Real-time audit leverages continuous data monitoring and automated controls to detect anomalies immediately, enhancing accuracy and reducing risks in financial reporting. Batch audit processes historical data in groups at scheduled intervals, which may delay error detection but allows comprehensive review of complete datasets. Explore the detailed advantages and use cases of real-time versus batch audits to optimize your accounting strategy.
Why it is important
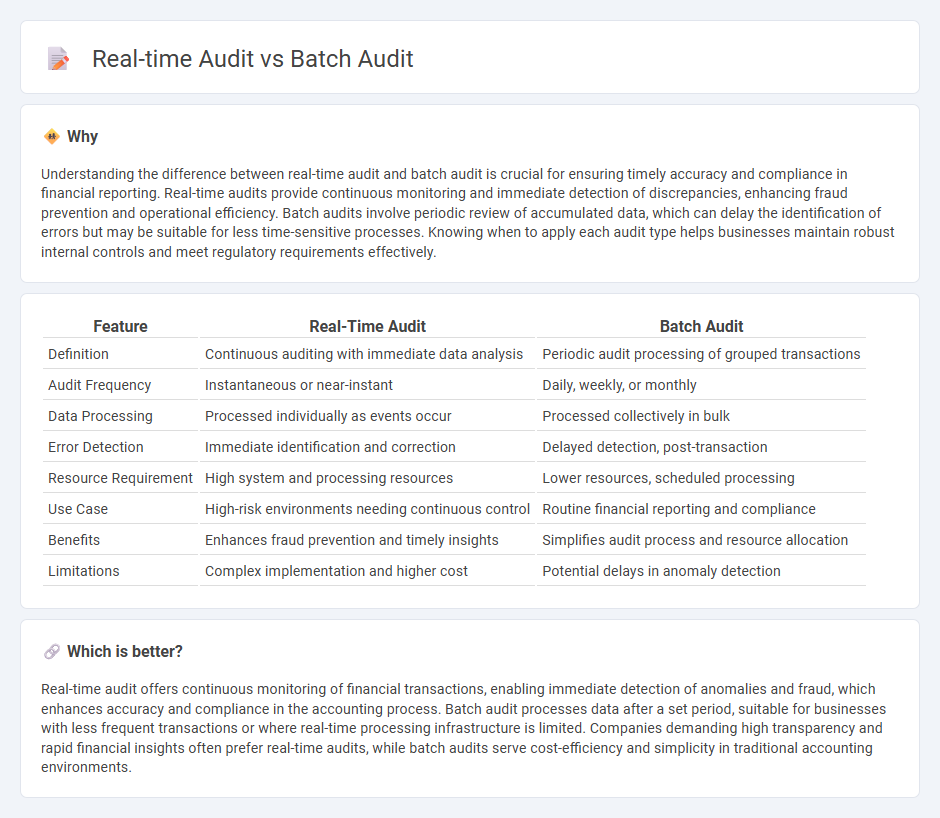
Understanding the difference between real-time audit and batch audit is crucial for ensuring timely accuracy and compliance in financial reporting. Real-time audits provide continuous monitoring and immediate detection of discrepancies, enhancing fraud prevention and operational efficiency. Batch audits involve periodic review of accumulated data, which can delay the identification of errors but may be suitable for less time-sensitive processes. Knowing when to apply each audit type helps businesses maintain robust internal controls and meet regulatory requirements effectively.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Real-Time Audit | Batch Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Continuous auditing with immediate data analysis | Periodic audit processing of grouped transactions |
| Audit Frequency | Instantaneous or near-instant | Daily, weekly, or monthly |
| Data Processing | Processed individually as events occur | Processed collectively in bulk |
| Error Detection | Immediate identification and correction | Delayed detection, post-transaction |
| Resource Requirement | High system and processing resources | Lower resources, scheduled processing |
| Use Case | High-risk environments needing continuous control | Routine financial reporting and compliance |
| Benefits | Enhances fraud prevention and timely insights | Simplifies audit process and resource allocation |
| Limitations | Complex implementation and higher cost | Potential delays in anomaly detection |
Which is better?
Real-time audit offers continuous monitoring of financial transactions, enabling immediate detection of anomalies and fraud, which enhances accuracy and compliance in the accounting process. Batch audit processes data after a set period, suitable for businesses with less frequent transactions or where real-time processing infrastructure is limited. Companies demanding high transparency and rapid financial insights often prefer real-time audits, while batch audits serve cost-efficiency and simplicity in traditional accounting environments.
Connection
Real-time audit and batch audit are interconnected through their roles in financial data verification, where real-time audit continuously monitors transactions as they occur, ensuring immediate detection of discrepancies. Batch audit processes accumulated data at designated intervals, providing comprehensive reviews that validate and complement real-time audit findings. This integration enhances overall audit accuracy, compliance, and financial integrity in accounting systems.
Key Terms
Transaction Processing
Batch audit processes accumulate transaction data over a specific period, enabling comprehensive analysis and error detection after the fact, which is ideal for high-volume, lower-risk environments. Real-time audit continuously monitors transactions as they occur, facilitating immediate identification of anomalies and compliance violations, critical for dynamic, high-risk transaction environments. Discover more about how these auditing methods impact transaction processing efficiency and risk management.
Time Lag
Batch audits involve processing large volumes of data at scheduled intervals, resulting in a notable time lag between transaction occurrence and audit completion. Real-time audits analyze transactions instantaneously, minimizing time lag and enabling immediate detection of anomalies or fraud. Explore the benefits and applications of both auditing methods to optimize your organization's compliance strategy.
Error Detection
Batch audit processes large volumes of data periodically to detect errors by comparing compiled records, which can lead to delayed identification but thorough error review. Real-time audit continuously monitors transactions and events as they occur, enabling immediate error detection and swift corrective actions, thus reducing risk exposure. Explore further to understand which audit method best suits your organizational needs for error management.
Source and External Links
How to Create an Audit Batch - An audit batch allows clients to manage and compartmentalize groups of audited records such as I-9 files by worksite or manager, including tools to view, edit, and report audit results.
Batch Listing: Audit - For each batch processed, audit checks are performed and recorded in an audit trail that details each stage of processing, including field-level audits if enabled.
Audit a Batch | ACSTechnologies Help Center - Auditing a batch is the final step before submission, involving verifying all batch items and comparing details for accuracy before completing the batch status.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com