Data lake auditing focuses on verifying data integrity, access management, and compliance within large-scale data storage platforms, ensuring accurate financial reporting and regulatory adherence. IT general controls (ITGC) auditing examines foundational system controls such as access permissions, change management, and backup procedures critical for safeguarding accounting systems. Explore the distinctions between these auditing approaches to enhance your organization's financial data security.
Why it is important
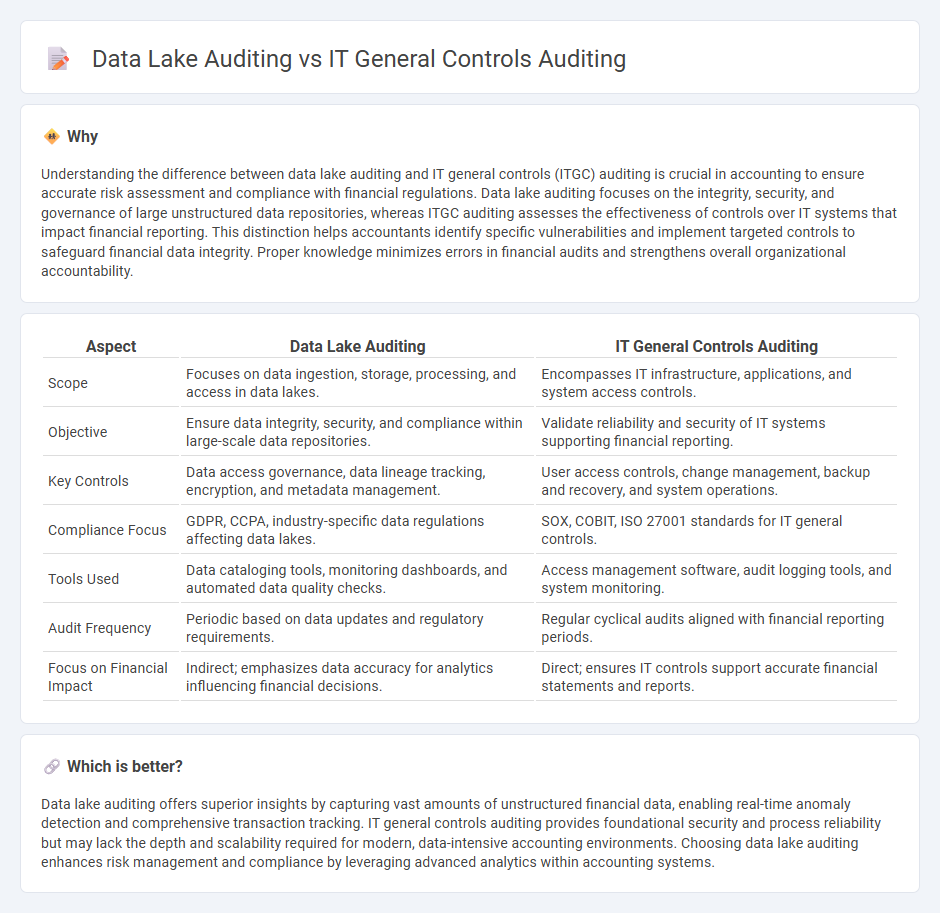
Understanding the difference between data lake auditing and IT general controls (ITGC) auditing is crucial in accounting to ensure accurate risk assessment and compliance with financial regulations. Data lake auditing focuses on the integrity, security, and governance of large unstructured data repositories, whereas ITGC auditing assesses the effectiveness of controls over IT systems that impact financial reporting. This distinction helps accountants identify specific vulnerabilities and implement targeted controls to safeguard financial data integrity. Proper knowledge minimizes errors in financial audits and strengthens overall organizational accountability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Data Lake Auditing | IT General Controls Auditing |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Focuses on data ingestion, storage, processing, and access in data lakes. | Encompasses IT infrastructure, applications, and system access controls. |
| Objective | Ensure data integrity, security, and compliance within large-scale data repositories. | Validate reliability and security of IT systems supporting financial reporting. |
| Key Controls | Data access governance, data lineage tracking, encryption, and metadata management. | User access controls, change management, backup and recovery, and system operations. |
| Compliance Focus | GDPR, CCPA, industry-specific data regulations affecting data lakes. | SOX, COBIT, ISO 27001 standards for IT general controls. |
| Tools Used | Data cataloging tools, monitoring dashboards, and automated data quality checks. | Access management software, audit logging tools, and system monitoring. |
| Audit Frequency | Periodic based on data updates and regulatory requirements. | Regular cyclical audits aligned with financial reporting periods. |
| Focus on Financial Impact | Indirect; emphasizes data accuracy for analytics influencing financial decisions. | Direct; ensures IT controls support accurate financial statements and reports. |
Which is better?
Data lake auditing offers superior insights by capturing vast amounts of unstructured financial data, enabling real-time anomaly detection and comprehensive transaction tracking. IT general controls auditing provides foundational security and process reliability but may lack the depth and scalability required for modern, data-intensive accounting environments. Choosing data lake auditing enhances risk management and compliance by leveraging advanced analytics within accounting systems.
Connection
Data lake auditing ensures the integrity and security of vast financial datasets by monitoring data access, transformations, and storage, which supports accurate accounting records. IT general controls auditing evaluates the effectiveness of underlying systems, including access controls, change management, and data backup procedures crucial for data lakes. Together, they provide a comprehensive framework that safeguards financial information, enhances compliance with accounting standards like SOX, and mitigates risks of data manipulation or loss.
Key Terms
**IT General Controls Auditing:**
IT general controls auditing involves evaluating the policies, procedures, and activities that govern information technology infrastructure to ensure data integrity, confidentiality, and availability. Key components include access controls, change management, and backup and recovery processes that mitigate risks related to unauthorized access and system failures. Explore the essential differences and methodologies by learning more about IT general controls auditing practices.
Access Controls
IT general controls auditing prioritizes access controls by verifying authentication protocols, user permissions, and system access logs to ensure compliance and prevent unauthorized system entry. Data lake auditing emphasizes granular access controls, monitoring data ingestion, data transformation processes, and role-based permissions to protect sensitive information across vast and diverse datasets. Explore in-depth strategies and methodologies to enhance access control effectiveness in both IT general controls and data lake environments.
Change Management
IT general controls auditing emphasizes comprehensive oversight of change management processes, ensuring that system modifications follow standardized approval, testing, and deployment protocols to maintain system integrity and security. Data lake auditing focuses specifically on tracking and validating changes in data ingestion, schema evolution, and metadata management to guarantee data consistency, lineage, and compliance within large-scale, unstructured data repositories. Explore detailed methodologies and best practices to enhance your organization's change management audit effectiveness across IT systems and data lakes.
Source and External Links
What are IT General Controls (ITGC)? - Metricstream - An ITGC audit evaluates effectiveness of controls in IT systems through planning, assessing documentation and procedures, testing controls like access and change management, reporting gaps, and following up on corrective actions to maintain compliance.
ITGC Audit: Types & Audit Process Breakdown - Zluri - The ITGC audit process involves testing control effectiveness through vulnerability scans and penetration tests, documenting detailed findings and recommendations, and then implementing corrective actions to improve IT control robustness.
What are IT General Controls (ITGC)? - SailPoint - Conducting an ITGC audit includes selecting a suitable framework, mapping internal controls to it, performing gap analysis, planning remediation, testing controls, and continuous monitoring to ensure controls meet enterprise and compliance requirements.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com