Integrated reporting combines financial and non-financial data to give a holistic view of an organization's performance, focusing on value creation over time. Corporate social responsibility (CSR) reporting centers on an organization's ethical impacts, social initiatives, and environmental stewardship, highlighting its commitment to sustainable development. Explore the distinctions and benefits of both reporting frameworks to enhance your understanding of modern accounting practices.
Why it is important
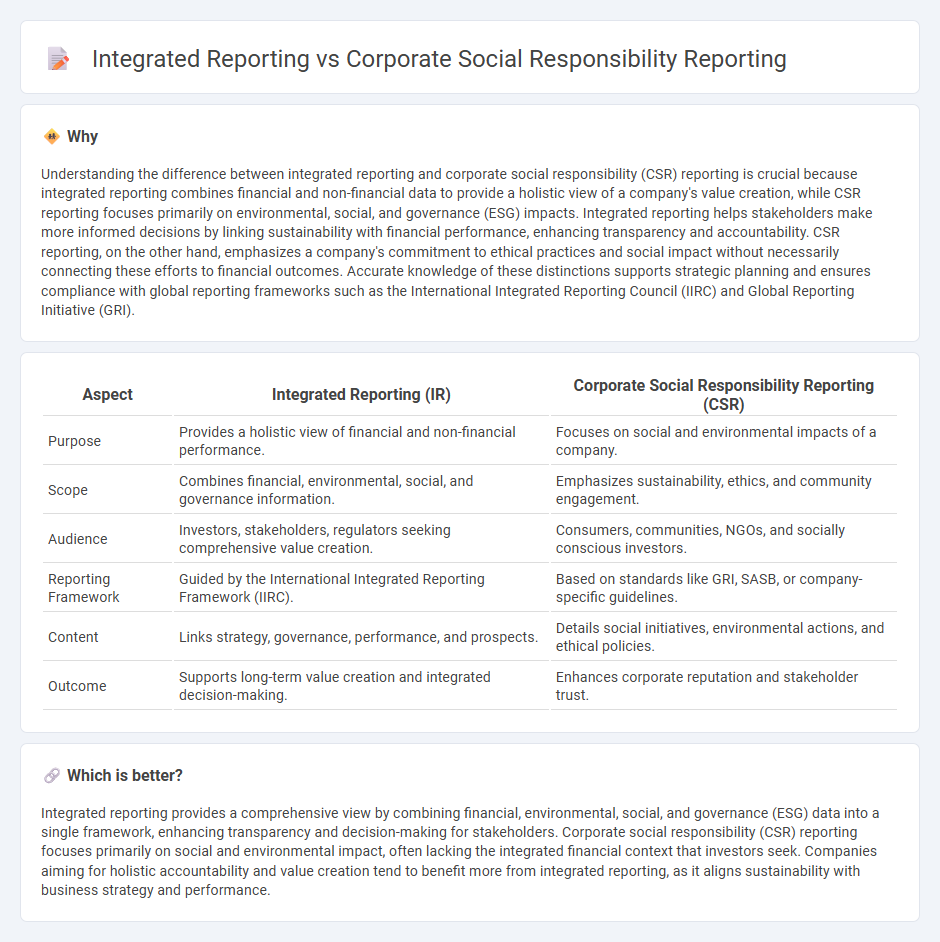
Understanding the difference between integrated reporting and corporate social responsibility (CSR) reporting is crucial because integrated reporting combines financial and non-financial data to provide a holistic view of a company's value creation, while CSR reporting focuses primarily on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) impacts. Integrated reporting helps stakeholders make more informed decisions by linking sustainability with financial performance, enhancing transparency and accountability. CSR reporting, on the other hand, emphasizes a company's commitment to ethical practices and social impact without necessarily connecting these efforts to financial outcomes. Accurate knowledge of these distinctions supports strategic planning and ensures compliance with global reporting frameworks such as the International Integrated Reporting Council (IIRC) and Global Reporting Initiative (GRI).
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Integrated Reporting (IR) | Corporate Social Responsibility Reporting (CSR) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Provides a holistic view of financial and non-financial performance. | Focuses on social and environmental impacts of a company. |
| Scope | Combines financial, environmental, social, and governance information. | Emphasizes sustainability, ethics, and community engagement. |
| Audience | Investors, stakeholders, regulators seeking comprehensive value creation. | Consumers, communities, NGOs, and socially conscious investors. |
| Reporting Framework | Guided by the International Integrated Reporting Framework (IIRC). | Based on standards like GRI, SASB, or company-specific guidelines. |
| Content | Links strategy, governance, performance, and prospects. | Details social initiatives, environmental actions, and ethical policies. |
| Outcome | Supports long-term value creation and integrated decision-making. | Enhances corporate reputation and stakeholder trust. |
Which is better?
Integrated reporting provides a comprehensive view by combining financial, environmental, social, and governance (ESG) data into a single framework, enhancing transparency and decision-making for stakeholders. Corporate social responsibility (CSR) reporting focuses primarily on social and environmental impact, often lacking the integrated financial context that investors seek. Companies aiming for holistic accountability and value creation tend to benefit more from integrated reporting, as it aligns sustainability with business strategy and performance.
Connection
Integrated reporting combines financial and non-financial data, highlighting a company's strategy, governance, and performance with emphasis on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors. Corporate social responsibility (CSR) reporting provides detailed insights into a company's social and environmental impact, feeding critical ESG information into the integrated report. This connection ensures transparency and accountability by aligning CSR metrics with business value creation for stakeholders.
Key Terms
Sustainability
Corporate social responsibility reporting primarily emphasizes a company's initiatives and impacts on social and environmental sustainability, detailing efforts in areas like community engagement and environmental stewardship. Integrated reporting combines financial, social, and environmental data into a unified framework, presenting a holistic view of how sustainability influences overall business value and long-term strategy. Explore further to understand how these reporting approaches enhance transparency and stakeholder trust in sustainable business practices.
Stakeholders
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) reporting primarily targets stakeholders by detailing a company's social, environmental, and ethical impacts, emphasizing accountability and transparency. Integrated reporting, however, combines financial and non-financial information to provide a holistic view of value creation over time, addressing the needs of diverse stakeholders including investors, employees, and communities. Explore the key differences and benefits of each reporting approach to better engage and inform your stakeholders.
Value Creation
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) reporting primarily emphasizes a company's environmental and social impact, focusing on sustainability and ethical practices, while integrated reporting combines financial and non-financial data to provide a holistic view of value creation over time. Integrated reporting aligns business strategy, governance, and performance, highlighting how organizations create value for stakeholders through multiple capitals such as financial, manufactured, intellectual, human, social, and natural. Explore comprehensive insights to understand how these reporting frameworks drive sustainable value creation in the modern corporate landscape.
Source and External Links
How do you structure a Corporate Responsibility Report? - Corporate social responsibility (CSR) reports are annual documents outlining a company's sustainability efforts including ESG goals, serving to enhance transparency, risk management, investor confidence, and regulatory compliance.
Pursuing Accountability: CSR Reporting Strategies & ... - CSR reporting provides evidence of a company's environmental, social, ethical, or economic impact, and while not currently mandatory in the U.S., it is encouraged for transparency and sustainable business practice.
What is CSR reporting? - CSR reporting is a voluntary but increasingly expected practice where organizations disclose non-financial metrics related to their social and environmental impact, often overlapping with ESG reporting.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com