Carbon accounting quantifies greenhouse gas emissions to measure an organization's carbon footprint, focusing on emissions reduction and regulatory compliance. Sustainability accounting covers a broader scope, evaluating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors to assess overall corporate impact and promote long-term sustainable growth. Discover more about how these specialized accounting practices drive responsible business strategies.
Why it is important
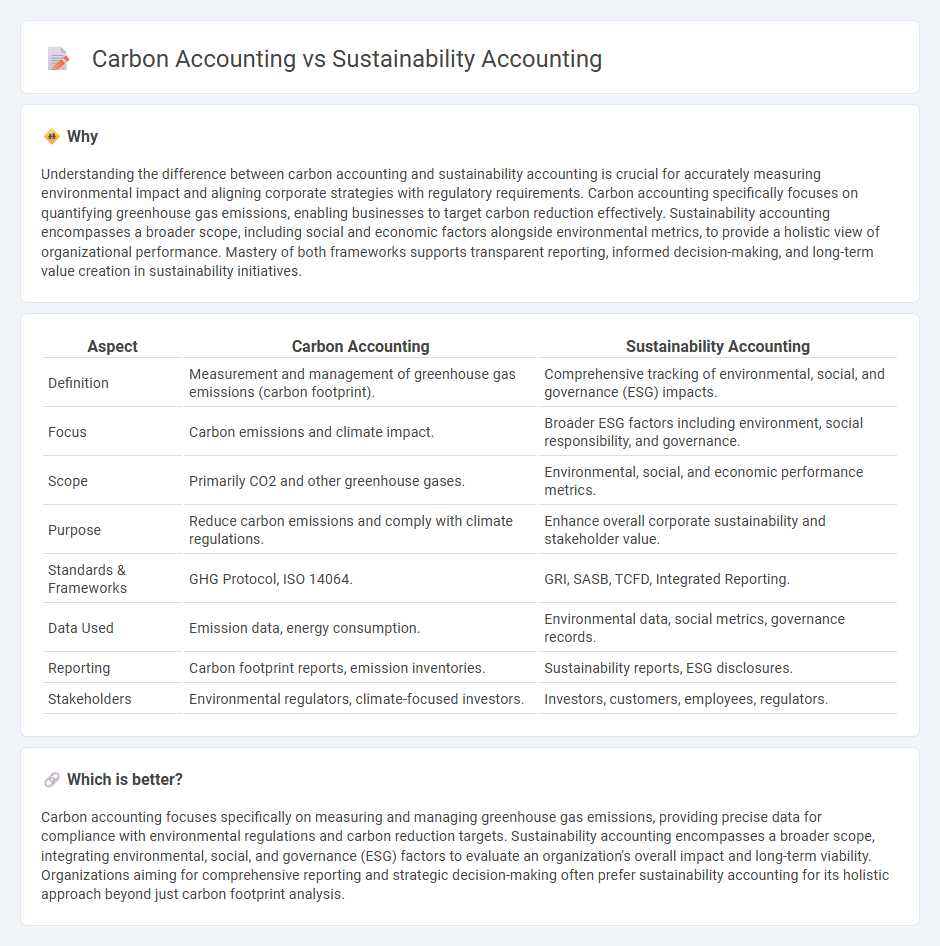
Understanding the difference between carbon accounting and sustainability accounting is crucial for accurately measuring environmental impact and aligning corporate strategies with regulatory requirements. Carbon accounting specifically focuses on quantifying greenhouse gas emissions, enabling businesses to target carbon reduction effectively. Sustainability accounting encompasses a broader scope, including social and economic factors alongside environmental metrics, to provide a holistic view of organizational performance. Mastery of both frameworks supports transparent reporting, informed decision-making, and long-term value creation in sustainability initiatives.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Carbon Accounting | Sustainability Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measurement and management of greenhouse gas emissions (carbon footprint). | Comprehensive tracking of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) impacts. |
| Focus | Carbon emissions and climate impact. | Broader ESG factors including environment, social responsibility, and governance. |
| Scope | Primarily CO2 and other greenhouse gases. | Environmental, social, and economic performance metrics. |
| Purpose | Reduce carbon emissions and comply with climate regulations. | Enhance overall corporate sustainability and stakeholder value. |
| Standards & Frameworks | GHG Protocol, ISO 14064. | GRI, SASB, TCFD, Integrated Reporting. |
| Data Used | Emission data, energy consumption. | Environmental data, social metrics, governance records. |
| Reporting | Carbon footprint reports, emission inventories. | Sustainability reports, ESG disclosures. |
| Stakeholders | Environmental regulators, climate-focused investors. | Investors, customers, employees, regulators. |
Which is better?
Carbon accounting focuses specifically on measuring and managing greenhouse gas emissions, providing precise data for compliance with environmental regulations and carbon reduction targets. Sustainability accounting encompasses a broader scope, integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors to evaluate an organization's overall impact and long-term viability. Organizations aiming for comprehensive reporting and strategic decision-making often prefer sustainability accounting for its holistic approach beyond just carbon footprint analysis.
Connection
Carbon accounting quantifies greenhouse gas emissions associated with business activities, providing critical data for sustainability reporting and environmental impact assessments. Sustainability accounting integrates carbon accounting metrics with broader environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors to evaluate a company's overall sustainable performance. This connection enables organizations to track carbon footprints, optimize resource use, and align financial goals with climate action targets.
Key Terms
Sustainability Accounting:
Sustainability accounting encompasses the measurement and reporting of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors to provide a comprehensive view of an organization's long-term impact on society and natural resources. This approach integrates financial and non-financial data, promoting transparency and informed decision-making aligned with global frameworks such as the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB). Explore more to understand how sustainability accounting drives corporate responsibility and strategic growth.
Triple Bottom Line
Sustainability accounting measures an organization's overall environmental, social, and economic impacts based on the Triple Bottom Line framework, encompassing people, planet, and profit. Carbon accounting, a subset of sustainability accounting, specifically quantifies greenhouse gas emissions to assess and manage carbon footprints. Explore further to understand how these accounting practices drive strategic sustainability initiatives.
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG)
Sustainability accounting encompasses comprehensive measurement and reporting of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors, integrating corporate responsibility and long-term impact on society and natural resources. Carbon accounting focuses specifically on quantifying greenhouse gas emissions to manage carbon footprints and comply with climate regulations. Explore how both frameworks drive sustainable business practices and ESG performance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com