Supply chain finance optimizes cash flow by enabling suppliers to receive early payments based on approved purchase orders, enhancing liquidity across the supply chain. Purchase order financing provides businesses with upfront capital to fulfill customer orders before payment is received, bridging funding gaps during production. Discover how these financial solutions can improve your company's working capital and operational efficiency.
Why it is important
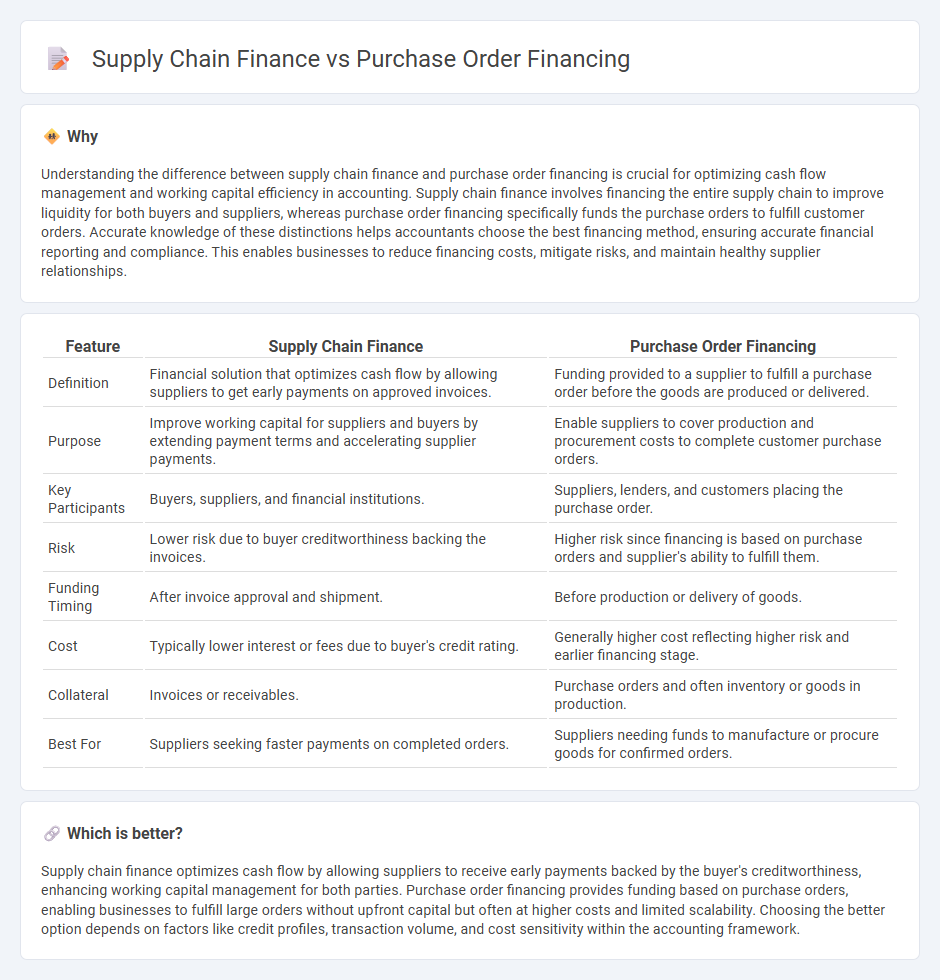
Understanding the difference between supply chain finance and purchase order financing is crucial for optimizing cash flow management and working capital efficiency in accounting. Supply chain finance involves financing the entire supply chain to improve liquidity for both buyers and suppliers, whereas purchase order financing specifically funds the purchase orders to fulfill customer orders. Accurate knowledge of these distinctions helps accountants choose the best financing method, ensuring accurate financial reporting and compliance. This enables businesses to reduce financing costs, mitigate risks, and maintain healthy supplier relationships.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Supply Chain Finance | Purchase Order Financing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Financial solution that optimizes cash flow by allowing suppliers to get early payments on approved invoices. | Funding provided to a supplier to fulfill a purchase order before the goods are produced or delivered. |
| Purpose | Improve working capital for suppliers and buyers by extending payment terms and accelerating supplier payments. | Enable suppliers to cover production and procurement costs to complete customer purchase orders. |
| Key Participants | Buyers, suppliers, and financial institutions. | Suppliers, lenders, and customers placing the purchase order. |
| Risk | Lower risk due to buyer creditworthiness backing the invoices. | Higher risk since financing is based on purchase orders and supplier's ability to fulfill them. |
| Funding Timing | After invoice approval and shipment. | Before production or delivery of goods. |
| Cost | Typically lower interest or fees due to buyer's credit rating. | Generally higher cost reflecting higher risk and earlier financing stage. |
| Collateral | Invoices or receivables. | Purchase orders and often inventory or goods in production. |
| Best For | Suppliers seeking faster payments on completed orders. | Suppliers needing funds to manufacture or procure goods for confirmed orders. |
Which is better?
Supply chain finance optimizes cash flow by allowing suppliers to receive early payments backed by the buyer's creditworthiness, enhancing working capital management for both parties. Purchase order financing provides funding based on purchase orders, enabling businesses to fulfill large orders without upfront capital but often at higher costs and limited scalability. Choosing the better option depends on factors like credit profiles, transaction volume, and cost sensitivity within the accounting framework.
Connection
Supply chain finance and purchase order financing are connected through their focus on improving cash flow between buyers and suppliers by providing working capital solutions. Supply chain finance optimizes cash flow by allowing suppliers to receive early payments based on approved purchase orders, while purchase order financing specifically funds suppliers to fulfill large orders before delivery. Both financial tools enhance liquidity, reduce supply chain risks, and support business growth by bridging payment gaps during production and delivery cycles.
Key Terms
Working Capital
Purchase order financing provides businesses with immediate funds to fulfill specific customer orders, improving short-term working capital by converting purchase orders into cash. Supply chain finance enhances working capital management across the entire supply chain by optimizing payment terms between buyers and suppliers, reducing liquidity constraints for all parties. Discover how these financing options can strategically unlock your working capital and boost operational efficiency.
Receivables
Purchase order financing provides funds to businesses upfront based on confirmed purchase orders, allowing companies to fulfill orders without impacting cash flow, while supply chain finance optimizes payment terms between buyers and suppliers by leveraging receivables to improve liquidity. Receivables play a critical role in supply chain finance as financiers use them to assess credit risk and structure payment schedules that benefit both parties. Explore more about how receivables influence financing decisions and optimize working capital management.
Third-party Financing
Third-party financing in purchase order financing involves external lenders advancing funds based on confirmed orders, while supply chain finance uses third-party financiers to optimize cash flow by paying suppliers early through buyer-approved credit lines. Both methods leverage external capital to enhance liquidity, but purchase order financing is tied directly to sales orders, whereas supply chain finance focuses on supplier relationships and payment terms. Explore more to understand how third-party financing solutions can streamline your working capital management.
Source and External Links
What Is Purchase Order Financing? Pros and Cons - This article explains how purchase order financing works and its pros and cons for businesses.
What is Purchase Order Financing? - This guide details the process and benefits of purchase order financing for businesses.
Purchase order financing guide - This guide provides insights into how purchase order financing can help small businesses grow by covering supplier costs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com