluates the significance of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors to a company's performance and stakeholder impact, guiding sustainable decision-making and reporting priorities. It involves identifying and prioritizing key issues based on stakeholder expectations, regulatory requirements, and business strategy, ensuring resource allocation aligns with critical risks and opportunities. Explore how materiality assessment enhances corporate responsibility and transparency by integrating stakeholder insights with strategic frameworks.
Thresholds
Materiality assessment determines the significance of information based on quantitative and qualitative thresholds to guide reporting accuracy and stakeholder relevance. Algorithmic compliance uses predefined threshold parameters to automate decision-making processes, ensuring adherence to regulatory standards and minimizing human bias. Explore how these threshold-driven approaches optimize governance and compliance strategies.
Relevance
Materiality assessment identifies the most significant environmental, social, and governance (ESG) issues impacting a company's stakeholders and business performance, emphasizing relevance through stakeholder engagement and data analysis. Algorithmic compliance automates regulatory adherence by applying predefined rules, prioritizing relevance through accuracy and real-time monitoring of applicable laws and standards. Discover how integrating materiality assessment with algorithmic compliance enhances strategic decision-making and regulatory effectiveness.
Source and External Links
Materiality assessment: A guide to a better ESG performance - This guide explains how to conduct a materiality assessment to identify and manage key environmental, social, and governance issues important to stakeholders and business strategy.
The Essentials of Materiality Assessment - This document provides a structured approach to materiality assessments, including phases for defining purpose, identifying topics, and engaging stakeholders.
What is a Materiality Assessment? - This article explains materiality assessments as tools for prioritizing sustainability issues using methods like materiality matrices, which are supported by standards like GRI and SASB.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com