Greenwashing detection identifies misleading claims about a company's environmental practices by analyzing inconsistencies in sustainability reporting and marketing materials using data analytics and machine learning models. Stakeholder engagement analysis assesses the quality and impact of interactions between organizations and their stakeholders, measuring transparency, responsiveness, and trust through surveys, sentiment analysis, and communication metrics. Explore the techniques and tools that enhance accountability and transparency in corporate sustainability efforts.
Why it is important
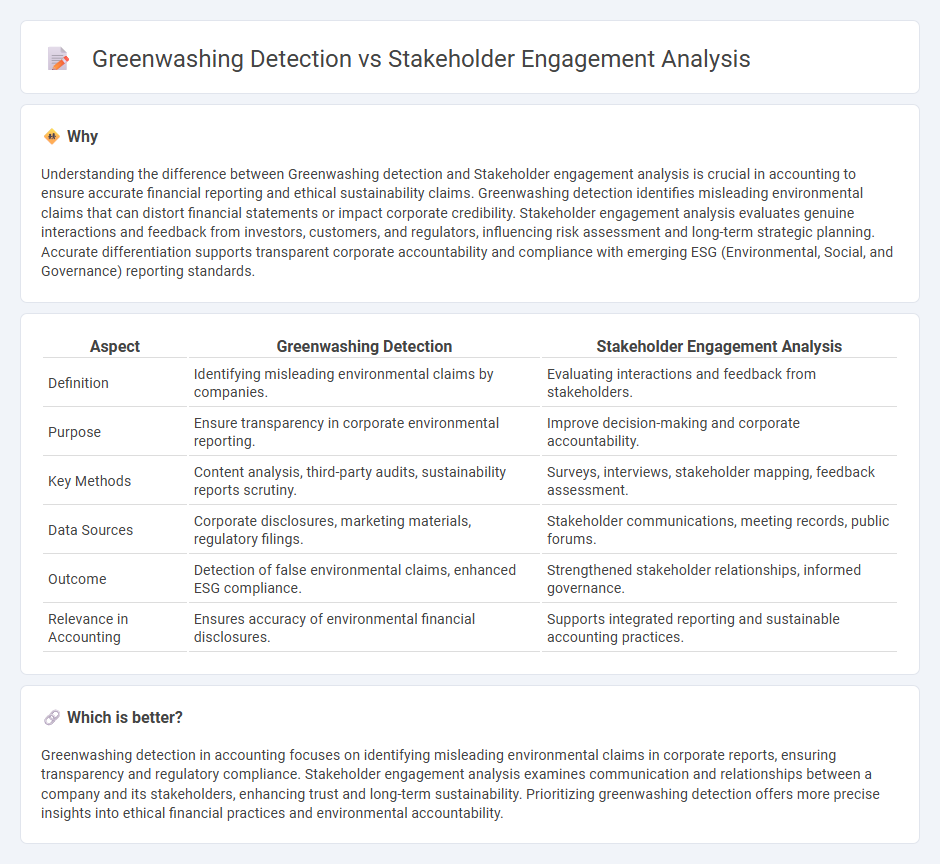
Understanding the difference between Greenwashing detection and Stakeholder engagement analysis is crucial in accounting to ensure accurate financial reporting and ethical sustainability claims. Greenwashing detection identifies misleading environmental claims that can distort financial statements or impact corporate credibility. Stakeholder engagement analysis evaluates genuine interactions and feedback from investors, customers, and regulators, influencing risk assessment and long-term strategic planning. Accurate differentiation supports transparent corporate accountability and compliance with emerging ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) reporting standards.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Greenwashing Detection | Stakeholder Engagement Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Identifying misleading environmental claims by companies. | Evaluating interactions and feedback from stakeholders. |
| Purpose | Ensure transparency in corporate environmental reporting. | Improve decision-making and corporate accountability. |
| Key Methods | Content analysis, third-party audits, sustainability reports scrutiny. | Surveys, interviews, stakeholder mapping, feedback assessment. |
| Data Sources | Corporate disclosures, marketing materials, regulatory filings. | Stakeholder communications, meeting records, public forums. |
| Outcome | Detection of false environmental claims, enhanced ESG compliance. | Strengthened stakeholder relationships, informed governance. |
| Relevance in Accounting | Ensures accuracy of environmental financial disclosures. | Supports integrated reporting and sustainable accounting practices. |
Which is better?
Greenwashing detection in accounting focuses on identifying misleading environmental claims in corporate reports, ensuring transparency and regulatory compliance. Stakeholder engagement analysis examines communication and relationships between a company and its stakeholders, enhancing trust and long-term sustainability. Prioritizing greenwashing detection offers more precise insights into ethical financial practices and environmental accountability.
Connection
Greenwashing detection relies on the analysis of stakeholder engagement to uncover discrepancies between corporate environmental claims and actual practices, enhancing transparency in sustainability reporting. Accounting professionals use this connection to assess the reliability of environmental disclosures, which influences investor confidence and regulatory compliance. Integrating stakeholder feedback with financial data ensures more accurate evaluation of a company's true environmental impact and ethical commitments.
Key Terms
**Stakeholder Engagement Analysis:**
Stakeholder engagement analysis systematically identifies and evaluates the interests, influence, and impact of all relevant parties in a project or organization to foster transparent communication and collaboration. This approach prioritizes authentic dialogue and responsiveness to stakeholder concerns, thereby building trust and driving sustainable outcomes. Explore how robust stakeholder engagement analysis enhances organizational accountability and mitigates risks effectively.
Materiality Assessment
Stakeholder engagement analysis evaluates the perspectives and priorities of relevant parties to identify genuine sustainability concerns, while greenwashing detection targets misleading claims that exaggerate environmental performance, both critically informing materiality assessments. Materiality assessment prioritizes issues based on their impact on business value and stakeholder interests, ensuring that companies address authentic risks rather than superficial narratives. Explore how integrating these approaches enhances transparency and accountability in sustainability reporting.
Stakeholder Mapping
Stakeholder engagement analysis involves identifying and prioritizing key stakeholders to enhance communication and collaboration, while greenwashing detection focuses on uncovering misleading claims about environmental practices. Stakeholder mapping visualizes relationships and influence among stakeholders, crucial for effective engagement and transparency assessment. Explore more to understand how stakeholder mapping strengthens greenwashing detection and promotes authentic sustainability efforts.
Source and External Links
Stakeholder Analysis: What Is and 3 Techniques To Approach - Stakeholder engagement analysis involves identifying, assessing, and understanding stakeholder perspectives to prioritize engagement, develop targeted strategies, anticipate reactions, and identify allies, with stakeholder mapping as a key technique to visualize and manage engagement efforts effectively.
Stakeholder Analysis & Engagement Decision Framework Overview - This framework assesses stakeholders by their commitment and engagement levels through an Involvement Matrix categorizing them as Advocates, Sponsors, Supporters, Apathetics, Adversaries, or Skeptics to guide engagement strategies tailored to their influence and attitude.
Stakeholder Impact Analysis: Decoding Influential Factors - Sopact - Stakeholder impact analysis systematically evaluates how organizational decisions affect stakeholders, focusing on dimensions such as what outcomes are impacted, who is affected, and the scale and duration of these impacts to inform responsible engagement and strategy development.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com