Continuous auditing utilizes automated tools and technology to provide real-time or near-real-time assurance on financial transactions and controls, enhancing the efficiency and timeliness of audits. Operational auditing focuses on evaluating the effectiveness and efficiency of business operations, including processes and controls, to improve organizational performance. Discover more about how these auditing methods optimize financial oversight and operational processes.
Why it is important
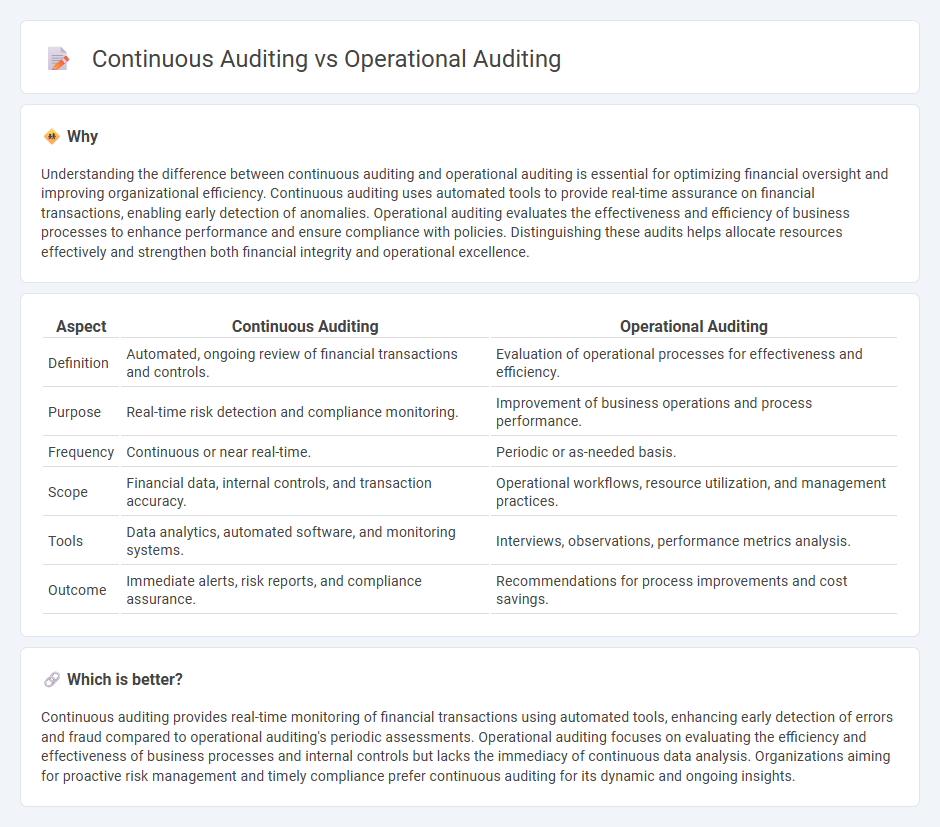
Understanding the difference between continuous auditing and operational auditing is essential for optimizing financial oversight and improving organizational efficiency. Continuous auditing uses automated tools to provide real-time assurance on financial transactions, enabling early detection of anomalies. Operational auditing evaluates the effectiveness and efficiency of business processes to enhance performance and ensure compliance with policies. Distinguishing these audits helps allocate resources effectively and strengthen both financial integrity and operational excellence.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Continuous Auditing | Operational Auditing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated, ongoing review of financial transactions and controls. | Evaluation of operational processes for effectiveness and efficiency. |
| Purpose | Real-time risk detection and compliance monitoring. | Improvement of business operations and process performance. |
| Frequency | Continuous or near real-time. | Periodic or as-needed basis. |
| Scope | Financial data, internal controls, and transaction accuracy. | Operational workflows, resource utilization, and management practices. |
| Tools | Data analytics, automated software, and monitoring systems. | Interviews, observations, performance metrics analysis. |
| Outcome | Immediate alerts, risk reports, and compliance assurance. | Recommendations for process improvements and cost savings. |
Which is better?
Continuous auditing provides real-time monitoring of financial transactions using automated tools, enhancing early detection of errors and fraud compared to operational auditing's periodic assessments. Operational auditing focuses on evaluating the efficiency and effectiveness of business processes and internal controls but lacks the immediacy of continuous data analysis. Organizations aiming for proactive risk management and timely compliance prefer continuous auditing for its dynamic and ongoing insights.
Connection
Continuous auditing leverages automated tools to provide real-time transaction analysis, enhancing the scope of operational auditing by continuously monitoring business processes and controls. Operational auditing evaluates the efficiency and effectiveness of organizational workflows, relying on insights gained from continuous auditing to identify areas for improvement. Integrating continuous auditing into operational auditing frameworks increases accuracy, reduces risks, and supports strategic decision-making.
Key Terms
**Operational Auditing:**
Operational auditing evaluates the efficiency, effectiveness, and compliance of an organization's processes, identifying areas for improvement and risk mitigation. It involves thorough examinations of financial and operational systems to ensure alignment with corporate goals and regulatory requirements. Discover how operational auditing can enhance your organization's performance and governance strategies.
Efficiency
Operational auditing assesses efficiency through periodic, in-depth evaluations of business processes to identify improvement opportunities and reduce waste. Continuous auditing leverages automated tools to provide real-time monitoring and instant feedback, enhancing timely decision-making and operational agility. Discover more about how these approaches optimize organizational efficiency and performance.
Effectiveness
Operational auditing evaluates the overall effectiveness of business processes by identifying inefficiencies, risks, and compliance issues through periodic comprehensive reviews. Continuous auditing uses real-time data and automated tools to monitor financial transactions and controls constantly, enhancing timely detection of anomalies and improving process effectiveness. Explore further to understand how businesses leverage these approaches for optimal performance and risk management.
Source and External Links
Operational Audit: Overview and Guide - Operational auditing systematically examines a company's internal policies, procedures, and controls to identify improvements that enhance efficiency and ensure compliance, focusing on optimizing internal processes and strengthening risk management.
A practical guide to operational audits - ITGRC Advisory - Operational auditing involves defining clear objectives, evaluating internal controls, collecting and analyzing data, developing an audit program, and reporting findings to improve organizational processes and manage risks effectively.
Guide To Operational Auditing: Definition, Process ... - The operational audit process includes planning with management to understand business concerns, setting audit scope and objectives, performing the audit internally or via external experts, and identifying process improvements aligned with company goals.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com