Greenwashing detection focuses on identifying misleading claims about a company's environmental practices, while fraud detection targets intentional deception in financial reporting to gain unfair advantages. Both require advanced analytical techniques, such as data mining and artificial intelligence, to uncover discrepancies and protect stakeholders. Explore these methods to understand how accounting professionals safeguard corporate integrity.
Why it is important
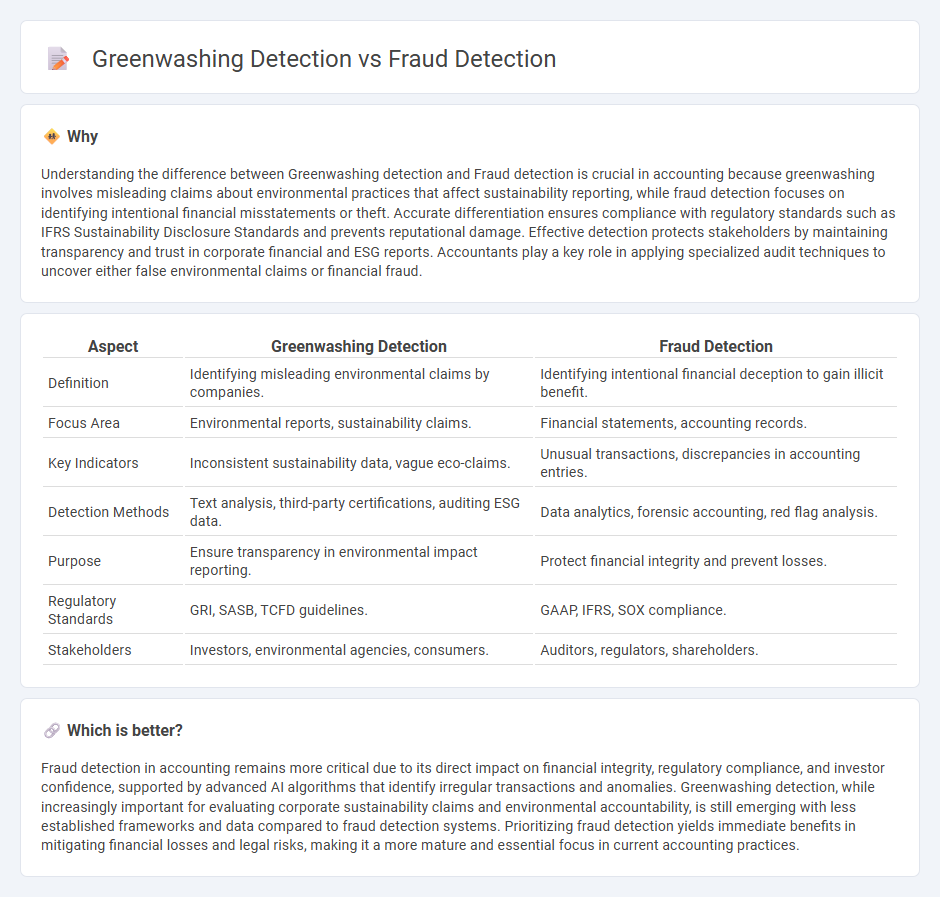
Understanding the difference between Greenwashing detection and Fraud detection is crucial in accounting because greenwashing involves misleading claims about environmental practices that affect sustainability reporting, while fraud detection focuses on identifying intentional financial misstatements or theft. Accurate differentiation ensures compliance with regulatory standards such as IFRS Sustainability Disclosure Standards and prevents reputational damage. Effective detection protects stakeholders by maintaining transparency and trust in corporate financial and ESG reports. Accountants play a key role in applying specialized audit techniques to uncover either false environmental claims or financial fraud.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Greenwashing Detection | Fraud Detection |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Identifying misleading environmental claims by companies. | Identifying intentional financial deception to gain illicit benefit. |
| Focus Area | Environmental reports, sustainability claims. | Financial statements, accounting records. |
| Key Indicators | Inconsistent sustainability data, vague eco-claims. | Unusual transactions, discrepancies in accounting entries. |
| Detection Methods | Text analysis, third-party certifications, auditing ESG data. | Data analytics, forensic accounting, red flag analysis. |
| Purpose | Ensure transparency in environmental impact reporting. | Protect financial integrity and prevent losses. |
| Regulatory Standards | GRI, SASB, TCFD guidelines. | GAAP, IFRS, SOX compliance. |
| Stakeholders | Investors, environmental agencies, consumers. | Auditors, regulators, shareholders. |
Which is better?
Fraud detection in accounting remains more critical due to its direct impact on financial integrity, regulatory compliance, and investor confidence, supported by advanced AI algorithms that identify irregular transactions and anomalies. Greenwashing detection, while increasingly important for evaluating corporate sustainability claims and environmental accountability, is still emerging with less established frameworks and data compared to fraud detection systems. Prioritizing fraud detection yields immediate benefits in mitigating financial losses and legal risks, making it a more mature and essential focus in current accounting practices.
Connection
Greenwashing detection and fraud detection intersect in accounting through the analysis of financial statements and disclosures to identify misleading or false environmental claims that can inflate a company's valuation or mislead investors. Both processes rely on forensic accounting techniques, including data analytics and auditing procedures, to uncover discrepancies between reported sustainability practices and actual business operations. Integrating greenwashing detection with traditional fraud detection enhances transparency and ensures compliance with regulatory standards on corporate social responsibility.
Key Terms
Fraud detection:
Fraud detection employs advanced analytics, machine learning algorithms, and pattern recognition to identify deceptive practices across various industries, significantly reducing financial losses and enhancing regulatory compliance. Key technologies include anomaly detection, transaction monitoring, and behavioral analysis, which enable real-time identification of fraudulent activities. Explore our in-depth guide to understand the latest innovations and strategies in fraud detection.
Forensic Accounting
Forensic accounting employs advanced analytical techniques to detect financial fraud by examining discrepancies in accounting records and transactions. Unlike fraud detection, greenwashing detection specifically targets misleading environmental claims by scrutinizing corporate reporting and sustainability disclosures for inconsistencies and exaggerations. Explore the methodologies and tools forensic accountants use to uncover both fraud and greenwashing in corporate practices.
Internal Controls
Fraud detection in internal controls emphasizes identifying financial misstatements and unauthorized transactions through rigorous audits, data analytics, and employee oversight to mitigate risk. Greenwashing detection within internal controls targets the verification of environmental claims by examining compliance with sustainability standards, transparency in reporting, and accurate tracking of corporate social responsibility initiatives. Explore advanced internal control methods to improve your organization's resilience against both fraud and greenwashing risks.
Source and External Links
What is Fraud Detection and Why Do You Need It? - Quantexa - Fraud detection is the systematic process of identifying and preventing fraudulent activities in financial transactions using a combination of AI, machine learning, real-time monitoring, data analysis, anomaly detection, and manual review techniques for comprehensive effectiveness.
What is fraud detection and why is it needed? - Fraud detection involves analyzing large datasets and behaviors to identify potentially fraudulent transactions, utilizing AI and machine learning to find patterns and anomalies, and implementing multi-stage processes including data warehousing and creation of association rules for uncovering fraud.
How Fraud Detection Works: Common Software and Tools | F5 - Fraud detection systems integrate data from multiple sources, apply feature engineering to highlight suspicious activities, and use AI and machine learning models to detect deviations from normal transaction behaviors, enabling banks and institutions to identify fraud such as money laundering and account takeovers.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com