Algorithmic compliance ensures organizations adhere to regulatory standards through automated processes, reducing human error and enhancing accuracy in financial reporting. Corrective controls focus on identifying and rectifying discrepancies after they occur, mitigating risks related to fraud and misstatements. Explore how integrating these approaches strengthens your accounting framework and regulatory adherence.
Why it is important
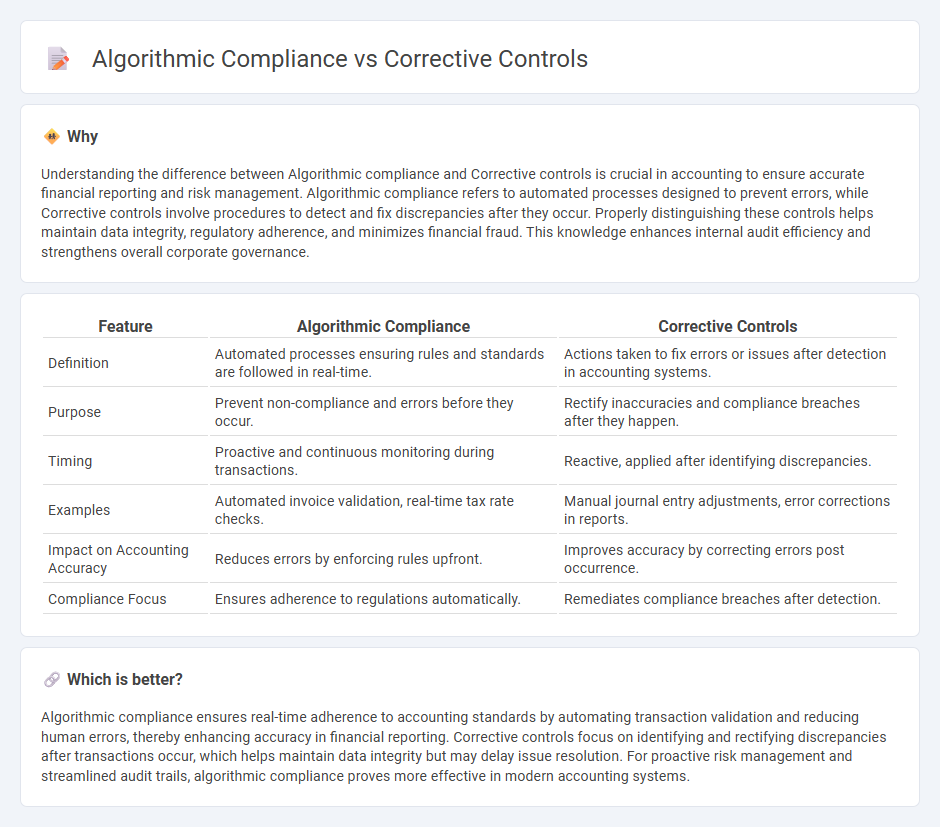
Understanding the difference between Algorithmic compliance and Corrective controls is crucial in accounting to ensure accurate financial reporting and risk management. Algorithmic compliance refers to automated processes designed to prevent errors, while Corrective controls involve procedures to detect and fix discrepancies after they occur. Properly distinguishing these controls helps maintain data integrity, regulatory adherence, and minimizes financial fraud. This knowledge enhances internal audit efficiency and strengthens overall corporate governance.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Algorithmic Compliance | Corrective Controls |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated processes ensuring rules and standards are followed in real-time. | Actions taken to fix errors or issues after detection in accounting systems. |
| Purpose | Prevent non-compliance and errors before they occur. | Rectify inaccuracies and compliance breaches after they happen. |
| Timing | Proactive and continuous monitoring during transactions. | Reactive, applied after identifying discrepancies. |
| Examples | Automated invoice validation, real-time tax rate checks. | Manual journal entry adjustments, error corrections in reports. |
| Impact on Accounting Accuracy | Reduces errors by enforcing rules upfront. | Improves accuracy by correcting errors post occurrence. |
| Compliance Focus | Ensures adherence to regulations automatically. | Remediates compliance breaches after detection. |
Which is better?
Algorithmic compliance ensures real-time adherence to accounting standards by automating transaction validation and reducing human errors, thereby enhancing accuracy in financial reporting. Corrective controls focus on identifying and rectifying discrepancies after transactions occur, which helps maintain data integrity but may delay issue resolution. For proactive risk management and streamlined audit trails, algorithmic compliance proves more effective in modern accounting systems.
Connection
Algorithmic compliance in accounting ensures that financial processes adhere to regulatory standards through automated decision-making algorithms. Corrective controls address discrepancies identified by these algorithms by initiating prompt resolution measures to maintain data accuracy and integrity. The integration of algorithmic compliance with corrective controls enhances risk management and enforces consistent adherence to financial regulations.
Key Terms
Error Detection
Corrective controls identify and rectify errors after they occur, ensuring data integrity by implementing mechanisms such as reconciliation and exception reporting. Algorithmic compliance emphasizes proactive error detection through automated rule-based checks, reducing manual intervention and enhancing real-time accuracy. Explore comprehensive strategies to optimize error detection and strengthen compliance frameworks.
Automated Reconciliation
Corrective controls identify and rectify errors after transactions occur, ensuring accuracy in financial records, while algorithmic compliance automates adherence to regulatory standards through predefined rules. Automated reconciliation leverages both approaches by using algorithms to detect discrepancies in real-time and apply corrective measures automatically, enhancing efficiency and reducing manual intervention. Explore how integrating these methods can transform your reconciliation processes and compliance strategies.
Policy Enforcement
Corrective controls identify and remediate policy violations after they occur, ensuring that deviations from compliance standards are addressed promptly. Algorithmic compliance enforces policies proactively through automated detection and prevention mechanisms embedded within systems, reducing the risk of breaches. Discover more about how combining both approaches enhances robust policy enforcement strategies.
Source and External Links
Risk Control Techniques: Preventive, Corrective, Directive - Corrective controls are designed to correct errors and irregularities and ensure they are not repeated.
Internal Control Types - Corrective controls in financial reporting focus on rectifying identified errors and preventing their recurrence.
Internal Control Types and Activities - Corrective controls are put in place when errors or irregularities have been detected.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com