Revenue recognition automation streamlines the process of identifying and recording income precisely when earned, enhancing financial accuracy and compliance with accounting standards like ASC 606 and IFRS 15. Accounts payable automation optimizes bill processing and payment workflows, reducing manual errors and accelerating supplier transactions for improved cash flow management. Explore how each automation transforms core accounting functions and drives operational efficiency.
Why it is important
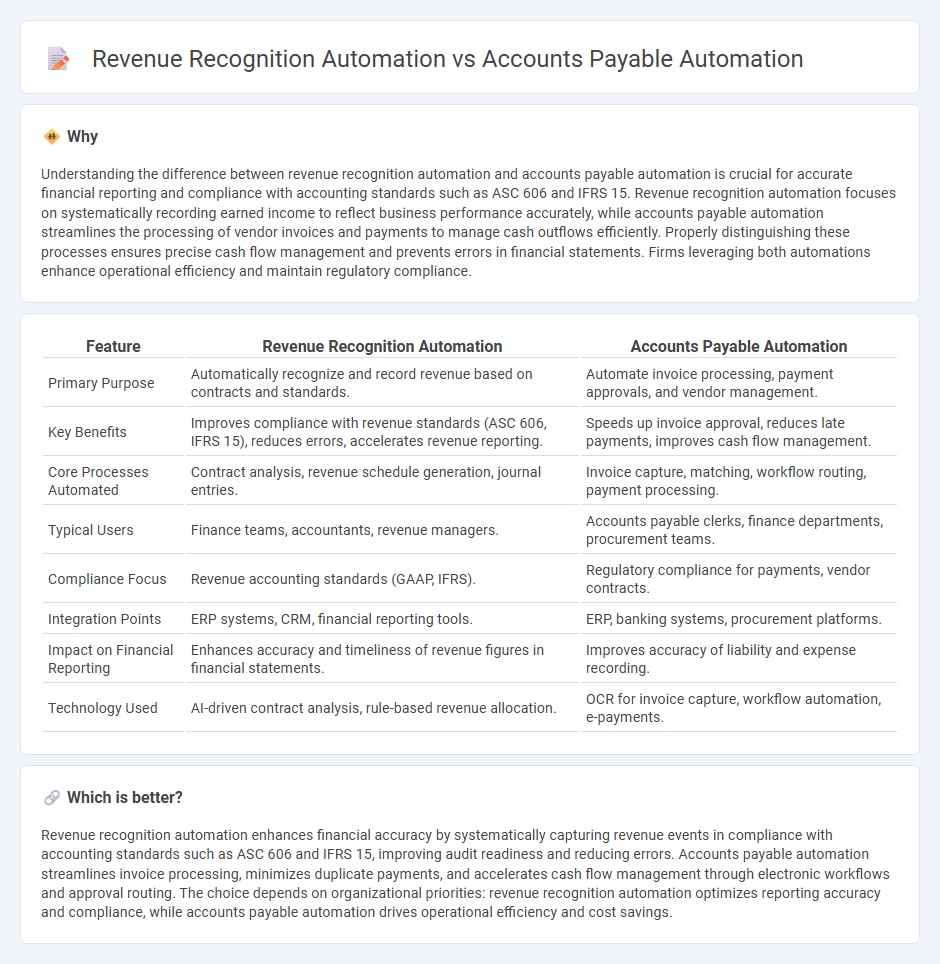
Understanding the difference between revenue recognition automation and accounts payable automation is crucial for accurate financial reporting and compliance with accounting standards such as ASC 606 and IFRS 15. Revenue recognition automation focuses on systematically recording earned income to reflect business performance accurately, while accounts payable automation streamlines the processing of vendor invoices and payments to manage cash outflows efficiently. Properly distinguishing these processes ensures precise cash flow management and prevents errors in financial statements. Firms leveraging both automations enhance operational efficiency and maintain regulatory compliance.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Revenue Recognition Automation | Accounts Payable Automation |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Automatically recognize and record revenue based on contracts and standards. | Automate invoice processing, payment approvals, and vendor management. |
| Key Benefits | Improves compliance with revenue standards (ASC 606, IFRS 15), reduces errors, accelerates revenue reporting. | Speeds up invoice approval, reduces late payments, improves cash flow management. |
| Core Processes Automated | Contract analysis, revenue schedule generation, journal entries. | Invoice capture, matching, workflow routing, payment processing. |
| Typical Users | Finance teams, accountants, revenue managers. | Accounts payable clerks, finance departments, procurement teams. |
| Compliance Focus | Revenue accounting standards (GAAP, IFRS). | Regulatory compliance for payments, vendor contracts. |
| Integration Points | ERP systems, CRM, financial reporting tools. | ERP, banking systems, procurement platforms. |
| Impact on Financial Reporting | Enhances accuracy and timeliness of revenue figures in financial statements. | Improves accuracy of liability and expense recording. |
| Technology Used | AI-driven contract analysis, rule-based revenue allocation. | OCR for invoice capture, workflow automation, e-payments. |
Which is better?
