Embedded finance accounting focuses on integrating financial services directly within non-financial platforms, streamlining transaction recording and reconciliation processes inherent to these ecosystems. Cross-border payments accounting addresses the complexities of multi-currency transactions, regulatory compliance, and foreign exchange management to ensure accurate financial reporting. Explore the distinctions and benefits of each approach to enhance your financial operations.
Why it is important
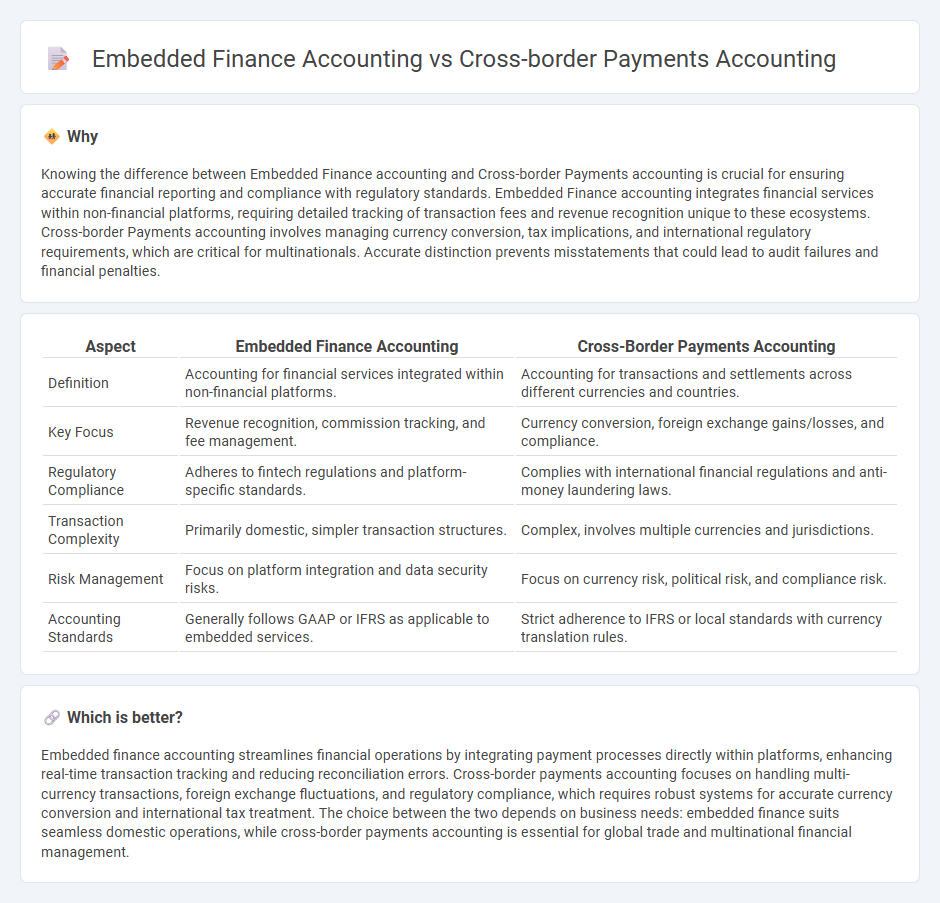
Knowing the difference between Embedded Finance accounting and Cross-border Payments accounting is crucial for ensuring accurate financial reporting and compliance with regulatory standards. Embedded Finance accounting integrates financial services within non-financial platforms, requiring detailed tracking of transaction fees and revenue recognition unique to these ecosystems. Cross-border Payments accounting involves managing currency conversion, tax implications, and international regulatory requirements, which are critical for multinationals. Accurate distinction prevents misstatements that could lead to audit failures and financial penalties.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Embedded Finance Accounting | Cross-Border Payments Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Accounting for financial services integrated within non-financial platforms. | Accounting for transactions and settlements across different currencies and countries. |
| Key Focus | Revenue recognition, commission tracking, and fee management. | Currency conversion, foreign exchange gains/losses, and compliance. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adheres to fintech regulations and platform-specific standards. | Complies with international financial regulations and anti-money laundering laws. |
| Transaction Complexity | Primarily domestic, simpler transaction structures. | Complex, involves multiple currencies and jurisdictions. |
| Risk Management | Focus on platform integration and data security risks. | Focus on currency risk, political risk, and compliance risk. |
| Accounting Standards | Generally follows GAAP or IFRS as applicable to embedded services. | Strict adherence to IFRS or local standards with currency translation rules. |
Which is better?
Embedded finance accounting streamlines financial operations by integrating payment processes directly within platforms, enhancing real-time transaction tracking and reducing reconciliation errors. Cross-border payments accounting focuses on handling multi-currency transactions, foreign exchange fluctuations, and regulatory compliance, which requires robust systems for accurate currency conversion and international tax treatment. The choice between the two depends on business needs: embedded finance suits seamless domestic operations, while cross-border payments accounting is essential for global trade and multinational financial management.
Connection
Embedded finance accounting integrates financial services directly into business platforms, streamlining transaction recording and expense tracking, which enhances the accuracy of cross-border payments accounting. Cross-border payments accounting relies on embedded finance systems to automatically process currency conversions, tax compliance, and multi-jurisdictional reporting, reducing manual intervention and errors. The synergy between embedded finance and cross-border payments accounting improves financial transparency, regulatory adherence, and real-time reconciliation across international transactions.
Key Terms
**Cross-border payments accounting:**
Cross-border payments accounting involves tracking and reconciling financial transactions across different countries, currencies, and regulatory frameworks, ensuring compliance with international tax laws and foreign exchange controls. It requires managing currency conversion gains or losses, transaction fees, and varying reporting standards specific to cross-border trade. Explore more to understand the complexities and best practices in cross-border payments accounting.
Foreign exchange gains/losses
Cross-border payments accounting involves tracking foreign exchange gains and losses resulting from currency conversion differences during transaction settlement, often recorded as realized or unrealized FX impacts on the income statement. Embedded finance accounting integrates financial services like FX conversion within non-financial platforms, requiring detailed recognition of FX gains/losses tied directly to customer transactions and platform usage. Explore how these differing approaches impact financial reporting and risk management in global business environments.
International transaction fees
Cross-border payments accounting involves managing international transaction fees, currency conversion costs, and compliance with varying regulatory requirements across jurisdictions. Embedded finance accounting integrates financial services directly within non-financial platforms, streamlining fee structures and reducing transaction costs related to international payments through native APIs and automated reconciliation. Explore how these accounting approaches optimize international transaction fees in global business operations.
Source and External Links
How to Integrate Cross-Border Payments into Bookkeeping - Managing cross-border payments in accounting involves automating currency conversions, maintaining compliance with international regulations like AML and tax laws, and using bookkeeping software that supports multi-currency transactions to ensure accurate, audit-ready records.
Cross Border Payments: Definition, Tips & Best Practices - Bill.com - Cross-border payment accounting requires due diligence on the recipient and the payment channels, adherence to AML regulations, and accurate documentation of payments between banks in different countries to comply with international standards.
Cross-Border Payments Overview - FedPayments Improvement - Accounting for cross-border payments is complex due to multiple intermediaries, currency conversions, and regulatory differences, requiring detailed tracking for cost, timing, transparency, and risk management in international financial transactions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com