Revenue recognition automation enhances accuracy and efficiency by systematically recording sales transactions in compliance with accounting standards such as ASC 606 and IFRS 15. Internal controls automation strengthens risk management and fraud prevention through continuous monitoring and automated alerts within financial processes. Explore how integrating these automation tools can transform your accounting operations and ensure regulatory compliance.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between revenue recognition automation and internal controls automation is crucial for ensuring accurate financial reporting and compliance with accounting standards like ASC 606. Revenue recognition automation specifically focuses on recording revenue transactions accurately and timely, which directly impacts financial statements. Internal controls automation involves monitoring and enforcing compliance policies to prevent errors and fraud throughout accounting processes. Businesses benefit by optimizing these distinct automations to strengthen financial integrity and regulatory adherence.
Comparison Table
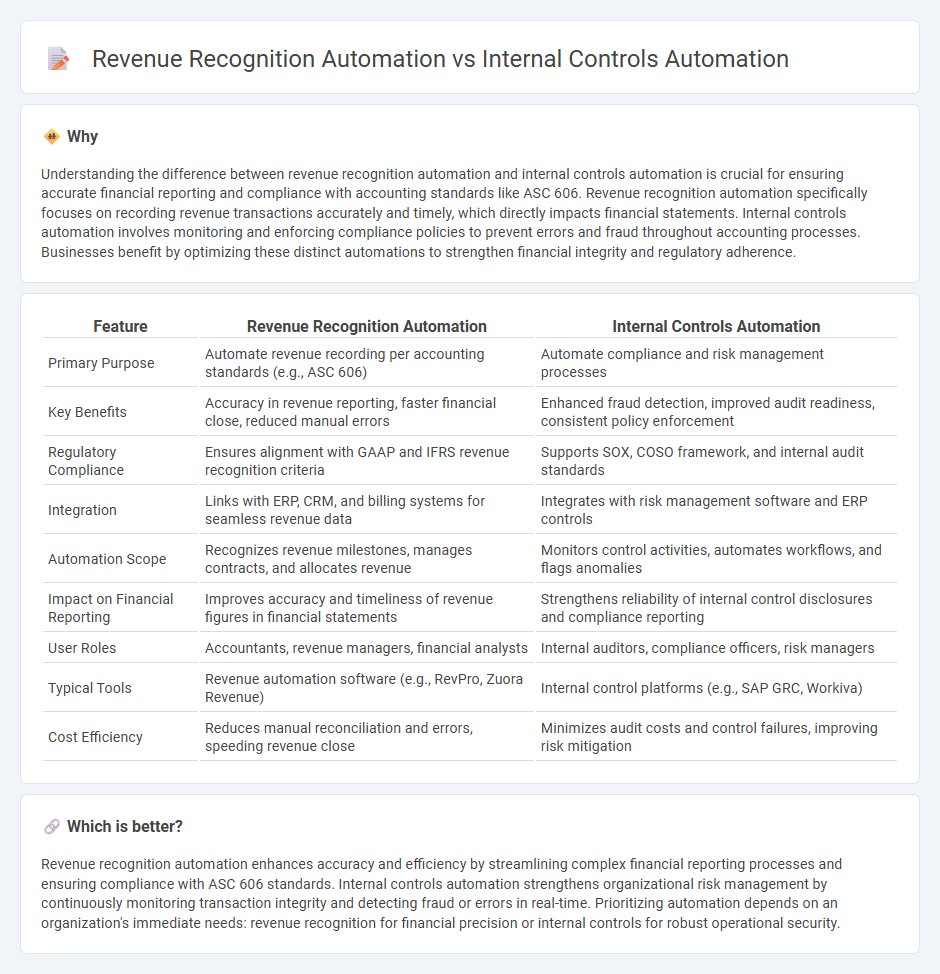
| Feature | Revenue Recognition Automation | Internal Controls Automation |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Automate revenue recording per accounting standards (e.g., ASC 606) | Automate compliance and risk management processes |
| Key Benefits | Accuracy in revenue reporting, faster financial close, reduced manual errors | Enhanced fraud detection, improved audit readiness, consistent policy enforcement |
| Regulatory Compliance | Ensures alignment with GAAP and IFRS revenue recognition criteria | Supports SOX, COSO framework, and internal audit standards |
| Integration | Links with ERP, CRM, and billing systems for seamless revenue data | Integrates with risk management software and ERP controls |
| Automation Scope | Recognizes revenue milestones, manages contracts, and allocates revenue | Monitors control activities, automates workflows, and flags anomalies |
| Impact on Financial Reporting | Improves accuracy and timeliness of revenue figures in financial statements | Strengthens reliability of internal control disclosures and compliance reporting |
| User Roles | Accountants, revenue managers, financial analysts | Internal auditors, compliance officers, risk managers |
| Typical Tools | Revenue automation software (e.g., RevPro, Zuora Revenue) | Internal control platforms (e.g., SAP GRC, Workiva) |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces manual reconciliation and errors, speeding revenue close | Minimizes audit costs and control failures, improving risk mitigation |
Which is better?
Revenue recognition automation enhances accuracy and efficiency by streamlining complex financial reporting processes and ensuring compliance with ASC 606 standards. Internal controls automation strengthens organizational risk management by continuously monitoring transaction integrity and detecting fraud or errors in real-time. Prioritizing automation depends on an organization's immediate needs: revenue recognition for financial precision or internal controls for robust operational security.
Connection
Revenue recognition automation integrates with internal controls automation by streamlining financial data processing while ensuring compliance with regulatory standards such as ASC 606 and IFRS 15. Automated systems reduce human error and enforce segregation of duties, enhancing accuracy and audit readiness in revenue reporting. This synergy improves transparency and strengthens the overall internal control environment within accounting operations.
Key Terms
**Internal Controls Automation:**
Internal controls automation enhances organizational risk management by streamlining processes such as compliance monitoring, fraud detection, and audit trail generation, thereby increasing accuracy and efficiency. This technology leverages AI and machine learning to continuously assess control effectiveness and identify anomalies in real time. Discover how internal controls automation can transform your governance framework and reduce operational risks.
Segregation of Duties
Internal controls automation enhances Segregation of Duties by systematically assigning distinct tasks to different individuals, minimizing risks of errors and fraud during financial processes. Revenue recognition automation streamlines compliance by enforcing predefined criteria for recording revenues while ensuring separation of responsibilities among sales, finance, and audit teams. Explore how integrating automation tools can strengthen Segregation of Duties and optimize both internal controls and revenue recognition workflows.
Access Controls
Internal controls automation enhances organizational security by streamlining access controls, ensuring that only authorized personnel can modify financial data or approve transactions, reducing the risk of fraud and errors. Revenue recognition automation focuses on accurately recording sales in compliance with accounting standards, but may lack the robust access control mechanisms needed for stringent security. Explore how integrating advanced access control automation can optimize both internal controls and revenue recognition processes for stronger financial governance.
Source and External Links
Why Accounting Needs Automated Internal Controls - Automated internal controls define data access, enforce regulatory compliance, and log all changes and access, protecting accounting data from errors and fraud while maintaining accountability and audit readiness.
Automating internal controls: What does it entail and what are the benefits? - Automating internal controls replaces manual, error-prone processes with system-driven operations, enabling real-time analysis of large data sets for faster detection of compliance issues and reducing risks associated with human intervention.
Internal Controls Automation: The Cornerstone of Financial Integrity and IPO Readiness - Automation streamlines SOX compliance by auto-testing controls, maintaining continuous documentation, and providing real-time fraud detection, thereby enhancing financial integrity and simplifying audit preparation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com