Accounting professionals often face high levels of occupational stress due to tight deadlines, complex financial regulations, and the pressure to maintain accuracy. Mental health challenges such as anxiety and burnout are increasingly recognized as critical issues within the accounting industry. Discover comprehensive strategies to manage stress and promote mental well-being in accounting.
Why it is important
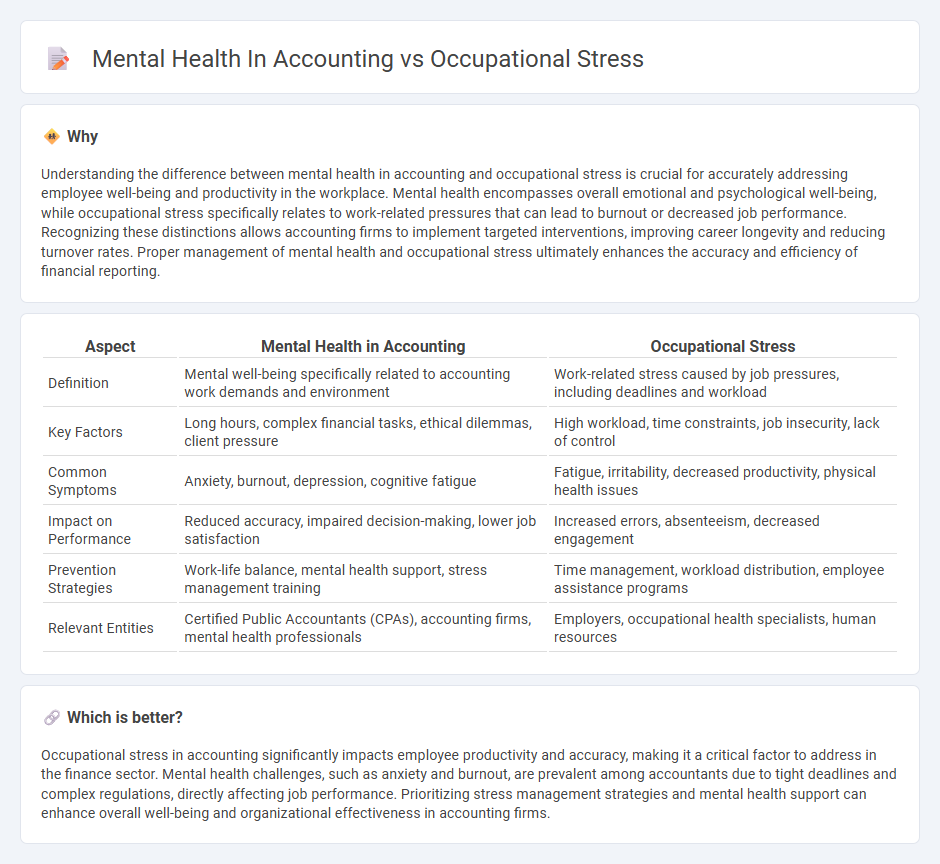
Understanding the difference between mental health in accounting and occupational stress is crucial for accurately addressing employee well-being and productivity in the workplace. Mental health encompasses overall emotional and psychological well-being, while occupational stress specifically relates to work-related pressures that can lead to burnout or decreased job performance. Recognizing these distinctions allows accounting firms to implement targeted interventions, improving career longevity and reducing turnover rates. Proper management of mental health and occupational stress ultimately enhances the accuracy and efficiency of financial reporting.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Mental Health in Accounting | Occupational Stress |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Mental well-being specifically related to accounting work demands and environment | Work-related stress caused by job pressures, including deadlines and workload |
| Key Factors | Long hours, complex financial tasks, ethical dilemmas, client pressure | High workload, time constraints, job insecurity, lack of control |
| Common Symptoms | Anxiety, burnout, depression, cognitive fatigue | Fatigue, irritability, decreased productivity, physical health issues |
| Impact on Performance | Reduced accuracy, impaired decision-making, lower job satisfaction | Increased errors, absenteeism, decreased engagement |
| Prevention Strategies | Work-life balance, mental health support, stress management training | Time management, workload distribution, employee assistance programs |
| Relevant Entities | Certified Public Accountants (CPAs), accounting firms, mental health professionals | Employers, occupational health specialists, human resources |
Which is better?
Occupational stress in accounting significantly impacts employee productivity and accuracy, making it a critical factor to address in the finance sector. Mental health challenges, such as anxiety and burnout, are prevalent among accountants due to tight deadlines and complex regulations, directly affecting job performance. Prioritizing stress management strategies and mental health support can enhance overall well-being and organizational effectiveness in accounting firms.
Connection
Occupational stress in accounting significantly impacts mental health due to high workloads, tight deadlines, and regulatory complexities that increase anxiety and burnout. Continuous exposure to financial accuracy demands and ethical responsibilities exacerbates psychological strain among accounting professionals. Effective stress management and workplace support are crucial to maintaining mental well-being and productivity in the accounting sector.
Key Terms
Burnout
Occupational stress in accounting, driven by tight deadlines, high workload, and regulatory pressures, significantly contributes to burnout, negatively affecting mental health. Burnout manifests as emotional exhaustion, depersonalization, and reduced personal accomplishment, leading to decreased productivity and increased risk of anxiety and depression among accountants. Explore effective strategies to manage burnout and enhance mental well-being in the accounting profession.
Work-life Balance
Occupational stress in accounting arises from high workloads, tight deadlines, and client demands, significantly impacting mental health by increasing anxiety and burnout rates. Poor work-life balance exacerbates stress levels, leading to decreased job satisfaction and impaired cognitive function among accounting professionals. Explore strategies to enhance work-life balance and improve mental well-being in the accounting industry.
Presenteeism
Occupational stress in accounting significantly impacts mental health, leading to increased levels of presenteeism where employees attend work despite being mentally unwell, reducing productivity and overall job satisfaction. High-pressure deadlines, complex financial regulations, and long working hours contribute to chronic stress, exacerbating anxiety and depression among accountants. Discover effective strategies to manage occupational stress and improve mental well-being in the accounting profession.
Source and External Links
Occupational stress - Wikipedia - Occupational stress is psychological stress related to one's job, often chronic, arising from factors like lack of supervisory support, limited job control, or imbalance of effort and rewards; it impacts emotional well-being, physical health, and job performance and causes significant health burdens including heart disease and stroke.
Managing Occupational Stress - BambooHR - Occupational stress results in negative psychological and physical effects, characterized by stages of alarm, resistance, and exhaustion, leading to symptoms like burnout, anxiety, sleep deprivation, and increased risk of diseases if untreated.
Workplace Stress - Work-related stress can enhance performance in small doses, but chronic stress leads to serious physical health issues (heart disease, headaches, sleep problems) and mental health challenges such as anxiety, depression, burnout, and increased suicide risk, particularly due to factors like high demands and low job control.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com