Accounting professionals often face high stress levels due to tight deadlines and the demand for accuracy, which can negatively impact their mental health and overall productivity. Studies indicate that poor mental health among accountants leads to increased errors and decreased efficiency in financial reporting. Explore effective strategies to balance mental well-being and maintain peak performance in the accounting field.
Why it is important
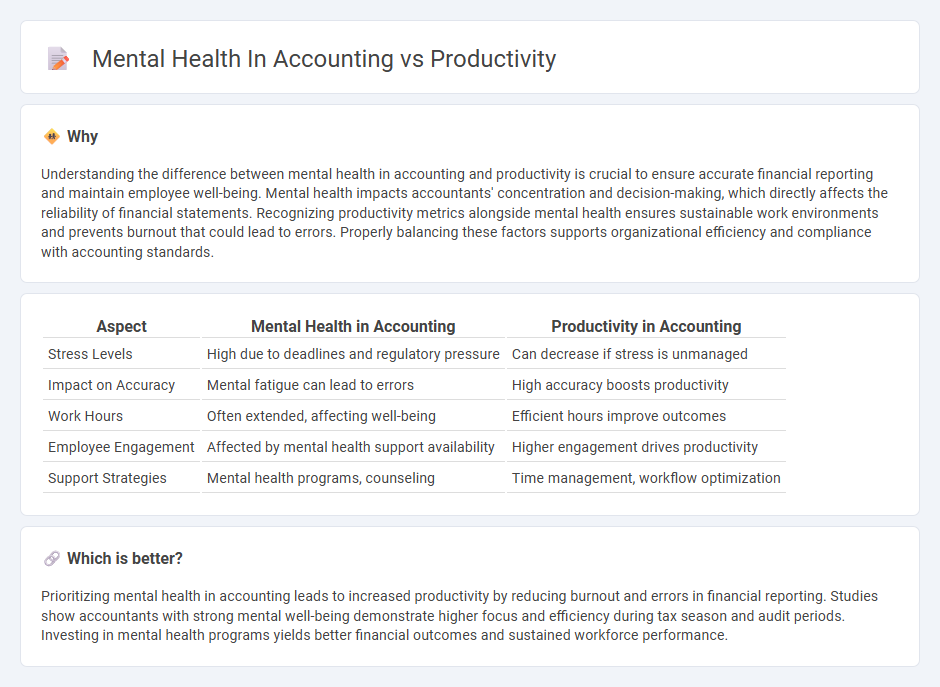
Understanding the difference between mental health in accounting and productivity is crucial to ensure accurate financial reporting and maintain employee well-being. Mental health impacts accountants' concentration and decision-making, which directly affects the reliability of financial statements. Recognizing productivity metrics alongside mental health ensures sustainable work environments and prevents burnout that could lead to errors. Properly balancing these factors supports organizational efficiency and compliance with accounting standards.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Mental Health in Accounting | Productivity in Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Stress Levels | High due to deadlines and regulatory pressure | Can decrease if stress is unmanaged |
| Impact on Accuracy | Mental fatigue can lead to errors | High accuracy boosts productivity |
| Work Hours | Often extended, affecting well-being | Efficient hours improve outcomes |
| Employee Engagement | Affected by mental health support availability | Higher engagement drives productivity |
| Support Strategies | Mental health programs, counseling | Time management, workflow optimization |
Which is better?
Prioritizing mental health in accounting leads to increased productivity by reducing burnout and errors in financial reporting. Studies show accountants with strong mental well-being demonstrate higher focus and efficiency during tax season and audit periods. Investing in mental health programs yields better financial outcomes and sustained workforce performance.
Connection
Mental health significantly impacts productivity in accounting by influencing focus, decision-making, and accuracy, which are critical for managing financial records and compliance. High stress levels and burnout can lead to errors, reduced efficiency, and increased absenteeism, directly affecting the quality of accounting outputs. Promoting mental health through supportive workplace practices enhances cognitive function and resilience, leading to improved overall performance in accounting tasks.
Key Terms
Burnout
Burnout in accounting significantly impairs productivity through chronic stress, emotional exhaustion, and reduced cognitive function, leading to increased errors and missed deadlines. The high-pressure environment, long hours, and stringent regulatory demands exacerbate mental health challenges, emphasizing the necessity for effective coping mechanisms and organizational support. Explore strategies to balance productivity and mental well-being in the accounting profession for sustainable career success.
Work-life balance
Maintaining a healthy work-life balance is crucial for accounting professionals, as excessive work hours can lead to burnout and decreased productivity. Research shows that accountants who prioritize mental health tend to have better focus, improved decision-making skills, and greater overall job satisfaction. Explore strategies to enhance both mental well-being and efficiency in the demanding field of accounting.
Efficiency
Efficiency in accounting hinges on balancing productivity with mental health to prevent burnout and maintain accuracy in financial reporting. High stress impairs cognitive function, leading to errors and decreased overall performance. Explore strategies to optimize both efficiency and well-being in accounting professionals.
Source and External Links
What is productivity? - Productivity measures the ratio of economic output to input, with labor productivity being the most common metric, and sustained economic growth increasingly depends on improving this ratio as workforce growth slows.
What is Productivity? - Productivity is an economic indicator that compares the quantity of goods and services produced (output) to the resources used in production (input), reflecting how efficiently inputs are converted into outputs.
Productivity - Productivity refers to the efficiency of producing goods or services, typically measured as a ratio of output to input, and its growth is driven by technology, innovation, skills, investment, and competition.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com