Revenue recognition automation enhances financial accuracy by systematically capturing revenue events in compliance with accounting standards such as ASC 606 and IFRS 15, improving audit readiness and reducing errors. Accounts payable automation streamlines invoice processing, minimizes duplicate payments, and accelerates cash flow management through electronic workflows and approval routing. The choice depends on organizational priorities: revenue recognition automation optimizes reporting accuracy and compliance, while accounts payable automation drives operational efficiency and cost savings.
Connection
Revenue recognition automation and accounts payable automation streamline financial workflows by improving data accuracy and reducing manual entry errors, which enhances overall financial reporting quality. Both systems leverage integrated software solutions to synchronize revenue streams with payment obligations, ensuring real-time visibility into cash flow and financial performance. This connectivity supports compliance with accounting standards such as ASC 606 and IFRS 15 by maintaining consistent, auditable transaction records across revenue and expense accounts.
Key Terms
**Accounts Payable Automation:**
Accounts payable automation streamlines invoice processing, reduces manual errors, and accelerates payment cycles by leveraging AI-driven tools and optical character recognition (OCR) technology. Implementing automated workflows enhances supplier relationships and improves cash flow management through real-time expense tracking and early payment discounts. Discover how integrating accounts payable automation can transform your financial operations and boost overall efficiency.
Invoice Processing
Accounts payable automation streamlines invoice processing by leveraging OCR technology and AI to extract invoice data, match purchase orders, and expedite payment approvals, reducing errors and accelerating cash flow management. Revenue recognition automation focuses on analyzing contracts and billing schedules to accurately recognize revenue per accounting standards, ensuring compliance and real-time financial reporting. Explore how automating invoice processing transforms financial operations and enhances overall business efficiency.
Payment Approval Workflow
Payment approval workflow in accounts payable automation streamlines invoice processing by automating vendor payments, reducing manual errors, and accelerating cash flow management. In contrast, revenue recognition automation focuses on validating and recording revenue transactions in compliance with accounting standards, ensuring accurate financial reporting without involving payment approvals. Discover how optimizing each process can enhance your organization's financial efficiency.
Source and External Links
What Is AP Automation and How Does it Work? - AP automation uses technology to automate routine accounts payable tasks such as invoice receipt, coding, approval routing, payment, and reconciliation, reducing processing time and errors while improving accuracy and compliance.
AP Automation: Benefits to the Accounts Payable Process - AP automation leverages AI and digital systems to handle invoice receipt, matching, approval, and payment processing, enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and providing real-time visibility across departments.
What is AP Automation? - AP automation digitizes the entire invoice process--from electronic receipt or scanning, through automated matching and approval workflows, to secure archiving--enabling faster processing, better audit trails, and easy access to invoice data.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com