Forensic accounting involves the investigation of financial discrepancies and fraud detection through detailed examination of financial records, often used in legal contexts. Risk assessment in accounting focuses on identifying potential financial threats and vulnerabilities to prevent future losses and ensure compliance. Explore more to understand how these disciplines protect financial integrity and support strategic decision-making.
Why it is important
Knowing the difference between forensic analysis and risk assessment is crucial in accounting to accurately address financial discrepancies and prevent potential losses. Forensic analysis involves investigating past financial records to detect fraud or legal violations, providing evidence for litigation. Risk assessment evaluates current financial practices to identify vulnerabilities and implement controls that mitigate future threats. Understanding these distinct processes enhances the accuracy of audits and strengthens overall financial governance.
Comparison Table
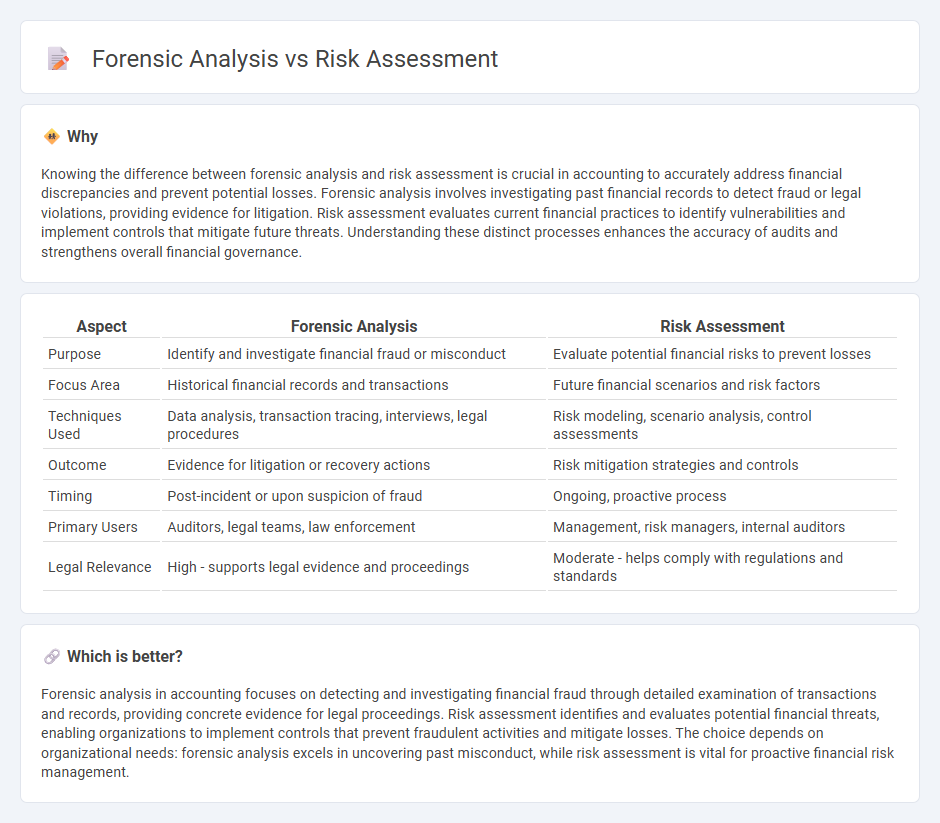
| Aspect | Forensic Analysis | Risk Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Identify and investigate financial fraud or misconduct | Evaluate potential financial risks to prevent losses |
| Focus Area | Historical financial records and transactions | Future financial scenarios and risk factors |
| Techniques Used | Data analysis, transaction tracing, interviews, legal procedures | Risk modeling, scenario analysis, control assessments |
| Outcome | Evidence for litigation or recovery actions | Risk mitigation strategies and controls |
| Timing | Post-incident or upon suspicion of fraud | Ongoing, proactive process |
| Primary Users | Auditors, legal teams, law enforcement | Management, risk managers, internal auditors |
| Legal Relevance | High - supports legal evidence and proceedings | Moderate - helps comply with regulations and standards |
Which is better?
Forensic analysis in accounting focuses on detecting and investigating financial fraud through detailed examination of transactions and records, providing concrete evidence for legal proceedings. Risk assessment identifies and evaluates potential financial threats, enabling organizations to implement controls that prevent fraudulent activities and mitigate losses. The choice depends on organizational needs: forensic analysis excels in uncovering past misconduct, while risk assessment is vital for proactive financial risk management.
Connection
Forensic analysis and risk assessment in accounting are interconnected through their focus on identifying and mitigating financial fraud and discrepancies. Forensic analysis investigates suspicious transactions and anomalies in financial records, providing detailed evidence that informs risk assessment models. Risk assessment leverages this forensic data to evaluate potential vulnerabilities, strengthening internal controls and preventing future fiscal misconduct.
Key Terms
**Risk Assessment:**
Risk assessment systematically identifies, evaluates, and prioritizes potential threats to an organization's assets, focusing on minimizing vulnerabilities and preventing security breaches. It uses quantitative and qualitative methods to analyze risk levels, often involving frameworks like ISO 31000 or NIST SP 800-30 for comprehensive risk management. Explore further to understand how risk assessment strengthens organizational resilience and drives informed decision-making.
Internal Controls
Risk assessment evaluates internal controls to identify potential vulnerabilities and prevent fraud or operational failures by analyzing control effectiveness, compliance, and risk exposure within an organization. Forensic analysis investigates suspected breaches or failures in internal controls through detailed examination of evidence, data, and transaction records to establish facts for legal or disciplinary actions. Explore how integrating risk assessment and forensic analysis enhances internal control frameworks for robust organizational security.
Inherent Risk
Inherent risk refers to the level of risk naturally present in a process or system before any controls or mitigations are applied, fundamental in risk assessment to prioritize potential vulnerabilities. Forensic analysis focuses on identifying and investigating risks after incidents have occurred, often revealing the inherent risks that were previously unrecognized or underestimated. Explore more to understand how inherent risk shapes both proactive risk management and reactive forensic investigations.
Source and External Links
Risk assessment is a structured process for identifying hazards, evaluating the likelihood and consequences of potential negative events, and determining actions to mitigate those risks.
Risk Assessment: Process, Tools, & Techniques - Risk assessment systematically identifies hazards, analyzes their potential impact, and helps decide which measures to eliminate or control risks, often required by regulations like OSHA.
Risk assessment: Steps needed to manage risk - The process involves identifying hazards, assessing their risks, controlling those risks, recording findings, and regularly reviewing controls to ensure workplace safety.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com